At its core, an induction coil is a type of transformer used for two primary purposes: producing high-voltage electrical arcs from a low-voltage source and rapidly heating conductive materials without direct contact. Both functions operate on the fundamental principle of electromagnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field is used to manipulate electrical energy.
An induction coil is fundamentally a device that uses a magnetic field to transform electricity. Its two primary applications—creating high-voltage sparks or inducing intense heat—both stem from its ability to convert a low-voltage, high-current input into a radically different form of energy.

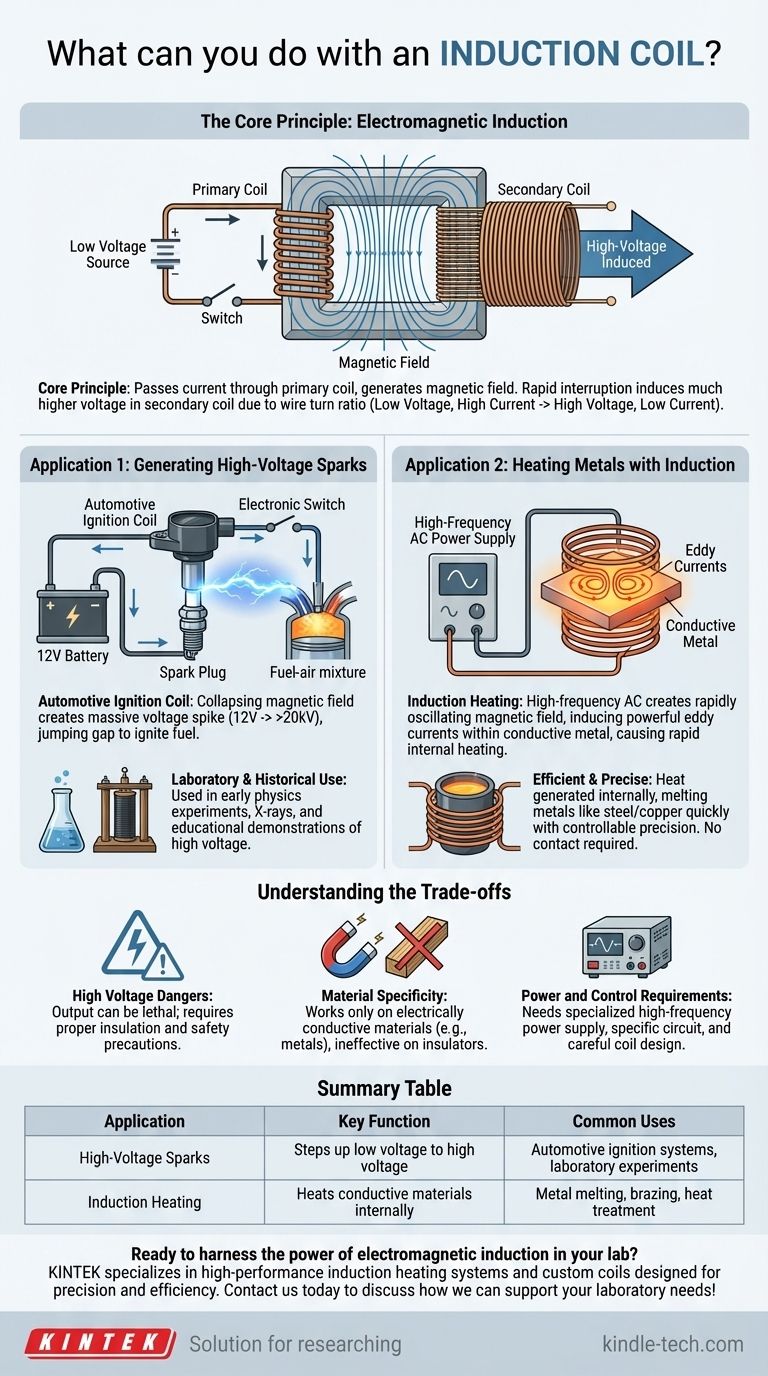
The Core Principle: How Induction Works
To understand what an induction coil can do, you must first grasp its operating principle. It's a clever application of physics that converts one form of electrical energy into another.
Electromagnetic Induction
An induction coil works by passing an electrical current through a primary coil of wire. This generates a magnetic field. When this current is rapidly interrupted or changed, the magnetic field collapses or fluctuates.
This rapidly changing magnetic field cuts across a second coil of wire (the secondary coil), inducing a much higher voltage in it.
The Role of Coil Windings
The "magic" of voltage transformation comes from the ratio of wire turns between the two coils. The primary coil has relatively few turns of thick wire, while the secondary coil has thousands of turns of very thin wire.
By interrupting a low-voltage current in the primary coil, you can induce an extremely high-voltage current in the secondary coil—transforming, for example, 12 volts into over 20,000 volts.
Application 1: Generating High-Voltage Sparks
The classic and most well-known use of an induction coil is to create a powerful electrical spark.
The Automotive Ignition Coil
This is the quintessential example. A car's 12-volt battery provides power to the ignition coil's primary winding. An electronic switch rapidly interrupts this current.
With each interruption, the collapsing magnetic field induces a massive voltage spike in the secondary winding. This high voltage is powerful enough to jump the gap in a spark plug, igniting the fuel-air mixture in the engine's cylinder.
Laboratory and Historical Use
Historically, large induction coils (known as Ruhmkorff coils) were crucial in early physics experiments exploring electricity and X-rays. They are still used in educational labs to safely demonstrate the principles of high voltage and electromagnetism.
Application 2: Heating Metals with Induction
A different configuration of the same principle allows an induction coil to heat metals with incredible speed and precision.
The Principle of Induction Heating
In this application, a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through a work coil. This creates a rapidly oscillating magnetic field.
When a conductive material like steel or copper is placed inside this field, the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents (called "eddy currents") directly within the metal itself. The metal's own electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly from the inside out.
Why It's So Efficient
The heat is generated inside the workpiece, not by an external flame or heating element. This process is exceptionally fast, clean, and controllable. You can heat a specific part of a metal object to a precise temperature without affecting the surrounding areas.
This is the principle used when heating metal inside a crucible, as the magnetic field transfers energy directly to the metal, causing it to melt.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction coils are not a universal solution and come with important considerations.
High Voltage Dangers
The output of an ignition-style induction coil is extremely high voltage and can be lethal. Proper insulation and safety precautions are non-negotiable when working with these devices.
Material Specificity
Induction heating only works on materials that are electrically conductive, such as metals. It has no effect on insulators like plastic, glass, wood, or ceramics.
Power and Control Requirements
These are not simple plug-and-play devices. An induction heater requires a specialized high-frequency power supply, and an ignition coil requires a circuit to rapidly switch the primary current. The design of the coil itself is critical to its effectiveness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your intended application determines how you will use an induction coil.
- If your primary focus is generating a high-voltage spark: You need a classic step-up coil with distinct primary and secondary windings and a method for rapidly interrupting the low-voltage input current.
- If your primary focus is to heat or melt metal: You need a high-frequency AC power supply and a carefully shaped work coil designed to efficiently couple the magnetic field with your workpiece.
- If your primary focus is to understand physics: The induction coil serves as a perfect hands-on tool for demonstrating the relationship between electricity and magnetism.
Ultimately, understanding that an induction coil is a tool for converting electricity via magnetism is the key to harnessing its power for any application.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| High-Voltage Sparks | Steps up low voltage to high voltage | Automotive ignition systems, laboratory experiments |
| Induction Heating | Heats conductive materials internally | Metal melting, brazing, heat treatment |
Ready to harness the power of electromagnetic induction in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems and custom coils designed for precision and efficiency. Whether you're melting metals, conducting experiments, or automating processes, our solutions deliver rapid, clean, and controllable heating. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Small Constant Temperature Heated Magnetic Stirrer Heater and Stirrer
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a good mini heat press? Achieve Professional Results on Small, Complex Items
- What role do molds play in the formation of Ruthenium sheets? Master High-Density Ruthenium Fabrication
- Is a heat press machine good for t-shirts? Unlock Professional, Custom Apparel Creation
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- Why are precision molds and pressure control essential for TlBr hot pressing? Enhance Semiconductor Performance



















