Choosing the right crucible for a muffle furnace is not about finding a single "correct" type, but about matching the crucible's material properties to your specific application. The most common materials are porcelain, alumina, and quartz, with specialized options like silicon carbide and platinum used for more demanding processes. Your choice directly impacts the success and accuracy of your work.
The selection of a muffle furnace crucible is a critical decision dictated by three factors: the maximum temperature of your process, the chemical reactivity between the crucible and your sample, and the material's resistance to thermal shock.

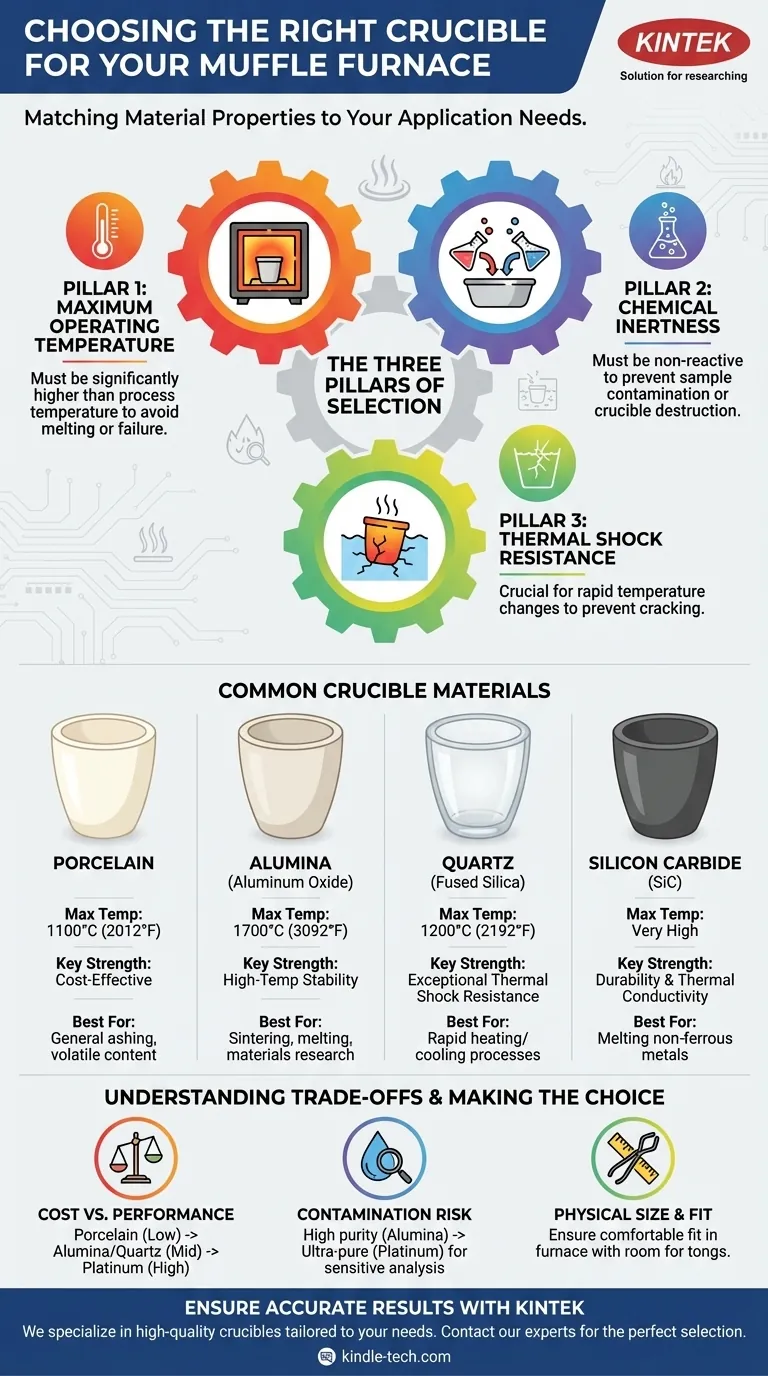
The Three Pillars of Crucible Selection
To select the correct crucible, you must first define the demands of your process. Every material represents a trade-off between performance and cost, and understanding these three pillars will guide you to the optimal choice.
Pillar 1: Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the first and most important filter. Exceeding a crucible's maximum use temperature will cause it to soften, melt, or fail, potentially destroying your sample and damaging the furnace.
Always choose a crucible material with a maximum operating temperature significantly higher than your planned working temperature.
Pillar 2: Chemical Inertness
A crucible should be a neutral container that does not react with your sample. A chemical reaction can contaminate your sample, give you inaccurate results (e.g., in ash testing), or even destroy the crucible itself.
Consider whether your sample is acidic, alkaline, or corrosive at high temperatures, and select a crucible material known for its resistance to those specific chemicals.
Pillar 3: Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock is the stress a material endures when its temperature changes rapidly. Materials with poor thermal shock resistance can crack or shatter if heated or cooled too quickly.
If your process involves rapid temperature cycling, a material like quartz is superior. If you are using a slow, controlled ramp rate, this factor is less critical.
Common Crucible Materials for Muffle Furnaces
With the three pillars in mind, we can evaluate the most common crucible materials.
Porcelain Crucibles
Porcelain is a cost-effective choice for general-purpose laboratory work. They are most commonly used for determining volatile content or ashing samples where trace metal contamination is not a concern.
They have a relatively low maximum use temperature, typically around 1100°C (2012°F), and are susceptible to thermal shock. They should be heated and cooled slowly.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) Crucibles
High-purity alumina is the workhorse for many high-temperature applications. It offers an excellent combination of high-temperature stability and good chemical resistance.
Alumina crucibles can typically be used up to 1700°C (3092°F), making them suitable for sintering, melting, and advanced materials research. They have moderate thermal shock resistance.
Quartz (Fused Silica) Crucibles
The defining feature of quartz is its exceptional resistance to thermal shock. You can take a red-hot quartz crucible and plunge it into water without it cracking.
This makes it ideal for processes requiring very fast heating or cooling. However, its maximum use temperature is lower than alumina, generally around 1200°C (2192°F) for continuous use.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
Silicon carbide is an excellent choice for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and copper due to its outstanding thermal conductivity and strength at very high temperatures.
These crucibles are extremely durable and resistant to thermal shock, making them suitable for use in various furnace types, including muffle furnaces, for high-temperature applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Factors
Choosing a crucible involves balancing performance against practical constraints.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between price and performance. Porcelain is inexpensive and disposable, while a platinum crucible (used for ultra-high purity analysis) can cost thousands of dollars. Alumina and quartz offer a mid-range balance.
Contamination Risk
For highly sensitive analysis (e.g., trace element analysis), even a high-purity alumina crucible can leach minute amounts of material into your sample. In these cases, ultra-pure materials like platinum or glassy carbon may be necessary.
Physical Size and Fit
As a final check, ensure the crucible's outer dimensions will comfortably fit inside your muffle furnace's chamber. You must leave enough room to safely place and retrieve the crucible with tongs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your specific goal as the final guide to your selection.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose ashing or simple heating below 1100°C: A porcelain crucible offers the best value.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature work (1100°C to 1700°C) with most common materials: A high-purity alumina crucible is your most reliable and versatile choice.
- If your primary focus is any process involving rapid heating, cooling, or thermal cycling: A quartz crucible is essential to prevent cracking.
- If your primary focus is melting metals or extreme temperature applications: A silicon carbide or other specialized crucible is required.
By matching the material to your specific temperature, chemical, and process needs, you ensure reliable and accurate results in your work.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Max Temperature | Key Strength | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain | 1100°C (2012°F) | Cost-Effective | General ashing, volatile content testing |
| Alumina | 1700°C (3092°F) | High-Temperature Stability | Sintering, melting, materials research |
| Quartz | 1200°C (2192°F) | Exceptional Thermal Shock Resistance | Rapid heating/cooling processes |
| Silicon Carbide | Very High | Durability & Thermal Conductivity | Melting non-ferrous metals |
Ensure Accurate and Reliable Results with the Right Crucible
Choosing the correct crucible is critical for the success of your high-temperature processes. The wrong material can lead to sample contamination, inaccurate data, or even equipment damage.
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing a wide range of high-quality crucibles tailored to your specific application needs. Whether you require cost-effective porcelain for routine ashing, high-purity alumina for advanced research, or specialized quartz for rapid thermal cycling, we have the expertise and products to support your work.
Let our specialists help you select the perfect crucible to maximize your lab's efficiency and data integrity. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure your muffle furnace operations are a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a muffle furnace? Achieve High-Purity Heating for Your Lab
- What is the principle working and use of muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is a muffle furnace in food analysis? A Guide to Precise Mineral Content Measurement
- How to use a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Operation
- How to maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety



















