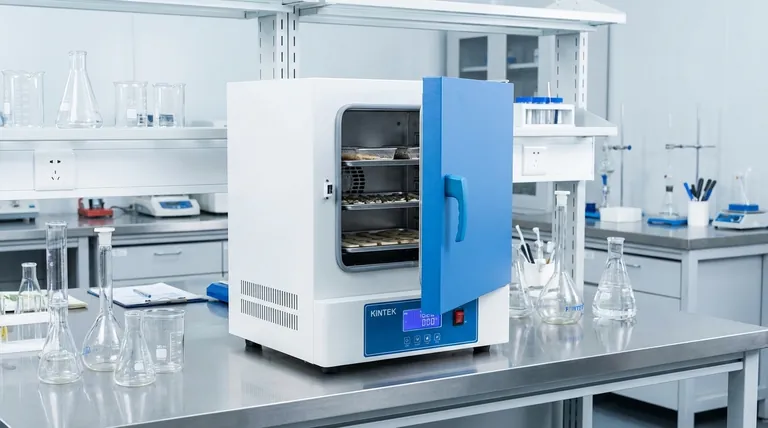
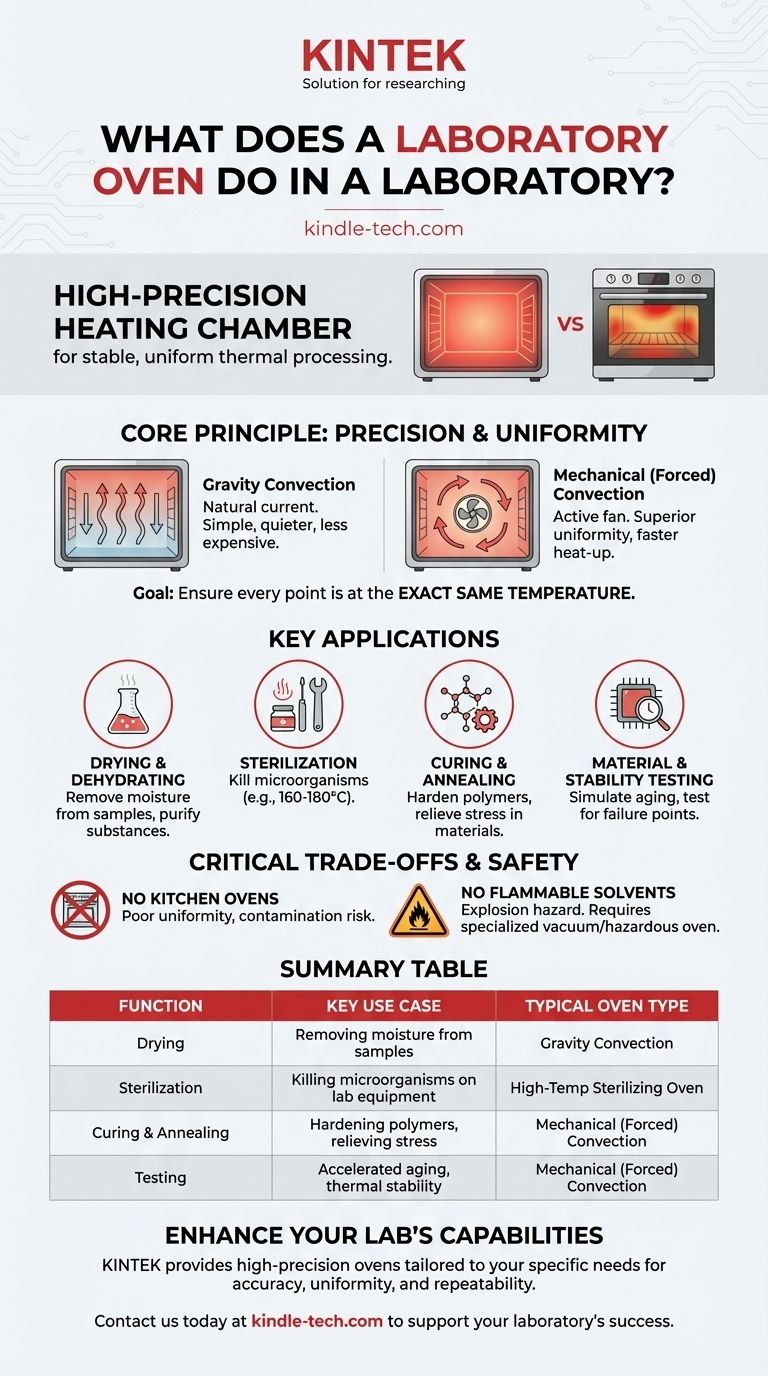
In essence, a laboratory oven is a high-precision heating chamber used to create a stable, uniform temperature environment. Unlike a conventional kitchen oven, its primary purpose is not cooking, but performing critical scientific and industrial processes such as drying, sterilizing, curing, and testing materials under controlled thermal conditions. Its value lies in its accuracy, temperature uniformity, and repeatability.
A laboratory oven is fundamentally a tool for thermal processing. Its core function is to maintain a precise and uniform temperature, which is a non-negotiable requirement for an enormous range of scientific, research, and quality control applications.
The Core Principle: Precision and Uniformity
A lab oven’s design is entirely focused on creating a predictable and homogenous thermal environment. This is what separates it from any other heating device.
Beyond Simple Heating
The goal is not just to make the chamber hot, but to ensure every point within it is at the exact same temperature. This uniformity is critical for experiments and processes where even a few degrees of variation could invalidate the results, ruin a sample, or cause a product to fail.
How It Achieves Uniformity
Most laboratory ovens use one of two methods to circulate air and maintain a consistent temperature:
- Gravity Convection: Hot air naturally rises and cooler, denser air falls. These ovens rely on this natural current. They are simpler, quieter, and less expensive.
- Mechanical (Forced) Convection: A fan actively circulates the air inside the chamber. This provides superior temperature uniformity and faster heat-up and recovery times after the door is opened.
The Importance of Temperature Control
Modern lab ovens use sophisticated microprocessor controls (like PID controllers) to manage the heating element. This allows the oven to reach the target temperature precisely without "overshooting" it, which could damage sensitive samples.
Key Applications in Science and Industry
The ability to create a controlled thermal environment makes lab ovens indispensable for a wide variety of tasks.
Drying and Dehydrating
This is one of the most common uses. It involves removing moisture from research samples, purifying substances, or simply drying laboratory glassware to ensure it is completely free of water before use.
Sterilization
High-temperature dry-heat sterilization is used to kill all microorganisms on laboratory equipment, typically metal or glass instruments. This process requires maintaining a high temperature (e.g., 160°C to 180°C) for a specific duration to ensure sterility.
Curing and Annealing
In materials science and manufacturing, ovens are used to cure materials like polymers, epoxies, and composites, causing them to harden and strengthen. They are also used for annealing, a process of heating and slow-cooling glass or metal to remove internal stresses and improve ductility.
Material and Stability Testing
Ovens are crucial for quality control. They subject products, components, and materials to elevated temperatures to simulate long-term aging, test for thermal failure points, or determine a product's shelf life. This is common in the electronics, pharmaceutical, and automotive industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or using a lab oven requires understanding its limitations and the different types available.
Gravity vs. Forced Convection
The biggest trade-off is between gravity and forced convection. A gravity oven is suitable for simple drying, but a forced-air oven is necessary for tasks requiring tight uniformity or for processing samples that could be disturbed by airflow, like fine powders. The fan in a forced-convection oven can sometimes increase sample evaporation.
Why You Can't Use a Kitchen Oven
A common question is whether a kitchen oven can be substituted. The answer is an emphatic no. Kitchen ovens have poor temperature uniformity (often with "hot spots"), lack the precise controls, and are not built to safely handle chemical vapors or prevent contamination of a sensitive experiment.
Safety and Venting
Laboratory ovens are not designed to heat flammable or volatile solvents. Doing so can cause vapors to build up and create a serious explosion hazard. For these applications, a specialized hazardous material or vacuum oven with specific safety and ventilation features is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct type of oven and process is critical for achieving valid, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is drying glassware or non-sensitive samples: A simple gravity convection oven is often sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is ensuring precise uniformity for testing or curing: A mechanical (forced-convection) oven is essential for reliable and repeatable outcomes.
- If your primary focus is sterilization of lab instruments: You must use a high-temperature, dry-heat sterilizing oven that can meet specific time and temperature protocols.
- If you are working with solvents or volatile compounds: It is mandatory to use a vacuum oven or a specialized oven designed with safety features for hazardous materials.
Using a laboratory oven correctly is fundamental to ensuring the accuracy, repeatability, and safety of your work.

Summary Table:
| Function | Key Use Case | Typical Oven Type |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | Removing moisture from samples, drying glassware | Gravity Convection |
| Sterilization | Killing microorganisms on lab equipment | High-Temperature Sterilizing Oven |
| Curing & Annealing | Hardening polymers, relieving stress in materials | Mechanical (Forced) Convection |
| Testing | Accelerated aging, thermal stability testing | Mechanical (Forced) Convection |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with the right thermal processing equipment?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-precision laboratory ovens and equipment tailored to your specific needs—whether for drying, sterilization, curing, or material testing. Our solutions ensure the accuracy, uniformity, and repeatability your research demands.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory-grade forced air drying oven required for alloy chip moisture analysis? Ensure Data Precision
- Why is a forced-air drying oven required for ZnS powder? Protect Sintered Ceramics from Cracking
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results



















