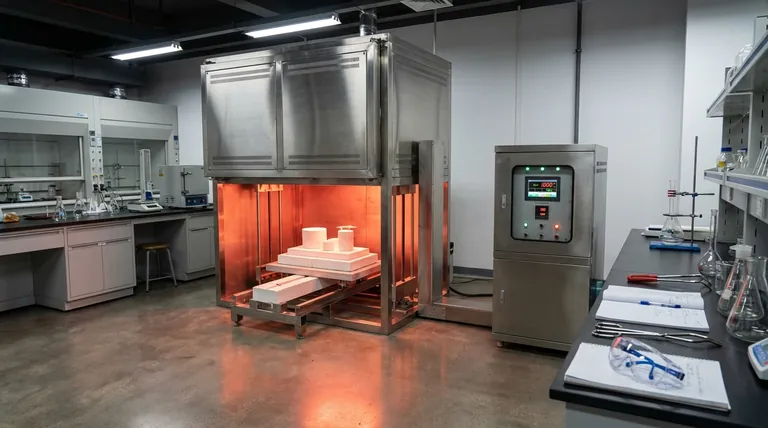
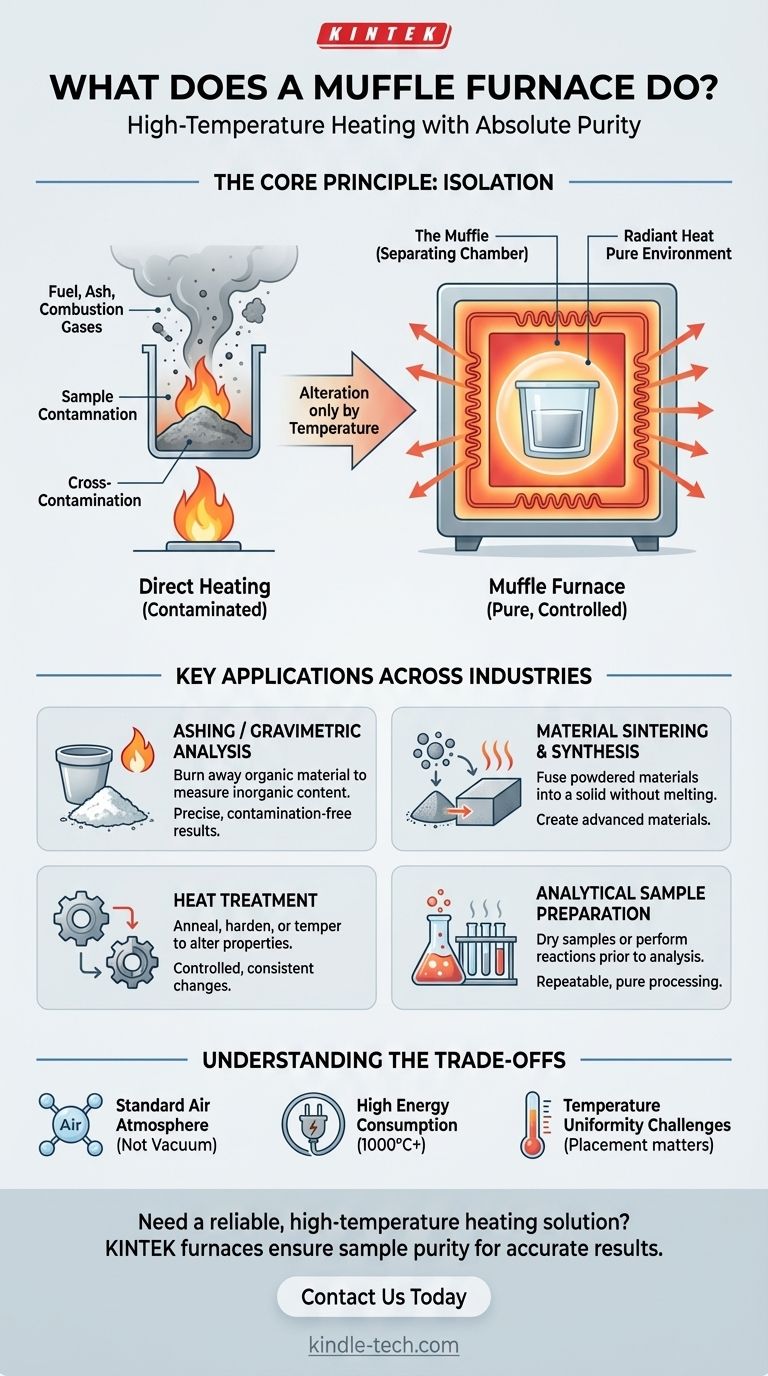
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that excels at one critical task: heating a material while isolating it from the direct heat source and any byproducts of combustion. This separation ensures that the sample is altered only by temperature, providing a pure, controlled environment for analysis and processing.
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace isn't just its ability to reach extreme temperatures, but its ability to do so cleanly. It guarantees that the material being heated is never contaminated by fuel, ash, or combustion gases, which is essential for accurate scientific analysis.

The Core Principle: Heating Without Contamination
A muffle furnace is designed to deliver thermal energy to a sample without any chemical interaction between the sample and the heating process itself.
What "Muffle" Actually Means
The term muffle refers to the separating chamber or barrier. In traditional fuel-fired furnaces, this was a physical, sealed container placed inside the larger oven.
Modern electric furnaces function more elegantly. The entire insulated inner chamber, which houses the sample, acts as the muffle. High-temperature heating coils are embedded within the insulated walls, radiating heat into the chamber without ever making direct contact with the sample's atmosphere.
The Critical Benefit of Isolation
This isolation is the furnace's primary advantage. It prevents cross-contamination, which is vital for any quantitative analysis.
When a material is analyzed, the results must reflect the properties of the material itself, not any residue left behind by a flame or fuel source. A muffle furnace provides this necessary purity.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to heat materials cleanly to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C makes the muffle furnace an indispensable tool in science and industry.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
This is one of the most common uses. Ashing is the process of completely burning away all organic components of a sample to precisely measure the weight of the remaining inorganic material (the ash).
This is critical in coal analysis for determining ash, moisture, and volatile content, and in food science for establishing mineral content.
Material Synthesis and Sintering
Creating advanced materials or ceramics often requires heating powdered components to high temperatures. Sintering uses heat to fuse particles together into a solid object without melting them.
The muffle furnace provides the stable, clean, and high-temperature environment needed for these reactions to occur correctly.
Heat Treatment of Materials
The furnace is used for processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering metals and other materials. These processes alter a material's microstructure to change its physical properties, such as its hardness or ductility.
Doing this in a controlled, contaminant-free chamber ensures consistent and predictable results.
Analytical Sample Preparation
In environmental science, pharmaceuticals, and chemistry, samples often need to be processed at high temperatures before they can be analyzed by other instruments.
A muffle furnace can be used to dry samples, perform specific chemical reactions, or prepare materials for further testing in a repeatable and clean manner.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, it's important to recognize the specific role of a standard muffle furnace.
Designed for an Air Atmosphere
A standard muffle furnace operates with a normal air atmosphere inside the chamber. It is not designed for processes that require a vacuum or a specific, reactive-free atmosphere like pure argon or nitrogen unless it is a specially modified model.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1000-1200°C is an energy-intensive process. These furnaces represent a significant power draw in any laboratory environment.
Temperature Uniformity
While modern furnaces have excellent controls, achieving perfect temperature uniformity in every corner of the chamber can be a challenge. For highly sensitive processes, the precise placement of the sample within the furnace is an important consideration.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The specific term you use for the process depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is determining inorganic content: You are performing ashing, using the furnace to burn away organic material for precise measurement.
- If your primary focus is altering a material's physical properties: You are performing heat treatment, relying on the furnace's clean, high-temperature environment to change the material's internal structure.
- If your primary focus is creating a new solid material from powders: You are using the furnace for sintering or synthesis, where controlled heating without contamination is paramount.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the tool of choice whenever you need absolute certainty that heat—and only heat—is affecting your sample.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing / Gravimetric Analysis | Burn away organic material to measure inorganic ash content. | Precise, contamination-free results for accurate analysis. |
| Material Sintering & Synthesis | Fuse powdered materials into a solid without melting. | Clean, high-temperature environment for creating advanced materials. |
| Heat Treatment | Anneal, harden, or temper materials to alter properties. | Controlled atmosphere ensures consistent and predictable material changes. |
| Sample Preparation | Dry samples or perform reactions prior to other analyses. | Repeatable, pure processing for reliable scientific testing. |
Need a reliable, high-temperature heating solution for your lab?
A muffle furnace from KINTEK is essential for applications where sample purity is non-negotiable. Whether you are in quality control, materials science, or research and development, our furnaces provide the clean, isolated environment required for accurate ashing, sintering, and heat treatment.
Let KINTEK, a specialist in lab equipment and consumables, provide the right furnace for your specific laboratory needs.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how our solutions can enhance your processes and ensure the integrity of your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental impacts of metal processing? A Guide to Sustainability and Solutions
- What is the meaning of debinding? Master the Critical Step to High-Performance Parts
- How is a muffle furnace used for sample digestion? A Guide to Dry Ashing for Accurate Analysis
- What are the methods of ash determination? Choosing the Right Technique for Accurate Mineral Analysis
- How do you run a muffle furnace? Master the Step-by-Step Process for Safe, Precise Results



















