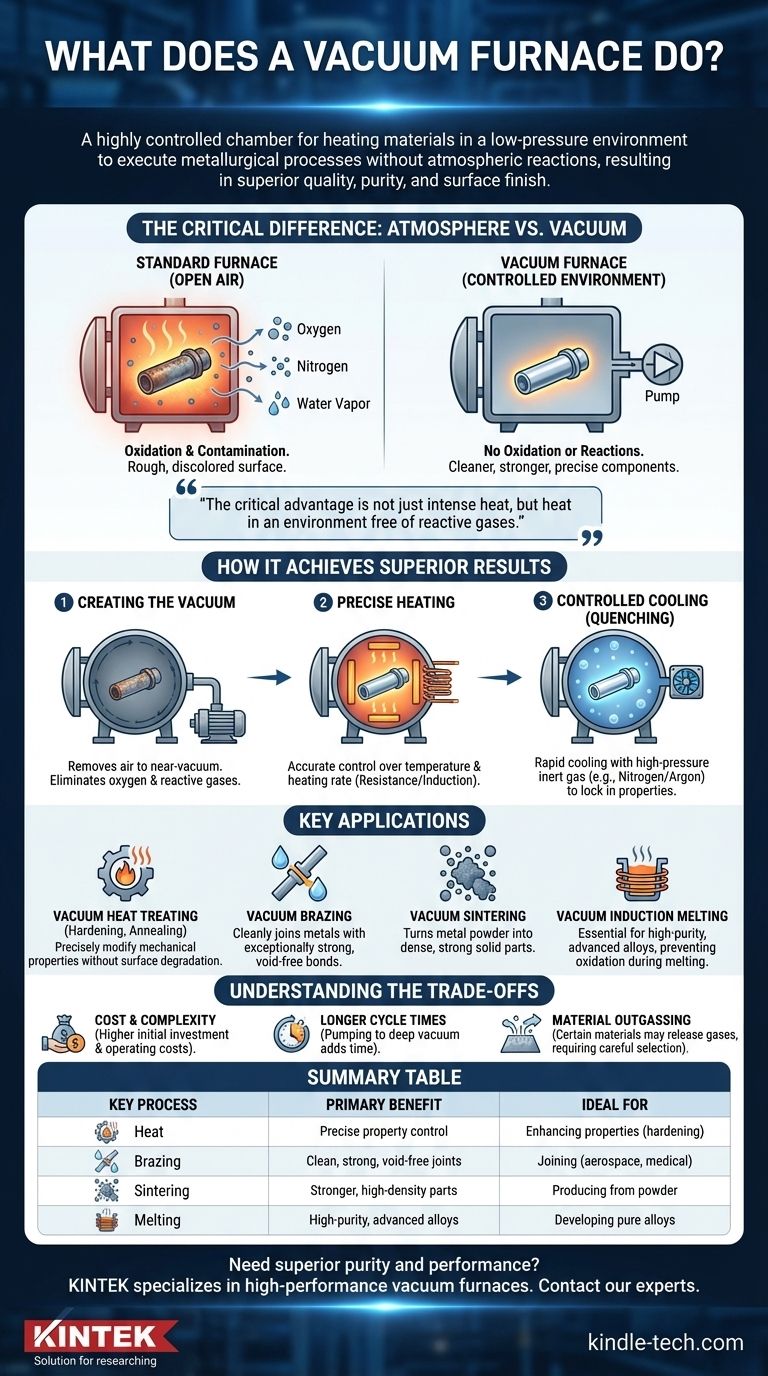
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a highly controlled chamber designed to heat materials to extreme temperatures in a low-pressure environment. Its primary function is to execute metallurgical processes like heat treatment, brazing, and sintering without the material reacting with atmospheric gases. This vacuum environment eliminates oxidation and other contaminants, resulting in components with superior quality, purity, and surface finish.
The critical advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just its ability to generate intense heat, but to do so in an environment free of oxygen and other reactive gases. This prevents oxidation and contamination, enabling metallurgical processes that result in cleaner, stronger, and more precise components.

How a Vacuum Furnace Achieves Superior Results
A standard furnace heats materials in the open air, which is full of oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. A vacuum furnace first removes the air and then applies heat, fundamentally changing the outcome of the process.
Creating the Controlled Environment
The furnace consists of a sealed, robust chamber connected to a powerful vacuum pump system. Before heating begins, these pumps remove the air, reducing the internal pressure to a near-vacuum.
This step is what eliminates virtually all oxygen and other reactive gases that would otherwise degrade the surface of the material being processed.
Precise Heating Mechanisms
Once the vacuum is established, internal heating elements raise the temperature. These can be resistance heaters (like in a toaster, but far more powerful) or induction coils that use electromagnetic fields to heat the metal directly.
Because the chamber is sealed and insulated, these systems allow for exceptionally precise control over the temperature, as well as the rate of heating.
The Critical Benefit: Preventing Reactions
In a conventional furnace, high temperatures cause metals to react with oxygen, forming a rough, discolored layer of oxide scale. A vacuum environment prevents this entirely.
This results in parts with a bright, clean surface finish right out of the furnace, eliminating the need for subsequent cleaning or machining. It also prevents decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface of steel—which preserves the material's intended hardness and strength.
Controlled Cooling (Quenching)
After the heating cycle, many processes require rapid cooling to lock in the desired material properties. Vacuum furnaces accomplish this by backfilling the chamber with a high-pressure, non-reactive inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon.
A powerful fan circulates this gas, removing heat from the part at a precisely controlled rate, a process known as gas quenching.
Key Applications of Vacuum Furnace Technology
The unique environment inside a vacuum furnace makes it essential for high-performance applications where material integrity is paramount.
Vacuum Heat Treating
This includes processes like hardening, annealing, and tempering. By heating and cooling metal in a vacuum, its mechanical properties (like hardness, toughness, and ductility) can be precisely modified without any surface degradation.
Vacuum Brazing
Brazing is a process for joining two pieces of metal using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature. Performing this in a vacuum ensures the filler flows cleanly into the joint, creating an exceptionally strong, pure, and void-free bond common in aerospace and medical applications.
Vacuum Sintering
Sintering turns compacted metal powder into a solid, dense part by heating it until the particles fuse. A vacuum prevents gases from becoming trapped between the powder particles, resulting in a stronger, higher-density final product.
Vacuum Induction Melting
This process uses induction heating to melt metals within a vacuum. It is essential for producing high-purity, advanced alloys, as the vacuum prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen or nitrogen, which would create impurities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the solution for every heating application. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts. They require complex vacuum pump systems, robust chamber construction, and sophisticated control systems.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping the chamber down to a deep vacuum takes time. This means the total cycle time per batch is often longer than in a conventional furnace, which can impact throughput.
Material Outgassing
Certain materials can release trapped gases or vaporize at low pressures and high temperatures, a phenomenon known as outgassing. This can contaminate the vacuum environment and affect the surface chemistry of the parts being processed, requiring careful material selection and process control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use a vacuum furnace should be driven by the required final properties and quality of the component.
- If your primary focus is enhancing material properties: Vacuum heat treating offers precise control over hardness and strength without the negative side effect of surface oxidation.
- If your primary focus is creating high-integrity joints: Vacuum brazing provides exceptionally clean and strong bonds, essential for mission-critical components.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity parts from powder: Vacuum sintering is the ideal method for creating dense components free from internal voids or contamination.
- If your primary focus is developing advanced, pure alloys: Vacuum induction melting is the required standard for preventing reactions with atmospheric gases during the melting process.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace is the definitive tool when the integrity, purity, and surface finish of a material cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Key Process | Primary Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Heat Treating | Precise control of hardness & strength without surface oxidation | Enhancing material properties (hardening, annealing) |
| Vacuum Brazing | Exceptionally clean, strong, void-free joints | Joining mission-critical components (aerospace, medical) |
| Vacuum Sintering | Stronger, higher-density parts from metal powder | Producing high-purity parts from powder |
| Vacuum Induction Melting | High-purity, advanced alloys without impurities | Developing advanced, pure alloys |
Need to achieve superior material purity and performance?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces for heat treating, brazing, sintering, and melting. Our solutions are designed to help you produce components with exceptional integrity, cleanliness, and strength, free from oxidation and contamination.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect vacuum furnace solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals undergo annealing? Unlock Ductility for Steel, Copper, Brass & Aluminum
- What are sintered products? Engineered Materials Built from Powder for Superior Performance
- Why is post-processing in a high-temperature furnace required for SLM nickel-based alloy parts? Key Benefits Explained
- How do vacuum furnaces heat? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- Where is sintering process used? Unlock Dense, Strong Parts from Powders
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum annealing furnace play in Ti-Cr-Al-Nb-V alloys? Optimize Phase Transformation
- What features are required in high-temperature furnace equipment for the large-scale pyrolysis of nano-packaging particles?
- How do you braze a furnace? A Guide to High-Volume, Precision Metal Joining



















