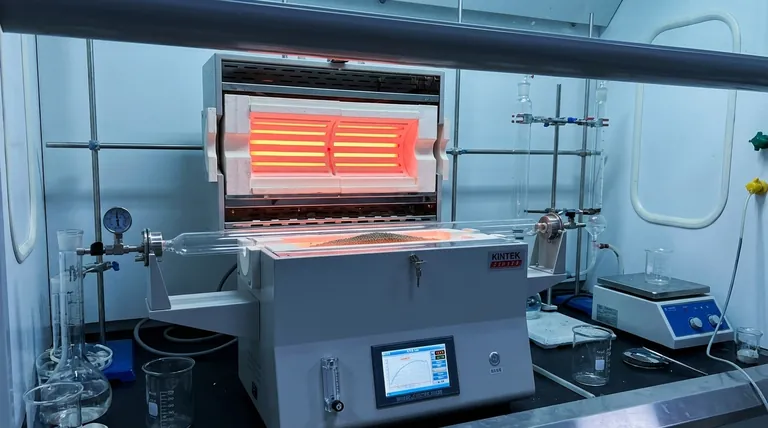
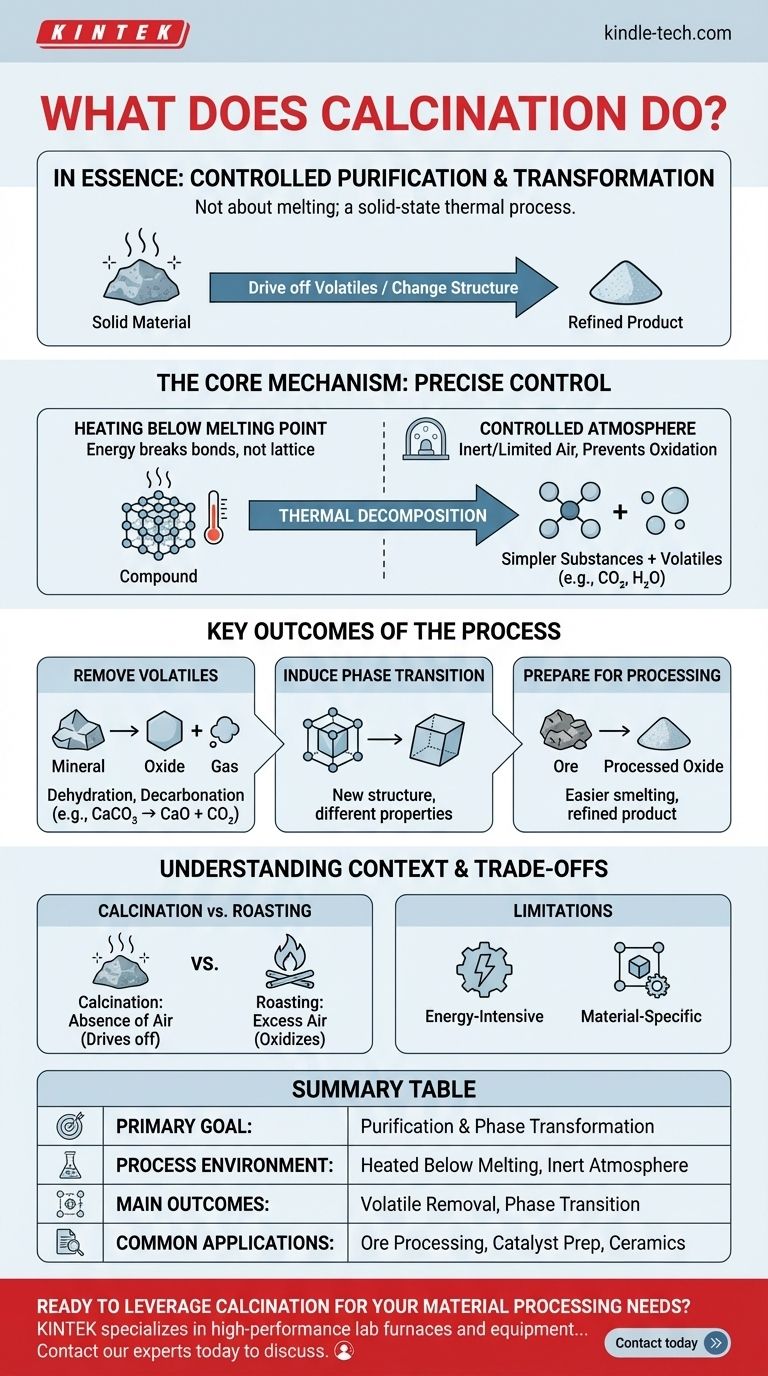
In essence, calcination is a highly controlled purification and transformation process. It involves heating a solid material to a high temperature, but below its melting point, in an environment with little to no oxygen. This precise heat treatment is designed to drive off volatile substances, such as water or carbon dioxide, or to change the material's internal crystal structure.
Calcination is not about melting; it is a solid-state thermal process used to deliberately decompose a material or alter its physical phase, effectively "baking out" impurities to yield a more refined or reactive product.

The Core Mechanism: How Calcination Works
Calcination's effectiveness comes from the precise control of two key variables: temperature and atmosphere. The goal is to induce specific chemical or physical changes without fundamentally destroying the material through melting or unwanted side reactions.
Heating Below the Melting Point
The entire process is conducted while the material remains a solid. By carefully managing the temperature, energy is introduced to break specific chemical bonds within the material's structure, but not enough energy is supplied to break down the entire solid lattice into a liquid.
A Controlled Atmosphere
Calcination is defined by its use of an inert or limited-air environment. This is a critical distinction, as it prevents oxidation. Without excess oxygen, the material doesn't "burn" or rust; it simply decomposes based on the heat applied.
Driving Thermal Decomposition
The primary purpose of the heat is to cause thermal decomposition. This is the process where a compound breaks down into simpler substances. A classic example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide gas, which escapes.
Key Outcomes of the Calcination Process
Depending on the material and the goal, calcination can produce several distinct outcomes, all of which prepare the material for a subsequent step or final use.
Removal of Volatile Substances
This is the most common application. Calcination is exceptionally effective at removing chemically bound water (dehydration) or carbon dioxide (decarbonation) from ores and other minerals. This purification step increases the concentration of the desired element.
Inducing a Phase Transition
Heat can also be used to change the internal crystalline structure of a material. This is called a phase transition. While the chemical formula remains the same, the new structure can have vastly different physical properties, such as hardness, density, or chemical reactivity.
Preparing Materials for Further Processing
Often, calcination is not the final step but a crucial preparatory one. For example, converting metal ores into their oxide forms makes them easier to process in a subsequent step, such as smelting, to extract the pure metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
While powerful, calcination is a specific tool for specific jobs. Understanding its context is key to appreciating its role in industry and materials science.
Calcination vs. Roasting
These terms are often confused. Calcination occurs in the absence of air to drive off volatiles. Roasting is done in the presence of excess air, specifically to react the material with oxygen (oxidation).
An Energy-Intensive Process
Heating large volumes of solid material to hundreds or thousands of degrees requires a significant amount of energy. This makes it a costly part of any industrial process and a major factor in operational planning.
Material-Specific Application
Calcination is not a universal purification method. It is only effective for materials that contain volatile components (like carbonates or hydrates) that can be driven off by heat or for materials that benefit from a specific heat-induced phase change.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying calcination effectively means aligning the process with your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is to produce a pure metal oxide from a carbonate ore: Calcination is the essential first step to drive off carbon dioxide before smelting.
- If your primary focus is to remove chemically bound water from a mineral: Controlled calcination provides the necessary heat for dehydration without altering or melting the target compound.
- If your primary focus is to create a more reactive final product: Calcination can be used to create a more porous structure or induce a phase transition that increases the material's surface area and reactivity.
By precisely applying heat in a controlled environment, calcination grants us the ability to transform and purify solid materials at a fundamental level.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Purification and phase transformation of solid materials. |
| Process Environment | Heated below melting point in a limited-oxygen or inert atmosphere. |
| Main Outcomes | Removal of volatile substances (e.g., water, CO₂); Induction of phase transitions. |
| Common Applications | Ore processing, catalyst preparation, ceramic production, and material synthesis. |
Ready to leverage calcination for your material processing needs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment designed for precise thermal treatments like calcination. Our solutions ensure the controlled environments and exact temperatures required to achieve your specific purification and transformation goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's efficiency and innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What are the typical heating zone configurations and maximum temperature capabilities of tube furnaces? Find the Right Setup for Your Lab



















