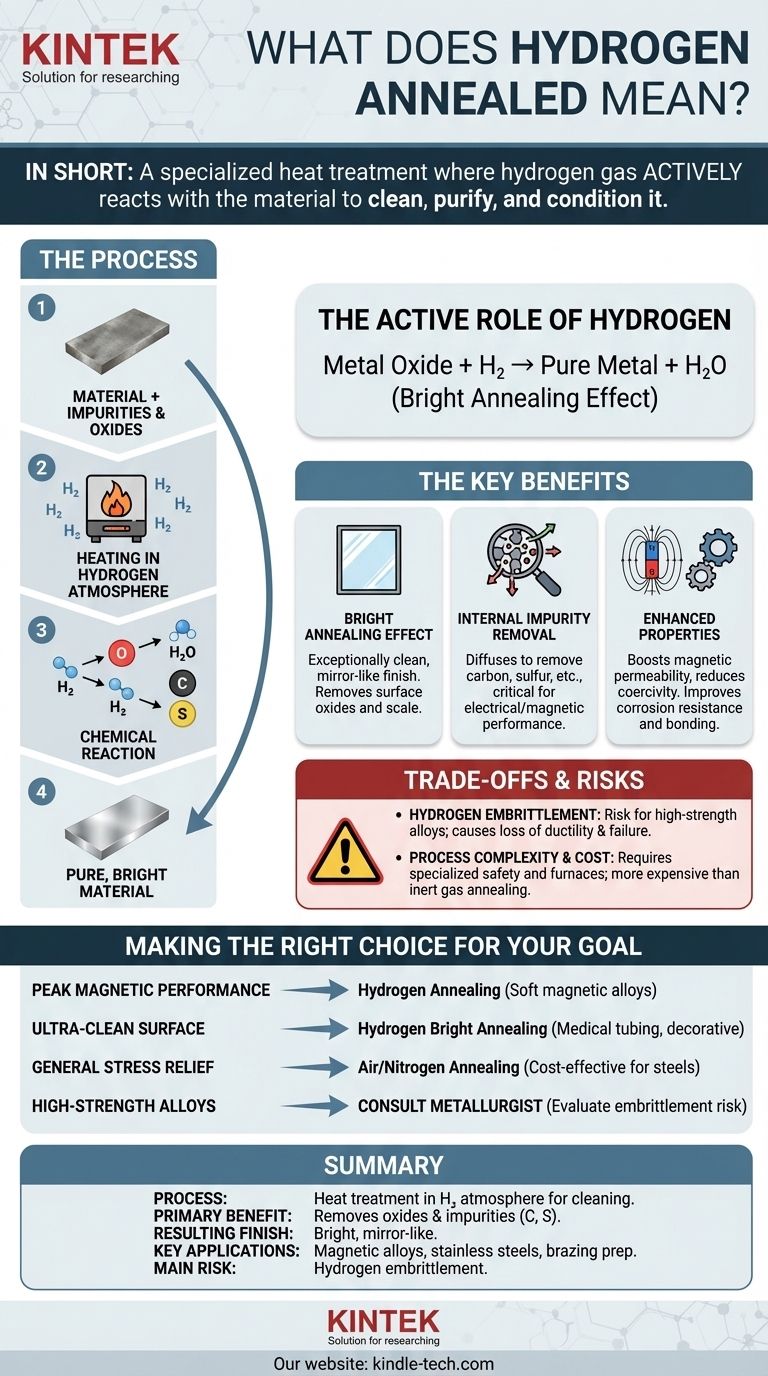
In short, hydrogen annealing is a specialized heat treatment process where a material is heated in a controlled atmosphere containing hydrogen gas. Unlike other atmospheres that are merely protective, the hydrogen actively reacts with the material, serving as a chemical agent to clean its surface and remove impurities. This "active" role is what makes the process unique and powerful for specific applications.
Hydrogen annealing is not just about heating a material; it is a chemical purification and conditioning process. It uses hydrogen's reactive properties to achieve a level of cleanliness and microstructural quality that is often unobtainable with other annealing methods.

The Fundamentals: Annealing in a Controlled Atmosphere
What is Annealing?
Annealing is a foundational heat treatment process in materials science. It involves heating a material to a specific temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it slowly.
This process alters the material's internal microstructure. The primary goals are to relieve internal stresses, increase softness and ductility (the ability to be shaped), and refine the grain structure.
The Need for an Atmosphere
When metals are heated to high temperatures, they readily react with oxygen in the air. This reaction, called oxidation, forms a layer of scale or oxide on the surface.
To prevent this, annealing is often performed in a controlled atmosphere. A common choice is an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, which simply displaces the oxygen and protects the material.
The Role of Hydrogen: From Protective to Active
Hydrogen as a Reducing Agent
This is where hydrogen annealing diverges. Hydrogen is not an inert gas; it is a powerful reducing agent. This means it actively strips oxygen atoms from other molecules.
When a hot metal part has existing oxides on its surface, the hydrogen gas will react with them, converting the metal oxides back into pure metal and creating water vapor (Metal Oxide + H₂ → Pure Metal + H₂O).
The "Bright Annealing" Effect
This chemical cleaning action results in an exceptionally clean, bright, and often mirror-like surface finish. This is why the process is frequently called bright hydrogen annealing.
It effectively scrubs the material's surface on a molecular level, a result that mechanical polishing often cannot achieve without introducing new surface stresses.
Removing Internal Impurities
Hydrogen's benefits extend beneath the surface. It can diffuse into the metal and react with other non-metallic impurities, most notably carbon and sulfur.
This purification is critical for certain applications, as these impurities can hinder electrical or magnetic performance.
Key Applications and Benefits
Enhancing Magnetic Properties
For soft magnetic materials like electrical steel, permalloy, and mu-metal, performance is directly tied to purity and a stress-free crystal structure.
Hydrogen annealing is critical for these alloys. By removing impurities like carbon and oxygen that "pin" magnetic domain walls, it dramatically increases magnetic permeability and reduces coercivity, making them far more efficient in transformers, sensors, and magnetic shields.
Improving Stainless Steels
In the manufacturing of stainless steel, particularly high-purity grades used in medical or semiconductor applications, hydrogen annealing provides a pristine, passive surface.
This bright-annealed finish is highly corrosion-resistant and does not require secondary acid pickling or polishing, which can introduce contaminants.
Preparing for Bonding and Brazing
Because it produces an atomically clean surface free of oxides, hydrogen annealing is an excellent preparatory step for brazing, metal-to-ceramic sealing, and other bonding processes. The clean surface allows for superior wetting and a stronger, more reliable joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The Danger of Hydrogen Embrittlement
The primary risk associated with this process is hydrogen embrittlement. In some materials, particularly high-strength steels, titanium, and certain nickel alloys, individual hydrogen atoms can diffuse into the metal.
These atoms disrupt the metal's crystal lattice, causing a significant loss of ductility and leading to premature, catastrophic failure under load. Proper material selection and process control are absolutely critical to avoid this.
Process Complexity and Cost
Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires specialized furnaces with advanced safety protocols. This makes hydrogen annealing a more complex and expensive process compared to annealing in air or with inert gases.
The decision to use it is therefore driven by applications where its unique chemical cleaning benefits justify the added cost and risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding if hydrogen annealing is necessary, your end goal is the most important factor.
- If your primary focus is peak magnetic performance: For soft magnetic alloys used in sensitive electronic components, hydrogen annealing is often the industry-standard requirement.
- If your primary focus is an ultra-clean, passive surface: For medical-grade tubing, high-purity fittings, or decorative parts, hydrogen bright annealing provides a superior finish without secondary processing.
- If your primary focus is stress relief for general-purpose steels: A simpler process using air or a nitrogen atmosphere is almost always more cost-effective and safer.
- If you are working with high-strength or exotic alloys: You must consult a metallurgist to evaluate the severe risk of hydrogen embrittlement before specifying this process.
Ultimately, hydrogen annealing is a precision tool used when a material's performance is critically dependent on its chemical purity and surface condition.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heat treatment in a hydrogen atmosphere for chemical cleaning. |
| Primary Benefit | Removes surface oxides and internal impurities like carbon and sulfur. |
| Resulting Finish | Bright, mirror-like surface ("Bright Annealing"). |
| Key Applications | Soft magnetic alloys, high-purity stainless steels, brazing preparation. |
| Main Risk | Hydrogen embrittlement in certain high-strength alloys. |
Need to achieve superior material purity and performance?
KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including hydrogen annealing. Our expertise ensures your lab's materials—from soft magnetic alloys to high-purity stainless steels—achieve the optimal surface finish, magnetic properties, and structural integrity required for critical applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can meet your specific material science needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What are the characteristics and risks of a hydrogen atmosphere in a furnace? Master the Balance of Power and Control
- What is the role of an atmosphere protection sintering furnace in LiFePO4/C synthesis? Optimize Battery Performance
- Why is argon used in steel making? For Superior Protection, Purity, and Performance
- What is the function of a tube atmosphere furnace in MLM? Optimize Your CNT/Cu Composite Production
- What is the role of an atmosphere control system for proton-conducting perovskites? Essential Performance Evaluation
- What is the primary function of an industrial atmosphere sintering furnace? Achieve Dense, High-Strength Components
- How to create an inert atmosphere in a furnace? Master the Vacuum-Purge Method for Oxidation-Free Results



















