In manufacturing, PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. It is a sophisticated vacuum coating process used to apply an extremely thin but highly durable film onto the surface of a product. This process is not about creating the object itself, but about modifying its surface to significantly enhance its durability, functionality, and aesthetic appearance.
The core purpose of PVD is to give an ordinary material extraordinary properties. By depositing a microscopic layer of a high-performance material, you can make a product harder, more resistant to wear, or imbue it with specific electrical or optical characteristics.
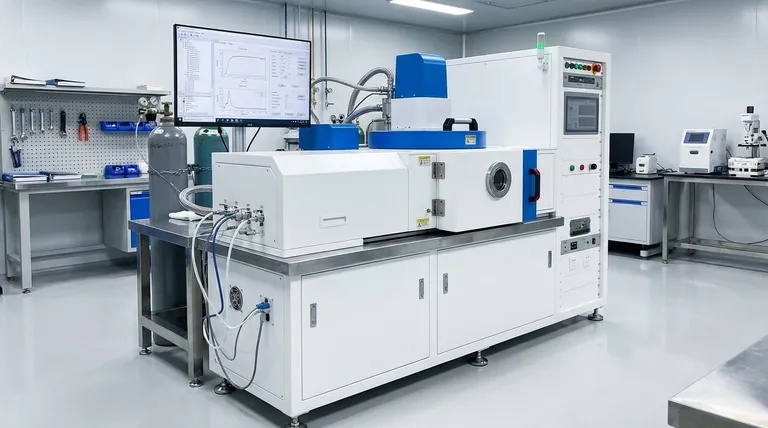

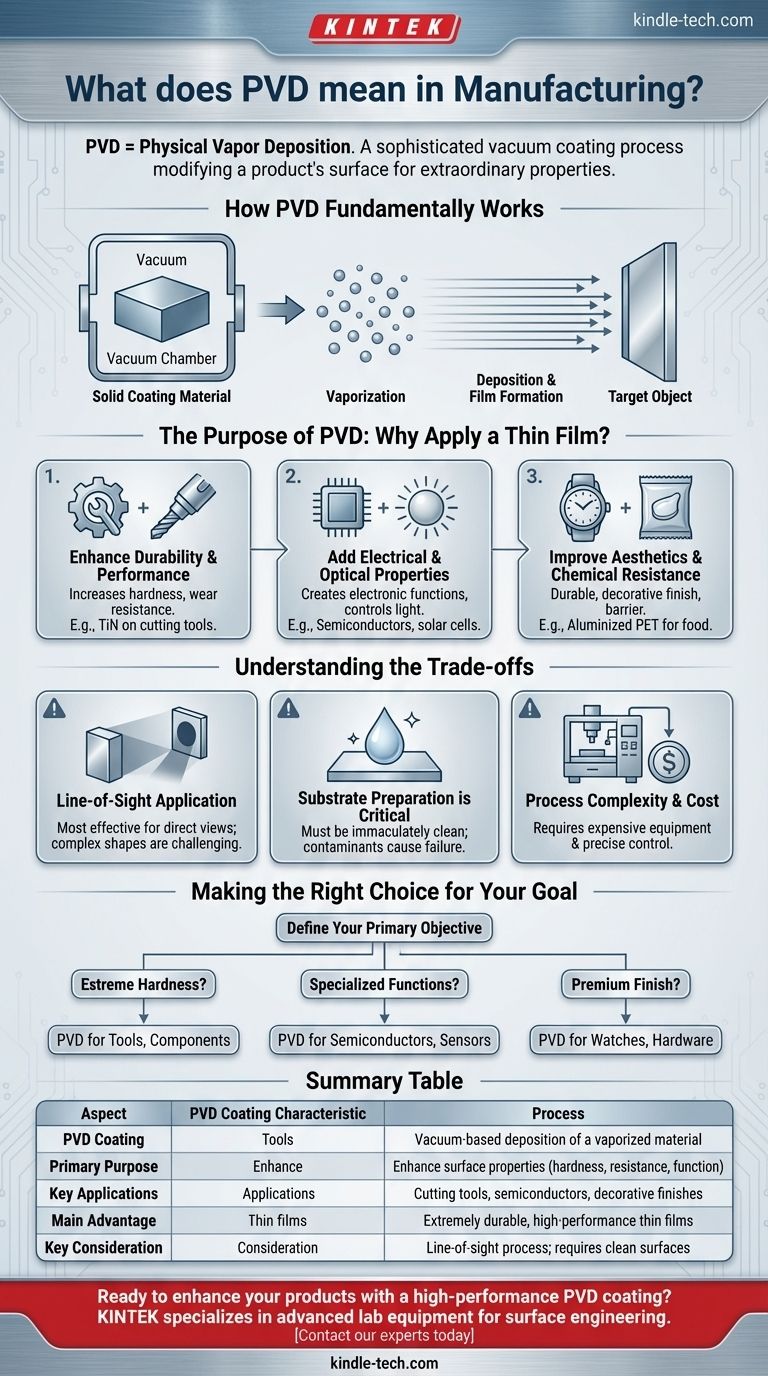
How PVD Fundamentally Works
The Concept of Deposition
At its heart, PVD is a process that takes place inside a high-vacuum chamber. It involves turning a solid coating material into a vapor.
This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto the target object, atom by atom, forming a thin, bonded, and extremely uniform film.
The Role of the Vacuum
The vacuum environment is critical. It removes air and other particles that could otherwise interfere with the process, ensuring the vaporized coating material travels in a straight line and adheres to the substrate with maximum purity and strength.
The Purpose of PVD: Why Apply a Thin Film?
PVD coatings are chosen to solve specific engineering and design challenges. The applied film gives the base material new capabilities it did not previously possess.
Enhancing Durability and Performance
One of the most common uses for PVD is to drastically increase the hardness and wear resistance of an object.
A classic example is coating metalworking cutting tools with titanium nitride (TiN). This hard ceramic layer allows the tool to last much longer and perform better under extreme stress.
Adding Electrical and Optical Properties
PVD is essential in high-tech manufacturing for creating layers with specific electronic or light-manipulating functions.
This is seen in the production of semiconductor devices and thin-film solar cells, where precise layers are deposited to control the flow of electricity or absorb light efficiently.
Improving Aesthetics and Chemical Resistance
PVD can apply a durable, decorative finish that is far superior to traditional plating or painting. It can also create a protective barrier.
For example, aluminized PET film used in food packaging is made using PVD. The thin aluminum layer provides a barrier against oxygen and light, preserving the contents within.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is a specialized industrial process with specific considerations. It is not a universal solution for all coating needs.
Line-of-Sight Application
The vaporized material travels in a straight line. This means that PVD is most effective for coating surfaces that have a direct line of sight to the source material. Coating complex internal shapes can be challenging.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The surface of the object being coated must be immaculately clean. Any contaminants like oil or dust will prevent the film from adhering properly, leading to defects or coating failure.
Process Complexity and Cost
PVD requires expensive vacuum equipment and a high degree of process control. It is a more complex and costly undertaking than simpler coating methods like painting, making it best suited for applications where high performance is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if PVD is the appropriate solution, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: PVD is an excellent choice for extending the life of tools, engine components, and other parts subject to high friction.
- If your primary focus is specialized electronic or optical functions: PVD is an indispensable technology for creating the micro-thin layers required in semiconductors, sensors, and optics.
- If your primary focus is a premium, durable decorative finish: PVD provides a wide range of colors with a level of toughness that far exceeds traditional methods, ideal for watches, hardware, and premium goods.
Ultimately, PVD is a transformative technology for imparting high-performance characteristics onto the surface of an object.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD Coating Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process | Vacuum-based deposition of a vaporized material |
| Primary Purpose | Enhance surface properties (hardness, resistance, function) |
| Key Applications | Cutting tools, semiconductors, decorative finishes |
| Main Advantage | Extremely durable, high-performance thin films |
| Key Consideration | Line-of-sight process; requires clean surfaces |
Ready to enhance your products with a high-performance PVD coating? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our solutions help you achieve superior durability, functionality, and aesthetics. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















