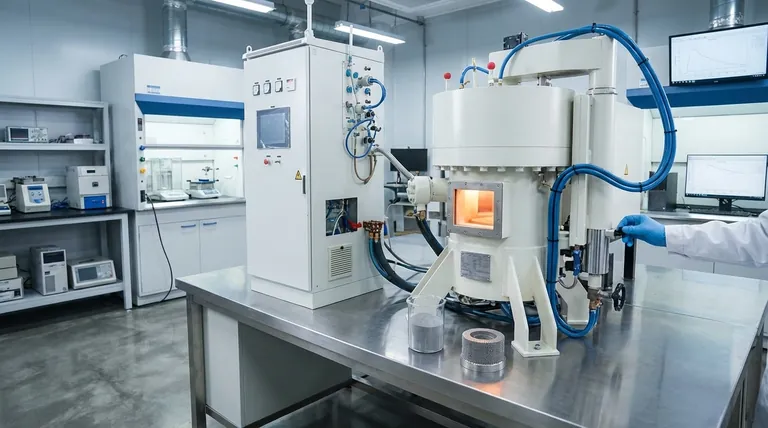
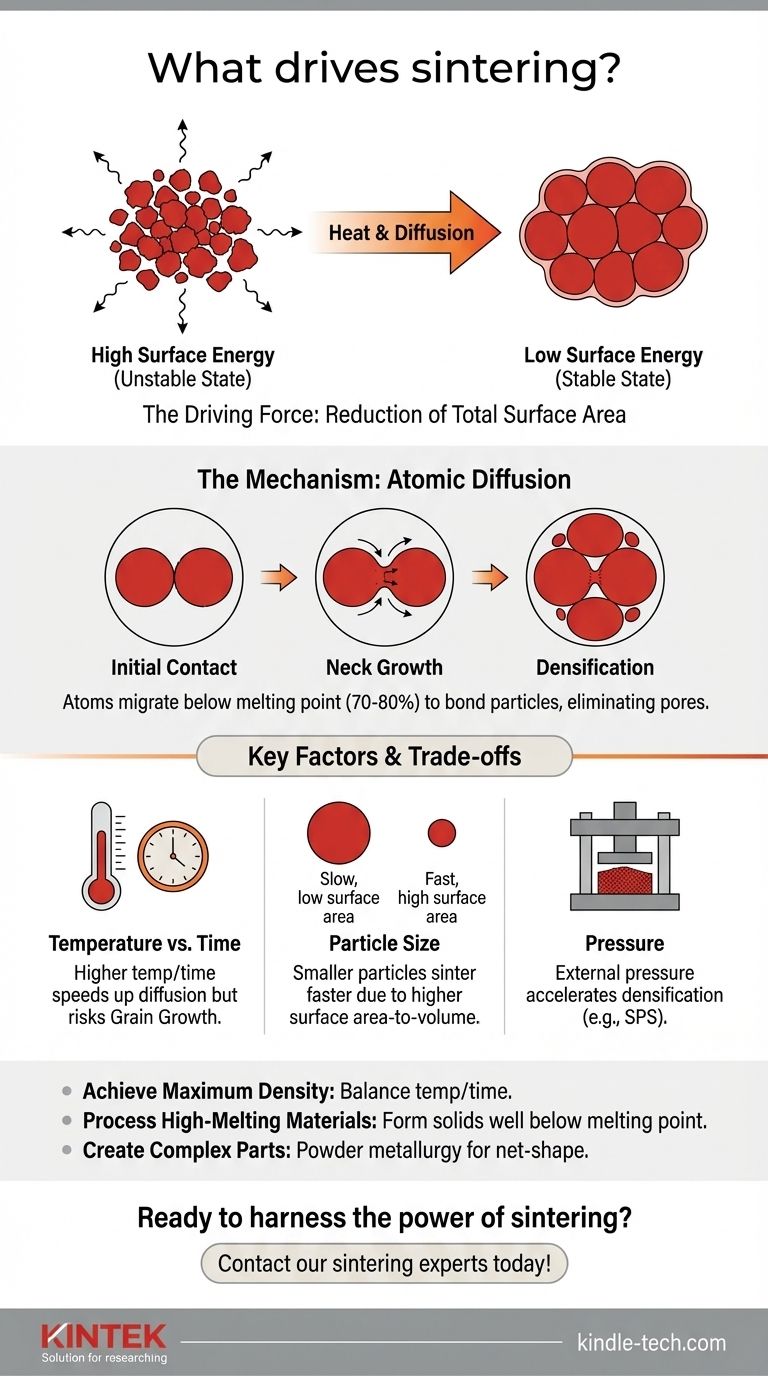
At its core, the driving force for sintering is the reduction of surface energy. A collection of fine powder particles possesses an immense amount of surface area, which represents a thermodynamically unstable, high-energy state. Sintering is the process by which the material, given sufficient heat, rearranges itself to minimize this surface area, resulting in a dense, solid mass.
Sintering is not a melting process. Instead, it leverages a material's natural tendency to reduce its high surface energy. Heat provides the energy for atoms to diffuse across particle boundaries, eliminating the surfaces between them and bonding the particles into a stronger, denser structure.

The Core Principle: Minimizing Surface Energy
Why Powder is a High-Energy State
A given volume of material has vastly more surface area when it's a fine powder compared to when it's a single solid block. This excess surface is associated with an excess of energy, similar to how surface tension causes small water droplets to merge into larger ones.
This high-energy state is inherently unstable. The system will always seek a path toward a lower, more stable energy state if given the opportunity.
How Sintering Provides the Path
Sintering provides that path through the application of heat. The thermal energy activates atomic movement, allowing the system to reconfigure itself to eliminate the high-energy surfaces between individual particles.
The result is the formation of strong bonds where there was once empty space, creating a more stable, lower-energy, and denser final part.
The Mechanism: How Atoms Reshape the Material
The Critical Role of Temperature
Sintering occurs at temperatures below the material's melting point, typically around 70-80% of the melting temperature in Kelvin.
This is a crucial distinction. The material doesn't liquefy. Instead, the heat provides the kinetic energy necessary for atoms in the solid state to move, or diffuse.
Atomic Diffusion at Particle Boundaries
At sintering temperatures, atoms become mobile enough to migrate across the boundaries where particles touch. This process is called solid-state diffusion.
Initially, "necks" form at these contact points. As more atoms diffuse to these necks, they grow, pulling the centers of the particles closer together.
The Stages of Densification
This atomic migration leads to a predictable transformation of the loose powder compact:
- Initial Bonding: Particles first fuse at their points of contact.
- Neck Growth: The contact areas grow, increasing the bond strength between particles.
- Pore Elimination: The empty spaces (pores) between particles become isolated and begin to shrink as material diffuses to fill them.
- Overall Shrinkage: As pores are eliminated, the entire component shrinks and its density increases significantly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Factors
Temperature vs. Time
A higher sintering temperature can dramatically speed up the diffusion process, leading to faster densification. However, excessively high temperatures or long hold times can cause undesirable grain growth, which can negatively impact the final mechanical properties of the material, such as its strength and toughness.
The Impact of Particle Size
The driving force for sintering is stronger for smaller particles. Finer powders have a higher surface area-to-volume ratio, which creates a greater thermodynamic incentive to reduce surface energy.
Consequently, finer powders can be sintered at lower temperatures and for shorter times compared to coarser powders.
The Role of Pressure
While not always required, applying external pressure can significantly aid the sintering process. Pressure forces the particles into closer contact, accelerating the diffusion and densification process.
Techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) or hot pressing utilize both heat and pressure to achieve high densities very quickly, which is especially useful for advanced materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the driving force behind sintering allows you to control the process to achieve specific outcomes.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density: You must carefully balance temperature and time to eliminate porosity without causing excessive grain growth that could compromise mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is processing high-melting-point materials: Sintering is the essential technique, as it allows you to form solid parts (from materials like tungsten or ceramics) at temperatures well below their impractical melting points.
- If your primary focus is creating complex net-shape parts: Powder metallurgy, which culminates in sintering, is a highly effective method for producing components with minimal need for post-process machining.
By controlling these parameters, you are fundamentally managing the rate at which a material seeks its lower-energy state.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Sintering |
|---|---|
| Surface Energy Reduction | The primary driving force; the system seeks a lower energy state. |
| Temperature | Provides energy for atomic diffusion (typically 70-80% of melting point). |
| Particle Size | Smaller particles sinter faster and at lower temperatures due to higher surface area. |
| Pressure | Accelerates densification by forcing particles into closer contact. |
Ready to harness the power of sintering for your materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your sintering processes. Whether you're developing new materials or optimizing production, our expertise and solutions can help you achieve maximum density, superior strength, and complex net-shape parts. Let's discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals.
Contact our sintering experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What technical advantages does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide? Enhance Fe-Ni/Zr2P2WO12 Composite Density
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate the high densification of Al-30%Sc alloys?
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance



















