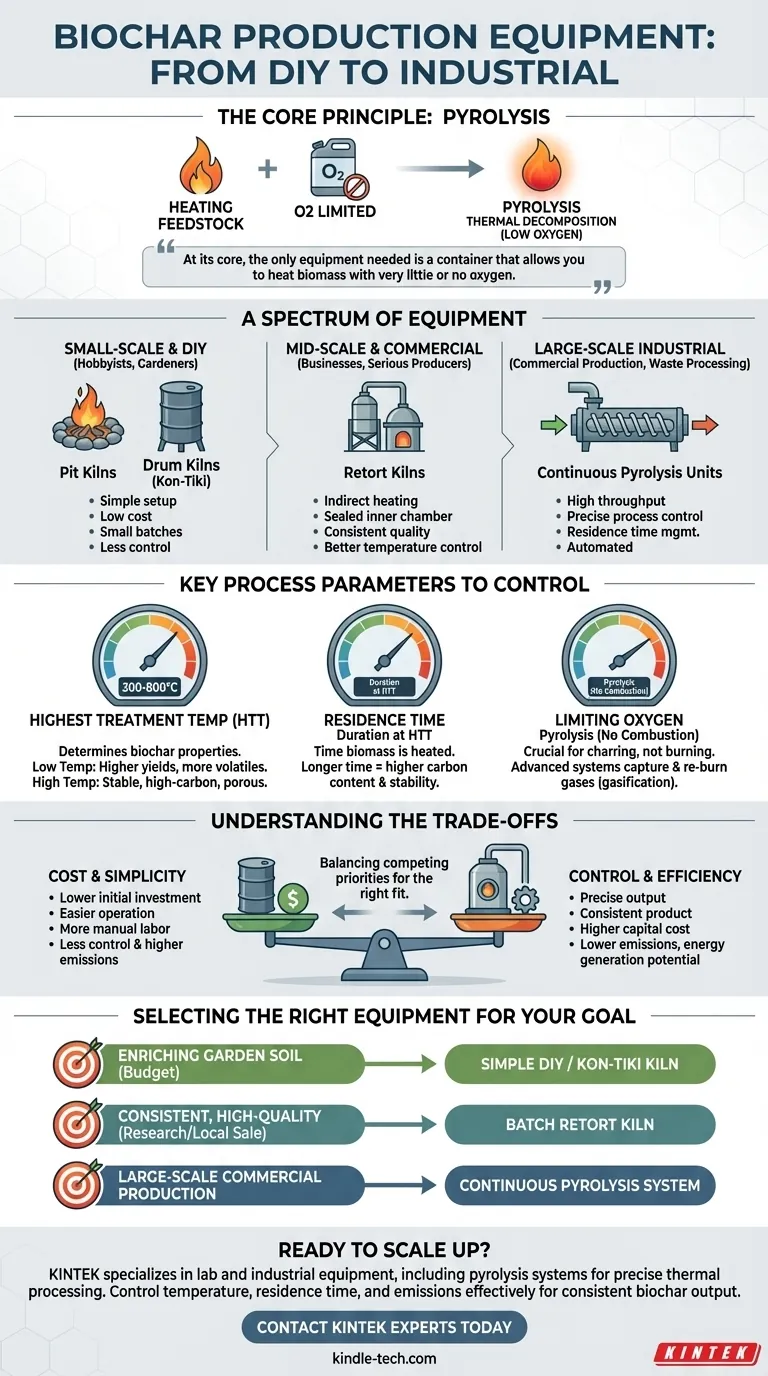
At its core, the only equipment needed to make biochar is a container that allows you to heat organic material (biomass) with very little or no oxygen. However, the specific equipment you choose will vary dramatically based on your intended scale, budget, and desired quality, ranging from simple backyard pits to sophisticated industrial reactors.
The choice of biochar equipment is not about finding a single "best" machine. It is about understanding the trade-off between production scale, cost, and the level of control required to create a final product with the specific properties you need.
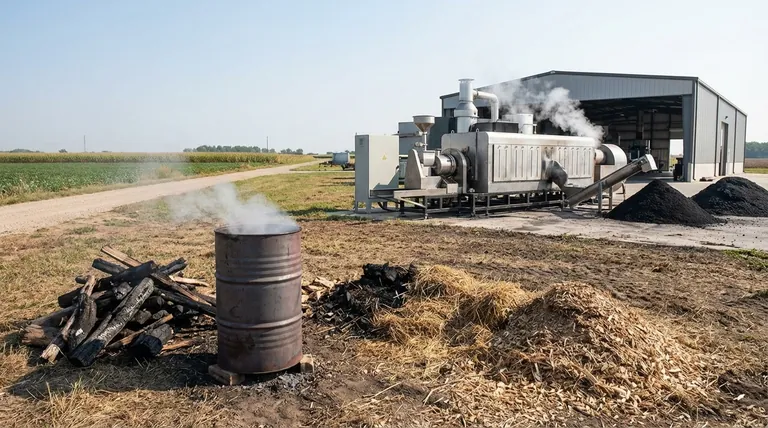

The Core Principle: What All Biochar Equipment Must Do
All biochar is created through a process called pyrolysis. This is simply the thermal decomposition of biomass in a low-oxygen environment. Any equipment, regardless of its complexity, must be designed to achieve this fundamental goal.
### Heating the Feedstock
The primary function of any biochar kiln or reactor is to heat the feedstock—such as wood chips, crop residue, or manure—to a target temperature. This temperature is a critical factor that determines the final characteristics of the biochar.
### Limiting Oxygen
If too much oxygen is present during heating, the biomass will simply burn away into ash via combustion. Biochar equipment must restrict airflow to ensure pyrolysis occurs instead. This is the most crucial design element separating a biochar kiln from a simple fire pit.
A Spectrum of Equipment: From DIY to Industrial
Biochar production technology exists on a wide spectrum, with accessible options for nearly any goal.
### Small-Scale & DIY Methods
For gardeners, hobbyists, or small-scale farmers, production can be achieved with minimal investment. These methods prioritize simplicity and low cost over precision.
- Pit Kilns: This ancient method involves digging a pit, starting a fire, and progressively layering biomass in a way that limits oxygen to the charring material at the bottom.
- Drum Kilns (Kon-Tiki): These are often made from modified metal barrels or purpose-built steel cones. They use a "top-lit" fire that creates a flame cap, preventing oxygen from reaching the biomass underneath as it turns into char. They are simple and relatively efficient for small batches.
### Mid-Scale & Commercial Systems
For businesses or serious producers, dedicated equipment offers far greater control over the final product. These systems are designed for consistency and higher throughput.
- Retort Kilns: These use an indirect heating method. The biomass is sealed in an inner chamber (the retort), while a fire is built in a separate outer chamber. This design completely separates the biomass from oxygen and combustion gases, offering excellent control over the process.
- Continuous Pyrolysis Units: Systems like screw pyrolyzers continuously feed biomass through a heated chamber. They allow for precise control over residence time (how long the material is heated) and temperature, producing a highly consistent product at a commercial scale.
Key Process Parameters Your Equipment Must Control
As the references highlight, the value of biochar is determined by its properties, which are a direct result of the production process. Your equipment's ability to manage these variables is key.
### Highest Treatment Temperature (HTT)
The maximum temperature reached during pyrolysis is arguably the most important variable.
- Low Temperatures (300-450°C): Produce higher yields of biochar but with more volatile compounds remaining.
- High Temperatures (550-800°C): Result in a more stable, higher-carbon biochar with greater porosity but generally a lower total yield. Advanced equipment offers precise temperature control to target these specific outcomes.
### Residence Time
This is the duration the biomass is held at the highest treatment temperature. Longer residence times can further increase the carbon content and stability of the char. Continuous systems offer the best control over this parameter.
### Feedstock Handling
The type and preparation of your feedstock (e.g., wood chips vs. straw) affects the process. While not part of the kiln itself, you may need supporting equipment like wood chippers, shredders, or dryers to prepare feedstock for consistent and efficient pyrolysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing equipment requires balancing competing priorities. There is no perfect solution, only the right fit for a specific objective.
### Cost vs. Control
Simple drum kilns are inexpensive but offer limited control over temperature and produce more smoke. Automated, continuous reactors provide precise control for creating designer chars but require a significant capital investment.
### Emissions vs. Simplicity
Basic, open-air methods like pit or drum kilns release smoke, which contains particulates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). More advanced systems are designed to capture and burn these gases—a process known as gasification—which both reduces emissions and can be used to generate energy to sustain the process.
### Batch vs. Continuous Flow
DIY and many retort systems operate in batches, where you load, run, cool, and unload the kiln. This is more labor-intensive. Industrial systems are typically continuous, constantly feeding in raw biomass and outputting finished biochar, which is essential for large-scale commercial production.
Selecting the Right Equipment for Your Goal
Your choice of equipment should be guided entirely by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is enriching garden soil on a budget: A simple DIY drum kiln or a Kon-Tiki style kiln is an excellent and cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is producing consistent, high-quality biochar for research or local sale: A purpose-built batch retort kiln offers the best balance of quality control and manageable investment.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial production or waste processing: A continuous screw pyrolysis system or rotary kiln is necessary to achieve the required throughput and consistency.
Ultimately, the right equipment is the one that empowers you to achieve your specific goal for producing biochar.
Summary Table:
| Equipment Type | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| DIY Pit/Drum Kilns | Gardeners, Hobbyists | Low cost, simple setup, small batches |
| Retort Kilns | Commercial Producers | Better temperature control, consistent quality |
| Continuous Pyrolysis Units | Large-Scale Industrial Use | High throughput, precise process control |
Ready to scale up your biochar production with reliable, high-performance equipment? KINTEK specializes in lab and industrial equipment, including pyrolysis systems and reactors designed for precise thermal processing. Whether you're a researcher developing new biochar formulations or a commercial producer needing consistent output, our solutions help you control temperature, residence time, and emissions effectively. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific biochar production goals and discover how KINTEK can support your project from pilot to production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















