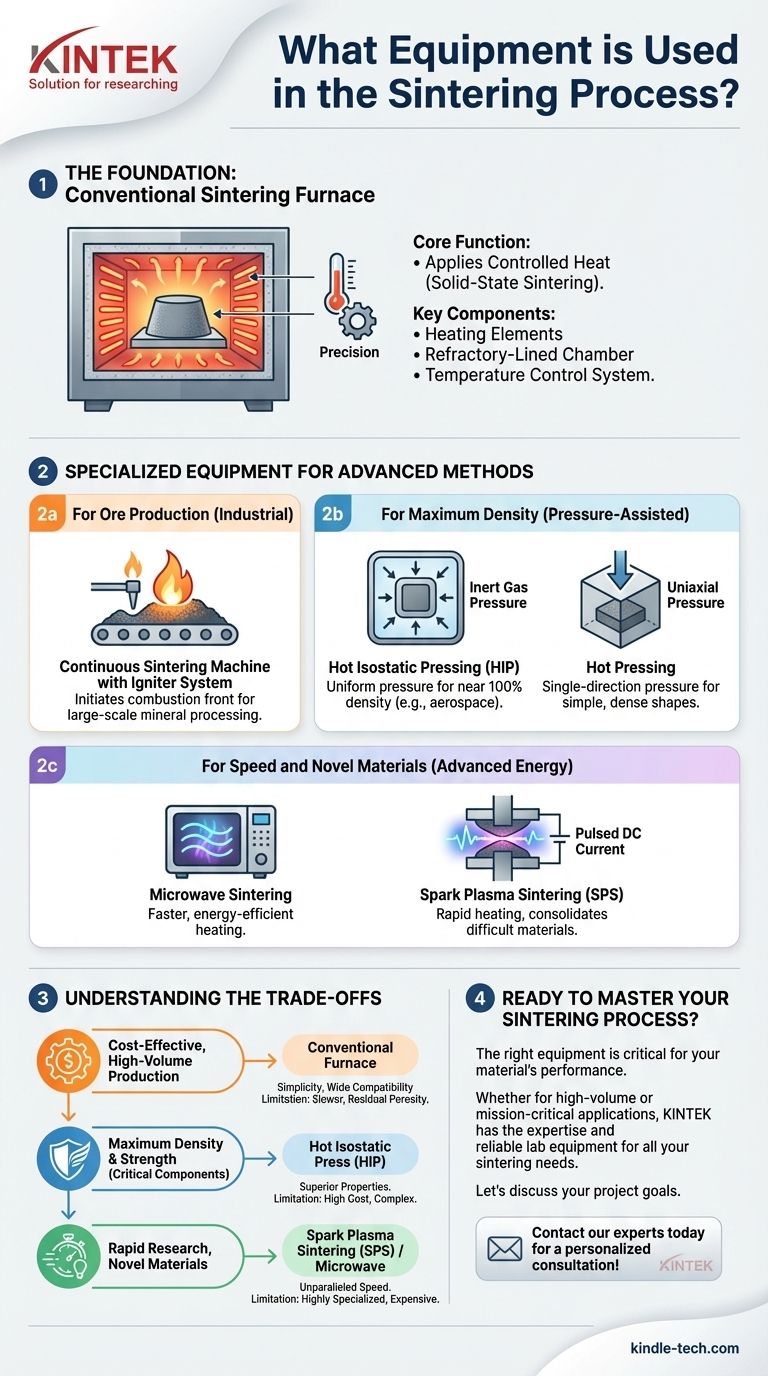
The primary equipment used in sintering is a specialized high-temperature furnace, but the specific type of machine varies significantly based on the technique being used. For basic solid-state sintering, a conventional furnace that applies controlled heat below the material's melting point is sufficient. However, more advanced processes require complex equipment like Hot Isostatic Presses (HIP) that add high pressure, or specialized systems that use microwaves or electric currents to accelerate the process.
The specific equipment chosen for sintering is not a minor detail—it defines the process. While all sintering relies on a controlled energy source, the choice between a simple furnace, a high-pressure press, or a rapid-heating system directly dictates the final material's density, strength, and overall performance.

The Foundation: The Conventional Sintering Furnace
The most common and fundamental piece of sintering equipment is the furnace. Its role is to execute the most basic form of sintering: solid-state sintering.
Core Function: Applying Controlled Heat
A sintering furnace's primary job is to heat a compacted powder part to a precise temperature, holding it just below the material's melting point. This thermal energy drives atomic diffusion, causing individual particles to bond and fuse together, which increases the part's density and strength.
Key Components
This process relies on a few critical systems working in concert. This includes the heating elements that generate the temperature, a refractory-lined chamber to contain the heat and the part, and a sophisticated temperature control system to manage the heating and cooling cycles with high precision.
Specialized Equipment for Advanced Methods
Beyond the basic furnace, highly specialized equipment has been developed to enhance the sintering process for specific outcomes like higher density, faster production, or unique material properties.
For Ore Production: The Igniter System
In large-scale industrial applications like producing iron ore sinter, the process often uses a continuous sintering machine. A key component here is the igniter, which provides a short, intense burst of heat to the top layer of the material mixture, initiating a combustion front that travels down through the material bed to complete the sintering.
For Maximum Density: Pressure-Assisted Sintering
To create parts with minimal porosity and maximum strength, pressure is added to the process.
- Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): This equipment places a part in a high-temperature furnace that is also a high-pressure vessel. An inert gas is used to apply uniform pressure from all directions, collapsing internal voids and creating nearly 100% dense components.
- Hot Pressing: This method uses a die to apply uniaxial (single-direction) pressure to the powder compact while it is being heated. This is common for producing simpler shapes with high density.
For Speed and Novel Materials: Advanced Energy Sources
Newer methods use alternative energy sources to dramatically reduce processing time.
- Microwave Sintering: This technique uses a specialized furnace that heats the material with microwaves. This can lead to much faster and more energy-efficient heating compared to conventional methods.
- Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): This advanced equipment passes a pulsed DC electric current directly through the powder and the die, while also applying mechanical pressure. This creates incredibly rapid heating and allows for the consolidation of materials that are difficult to sinter otherwise.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of sintering equipment involves a direct trade-off between cost, complexity, and the desired quality of the final product.
Conventional Furnaces: Simplicity vs. Performance
A standard sintering furnace is relatively simple, cost-effective, and suitable for a wide range of materials like bronze, steel, and some ceramics. However, the process is slow, and achieving full density is often impossible, leaving residual porosity that can limit mechanical performance.
Pressure-Assisted Systems (HIP/Hot Press): Density vs. Complexity
Using a HIP or Hot Press produces parts with superior density and mechanical properties. This is critical for high-performance applications in aerospace or medical implants. The downside is significant: the equipment is extremely expensive, cycle times can be long, and the process is far more complex to operate.
Advanced Energy Sources (Microwave/SPS): Speed vs. Specialization
Microwave and SPS systems offer unparalleled speed, enabling rapid prototyping and the creation of unique nanostructured materials. However, this equipment is highly specialized, expensive, and may not be suitable for all material types or part geometries due to challenges with uniform heating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct equipment requires aligning the machine's capabilities with your end goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of standard parts: A conventional solid-state sintering furnace is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and peak mechanical strength for critical components: A Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) is the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid research, material development, or sintering difficult materials: A specialized system like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) offers capabilities that traditional methods cannot match.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial mineral processing: An automated sintering line featuring a specialized igniter system is the required equipment.
Ultimately, understanding that different equipment enables different physical processes is the key to mastering sintering for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Equipment Type | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Furnace | Cost-effective, high-volume production | Simplicity, wide material compatibility | Slower process, residual porosity |
| Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) | Maximum density for critical components (aerospace, medical) | Near 100% density, superior strength | High cost, complex operation |
| Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Rapid research, difficult materials | Unparalleled speed, unique microstructures | High cost, specialized use |
| Microwave Sintering | Energy-efficient, faster heating | Reduced processing time | Challenges with uniform heating |
Ready to Master Your Sintering Process?
The right sintering equipment is critical to achieving your material's target density, strength, and performance. Whether you need a standard furnace for high-volume production or a high-performance HIP system for mission-critical components, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
We specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for all your sintering applications. Let's discuss your project goals and find the perfect solution. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What role does the vacuum hot-press furnace play in C-SiC-B4C-TiB2 synthesis? Achieve 2000°C Precision Densification
- Why is precise temperature control required in vacuum hot pressing? Master Amorphous Powder Consolidation

















