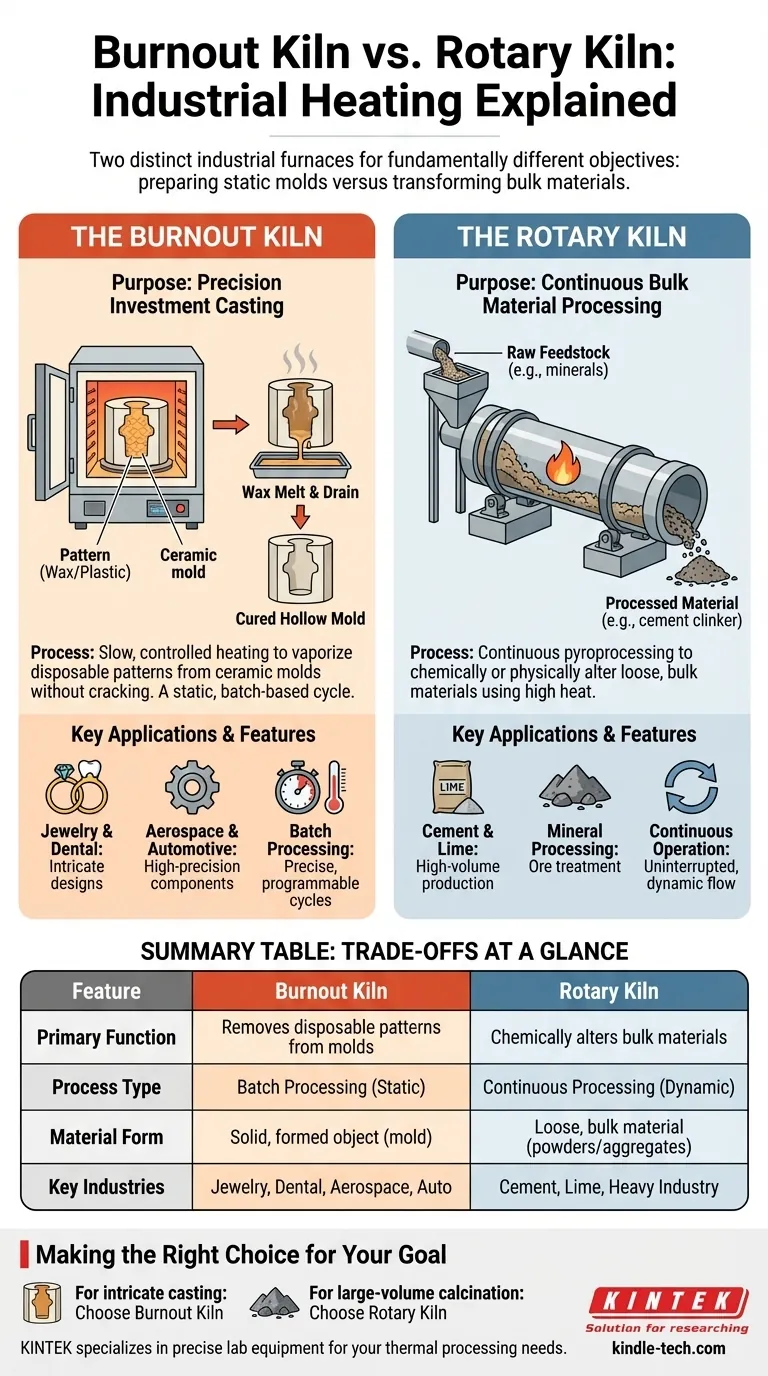
In the world of industrial heating, a burnout kiln is a furnace specifically designed to vaporize or "burn out" disposable patterns, such as wax or plastic, from a ceramic mold. This process, known as investment casting or lost-wax casting, requires a very slow and precisely controlled heating cycle to ensure the mold does not crack as the pattern melts and turns to gas. This function is distinct from that of a rotary kiln, which is built for the continuous high-temperature processing of bulk materials.
The core distinction lies in the objective: a burnout kiln prepares a hollow mold for casting by removing an internal pattern, while a rotary kiln continuously processes and chemically alters bulk materials like cement clinker or minerals. One is for creating a static cavity; the other is for transforming a moving substance.

The Core Function of a Burnout Kiln
A burnout kiln's purpose is defined by the delicate process it facilitates. It is not simply about high heat, but about the controlled application of that heat over time.
The Burnout Cycle Explained
The primary goal is to remove the pattern material (like wax) without damaging the surrounding investment mold. This is achieved through a multi-stage heating schedule.
First, the temperature is raised slowly to melt the bulk of the wax, allowing it to drain out. Then, the temperature is increased further and held for several hours to completely incinerate any residual pattern material and cure the mold, making it strong enough to receive molten metal.
Key Applications: Investment Casting
Burnout kilns are fundamental tools in any industry that relies on investment casting.
This includes the manufacturing of jewelry, dental crowns, and complex, high-precision industrial components for the aerospace and automotive industries. The process allows for intricate designs that would be impossible to create with traditional molding techniques.
Typical Design: Batch Processing
Unlike a continuous-feed rotary kiln, a burnout kiln is a batch-processing device. Molds are loaded into the chamber, the door is closed, and the kiln runs through its pre-programmed heating cycle. This allows for the precise control needed for each batch.
Understanding the Rotary Kiln
The information you've encountered describes a rotary kiln, which serves a completely different industrial purpose. Its design is engineered for high-volume, continuous production.
The Principle of Continuous Processing
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical vessel inclined at a slight angle. Raw material is fed into the higher end, and as the kiln slowly turns, the material tumbles and mixes as it travels down toward the heat source at the lower end.
The Role of High-Temperature Calcination
The main function of a rotary kiln is pyroprocessing, or altering materials with high heat. This often involves calcination, a process that drives off moisture, removes volatile compounds, or causes a phase transition or chemical reaction.
Common Industrial Uses
Rotary kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry. They are used to produce cement, lime, and to process a wide range of ores and minerals. Their design is optimized for transforming massive quantities of raw feedstock into a finished product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Burnout vs. Rotary
The choice between these two types of kilns is not a matter of preference but of fundamental operational requirements. There is no overlap in their application.
Batch vs. Continuous Operation
A burnout kiln is for static, batch-based work. You place a finite number of items inside and run a complete cycle.
A rotary kiln is for dynamic, continuous work. Material is constantly fed in one end and discharged from the other, allowing for uninterrupted production.
Material Form and Goal
A burnout kiln acts on a solid, formed object (the mold) with the goal of creating an empty cavity inside it.
A rotary kiln acts on loose, bulk material (powders, aggregates) with the goal of changing the material's chemical or physical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct equipment requires a clear understanding of your end goal. The name of the kiln itself often describes its function.
- If your primary focus is creating hollow molds for casting intricate parts (like jewelry or industrial components): You require a burnout kiln for its precise, programmable heating cycles tailored to protect the mold.
- If your primary focus is processing large volumes of raw, loose materials to induce a chemical change (like making cement): You require a rotary kiln designed for high-throughput, continuous operation.
Ultimately, the correct choice is dictated by whether your process is about carefully preparing a static mold or continuously transforming a bulk material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Burnout Kiln | Rotary Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Removes disposable patterns (wax/plastic) from molds | Chemically alters bulk materials (e.g., cement, minerals) |
| Process Type | Batch Processing | Continuous Processing |
| Material Form | Solid, formed molds | Loose, bulk materials |
| Key Industries | Jewelry, Dental, Aerospace, Automotive | Cement, Lime, Mineral Processing |
Need the Right Kiln for Your Lab or Production Line?
Choosing between a burnout kiln for precision casting or a rotary kiln for bulk material processing is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise heating needs of laboratories and manufacturers.
We can help you select the ideal kiln for your application, ensuring optimal performance for investment casting, calcination, or other thermal processes.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste









