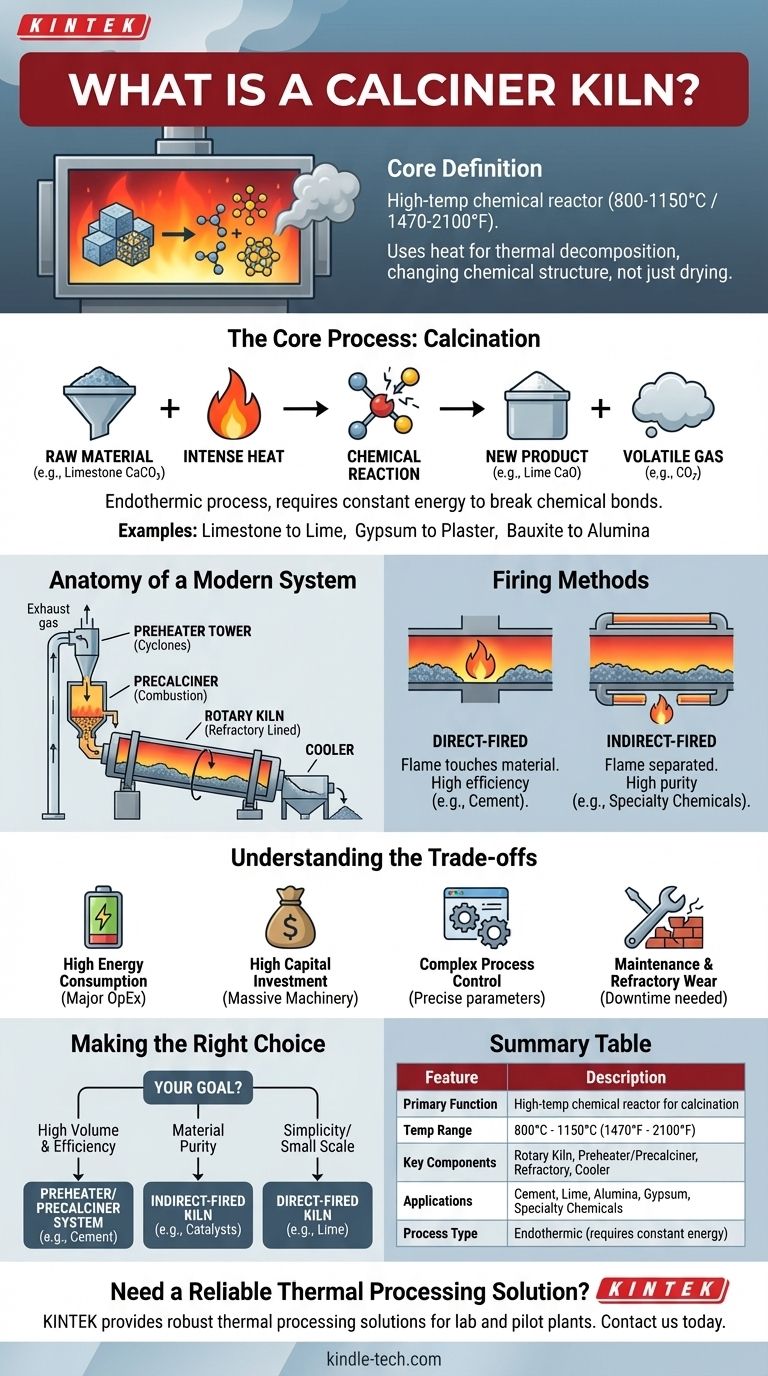
At its core, a calciner kiln is a high-temperature industrial furnace used for the process of calcination. It is not merely a dryer or an oven; it is a chemical reactor that uses intense heat (typically 800-1150°C or 1470-2100°F) to cause thermal decomposition in a solid material, fundamentally changing its chemical structure by driving off volatile components like carbon dioxide or water.
The most critical concept to understand is that a calciner’s purpose is to transform a material, not just heat it. It is the workhorse behind producing foundational industrial products like cement, lime, and alumina by breaking chemical bonds through controlled thermal energy.
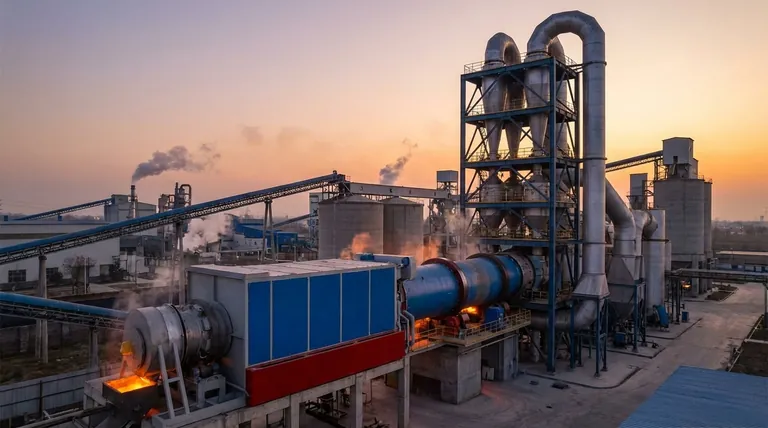

The Core Process: What is Calcination?
To understand the equipment, you must first understand the process it enables. Calcination is a specific, high-temperature reaction that purifies or changes a material.
A High-Temperature Chemical Reaction
Calcination is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a constant input of energy to sustain the chemical reaction. This reaction breaks down a compound into a more basic solid and a volatile gas.
Think of it like baking, but on a massive scale. You put in a raw ingredient (like limestone), apply intense heat, and a chemical change produces a completely new product (lime) and a byproduct (carbon dioxide gas).
Common Industrial Examples
- Limestone to Lime: Heating limestone (CaCO₃) drives off carbon dioxide (CO₂) to produce lime (CaO), a critical component for steel, chemical, and construction industries.
- Gypsum to Plaster: Heating gypsum (CaSO₄·2H₂O) removes water molecules to create plaster of Paris (CaSO₄·0.5H₂O).
- Bauxite to Alumina: Calcining hydrated aluminum oxide (bauxite) removes water to produce alumina (Al₂O₃), the primary raw material for producing aluminum metal.
Anatomy of a Modern Calciner System
While the term "calciner kiln" is often used, modern high-efficiency systems are more than just a single piece of equipment. They are an integrated series of components designed for maximum thermal efficiency.
The Rotary Kiln
The heart of the system is the rotary kiln itself. This is a large, rotating steel cylinder lined with heat-resistant brick (refractory). It is mounted on a slight incline.
Raw material is fed into the higher "feed end," and the slow rotation and angle cause it to tumble gradually toward the lower "discharge end." This tumbling action ensures the material is heated evenly and thoroughly.
The Preheater & Precalciner
This is the key innovation for efficiency. Before entering the rotary kiln, the raw material first passes through a series of cyclone separators called a preheater tower. Hot exhaust gases from the kiln are channeled up through this tower, directly against the flow of the incoming material.
This preheats the material to near-calcination temperatures, recovering immense amounts of energy. In a precalciner system, a dedicated combustion vessel (the "calciner") is added to the preheater tower. Here, a significant portion (60-95%) of the fuel is burned, and most of the calcination reaction occurs before the material even enters the rotary kiln.
The rotary kiln's primary job then becomes finishing the reaction and reaching the final, highest temperatures needed for processes like cement clinker formation.
The Heat Source & Firing Method
- Direct-Fired: The most common type. The flame and combustion gases are in direct contact with the material. This is highly efficient and suitable for materials like limestone and cement where direct contact is acceptable.
- Indirect-Fired: The kiln shell is heated from the outside, or heat is transferred through special tubes. The combustion gases never touch the material. This is essential for processing high-purity or heat-sensitive materials where contamination from fuel ash or gases is a concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Calciner kilns are powerful but come with significant operational considerations that must be managed carefully.
High Energy Consumption
Thermal processing is inherently energy-intensive. Fuel costs represent the single largest operational expense for any calciner operation. The drive for preheater and precalciner systems is a direct response to this reality.
Capital Investment
These are massive, complex pieces of machinery. The initial capital cost for a complete calciner kiln system, including the preheater tower, coolers, and control systems, is extremely high.
Process Control Complexity
Managing a stable and efficient calcination process requires precise control over feed rate, fuel rate, kiln rotational speed, and airflow. Imbalances can lead to incomplete reactions, wasted energy, or damage to the kiln's refractory lining.
Maintenance and Refractory Wear
The extreme temperatures and abrasive nature of the materials cause inevitable wear and tear on the kiln's internal refractory brick lining. This requires scheduled downtime for inspection and replacement, which is a major maintenance activity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal calciner design depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and energy efficiency (e.g., cement): A preheater/precalciner system is the industry standard and the only logical choice.
- If your primary focus is material purity and avoiding contamination (e.g., specialty chemicals, catalysts): An indirectly fired rotary kiln is necessary, despite its lower thermal efficiency.
- If your primary focus is simplicity for a smaller-scale operation (e.g., lime production): A classic, direct-fired rotary kiln without a precalciner may be a viable, lower-capital option.
Ultimately, the calciner kiln is a purpose-built tool designed to fundamentally re-engineer materials at the chemical level using heat.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | High-temperature chemical reactor for calcination (thermal decomposition). |
| Typical Temperature Range | 800°C to 1150°C (1470°F to 2100°F). |
| Key Components | Rotary Kiln, Preheater/Precalciner Tower, Refractory Lining, Cooler. |
| Common Applications | Cement, Lime, Alumina, Gypsum, and Specialty Chemicals production. |
| Process Type | Endothermic (requires constant energy input). |
Need a Reliable Thermal Processing Solution for Your Lab or Pilot Plant?
Calciner kilns are the cornerstone of industrial material transformation, but finding the right equipment for research, development, or small-scale production can be challenging. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing robust thermal processing solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Whether you are developing new materials, optimizing calcination parameters, or producing high-purity compounds, our expertise ensures you get the precise temperature control and reliability your work demands.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What type of process is calcination? A Guide to Precise Thermal Decomposition
- What is the application of pyrolysis in biomass? Converting Waste into Bio-Oil, Biochar, and Renewable Energy
- What are the steps involved in the design of a fluidized bed reactor? Achieve Optimal Reaction Efficiency and Stability
- What is calcination with example? A Guide to Thermal Decomposition Processes
- What is the structure of a rotary kiln? A Detailed Breakdown of Its Core Components
- What is the sintering process in kilns? Transform Powder into Dense, High-Strength Components
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is the chemical composition of pyrolysis gas? A Guide to Its Variable Fuel Components



















