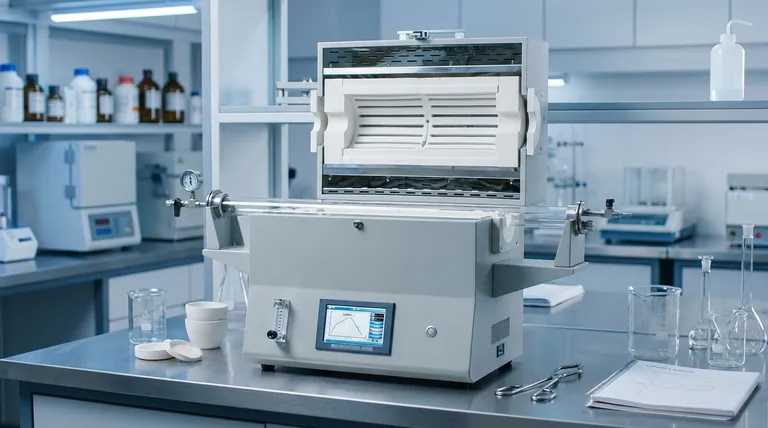
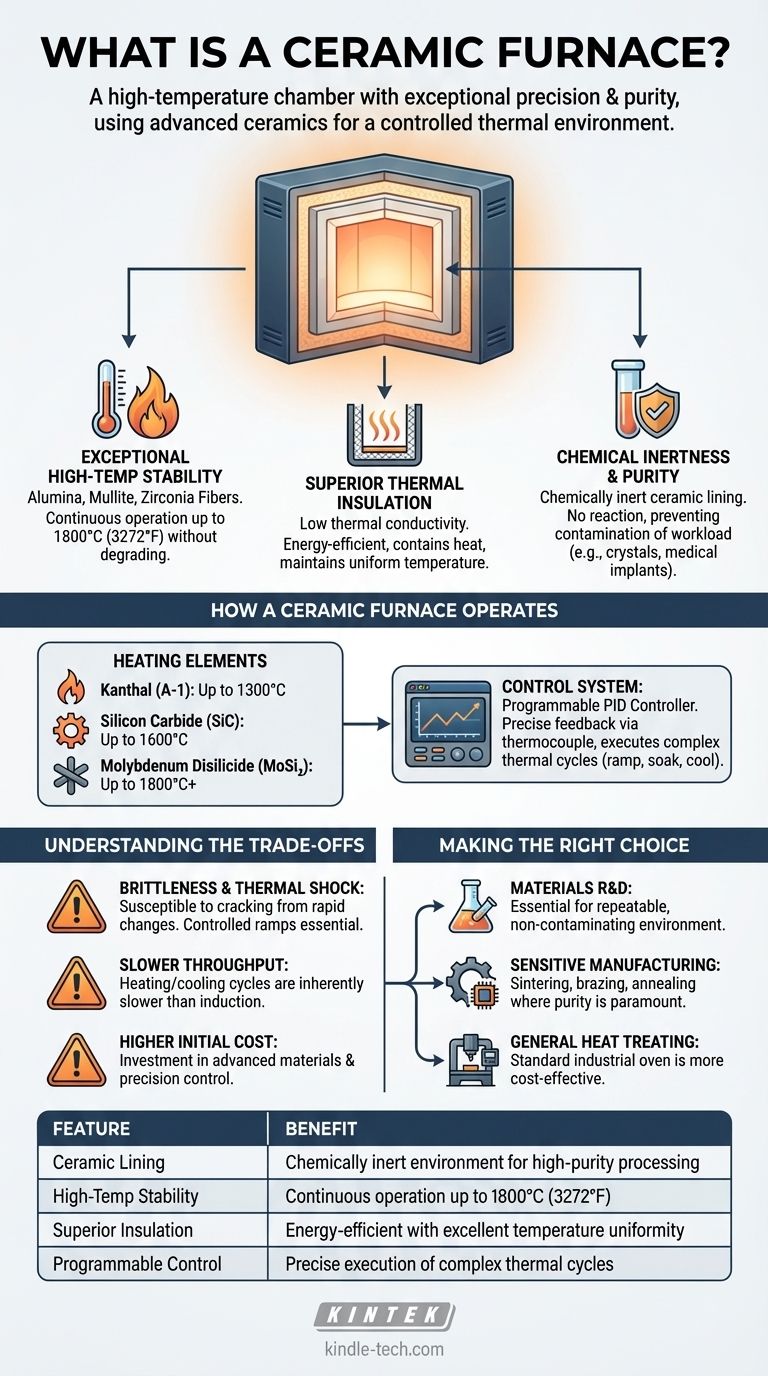
At its core, a ceramic furnace is a high-temperature chamber designed for processing materials with exceptional precision and purity. It uses advanced ceramic materials for its internal lining and insulation, allowing it to reach extremely high temperatures while maintaining a stable, uniform, and clean environment that would cause metallic furnaces to fail or contaminate the work product.
The true value of a ceramic furnace isn't just its ability to get hot; it's the power to create a precisely controlled thermal environment, free from chemical reactions. This makes it an indispensable tool for developing and processing advanced materials where purity and structural integrity are paramount.

The Defining Role of Ceramics
The "ceramic" in the name is the key to the furnace's unique capabilities. Unlike metals, which can melt, warp, or react at high temperatures, specific ceramics offer a combination of properties ideal for extreme thermal processing.
Exceptional High-Temperature Stability
Ceramics like high-purity alumina, mullite, and zirconia fibers form the furnace's core chamber. These materials can withstand continuous operation at temperatures often exceeding 1200°C (2200°F) and up to 1800°C (3272°F) or more, without degrading.
Superior Thermal Insulation
The low thermal conductivity of ceramic fiber insulation is what makes the furnace energy-efficient. It keeps the heat contained within the chamber, ensuring the exterior remains cool and that thermal energy isn't wasted. This property is also critical for maintaining a highly uniform temperature zone inside.
Chemical Inertness and Purity
This is perhaps the most critical attribute for scientific applications. The ceramic lining is chemically inert, meaning it won't react with or release impurities into the material being processed (known as the "workload"). This is essential for applications like growing crystals, sintering medical implants, or creating high-purity glass, where even trace contamination can ruin the final product.
How a Ceramic Furnace Operates
A ceramic furnace combines its robust chamber with a precision control system to execute complex thermal cycles. This system transforms it from a simple oven into a sophisticated piece of laboratory or production equipment.
The Heating Elements
To reach extreme temperatures, these furnaces use specialized heating elements. Common types include:
- Kanthal (A-1): A metallic alloy used for temperatures up to about 1300°C.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): A ceramic composite used for temperatures up to 1600°C.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂): A cermet element used for the highest ranges, often up to 1800°C or beyond.
The choice of element is dictated by the furnace's maximum required operating temperature.
The Control System
Modern ceramic furnaces are managed by a programmable controller, often a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This unit receives feedback from a thermocouple inside the chamber and precisely adjusts power to the heating elements. This allows the user to program complex heating profiles with specific ramp rates (how fast it heats up), soak times (how long it holds a temperature), and cooling rates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, ceramic furnaces are a specialized tool with specific limitations that must be considered.
Brittleness and Thermal Shock
The primary drawback of ceramics is their brittleness. The furnace chamber can crack if subjected to mechanical impact or, more commonly, thermal shock—heating or cooling too rapidly. This is why controlled ramp rates are not just a feature, but a necessity for ensuring the furnace's long life.
Slower Throughput
The same thermal mass that promotes temperature stability can also mean that heating and cooling cycles are inherently slower than in other systems like induction furnaces. While modern designs are highly efficient, they are not designed for instantaneous heating.
Higher Initial Cost
The advanced materials (high-purity ceramics, specialized elements) and precision control systems make these furnaces a significant investment compared to standard metal-lined industrial ovens. Their cost is a direct reflection of their high-performance capabilities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace depends entirely on the demands of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is materials research and development: A ceramic furnace is essential for its repeatable, programmable control and the non-contaminating environment needed to test and create new materials.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing sensitive components: Use a ceramic furnace for processes like sintering technical ceramics, brazing complex assemblies, or annealing medical-grade alloys where temperature uniformity and purity directly impact product quality.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating of robust steels: A more conventional and less expensive industrial oven is likely a better-suited and more cost-effective choice, as the extreme purity is not required.
Ultimately, choosing a ceramic furnace is a decision to prioritize a controlled, stable, and exceptionally clean high-temperature environment for the materials that demand it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Ceramic Lining | Chemically inert environment for high-purity processing |
| High-Temperature Stability | Continuous operation up to 1800°C (3272°F) |
| Superior Insulation | Energy-efficient with excellent temperature uniformity |
| Programmable Control | Precise execution of complex thermal cycles |
Ready to enhance your materials research or manufacturing with a high-purity thermal solution? KINTEK specializes in high-performance ceramic furnaces and lab equipment, providing the precise, contamination-free environment your sensitive materials demand. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect furnace for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















