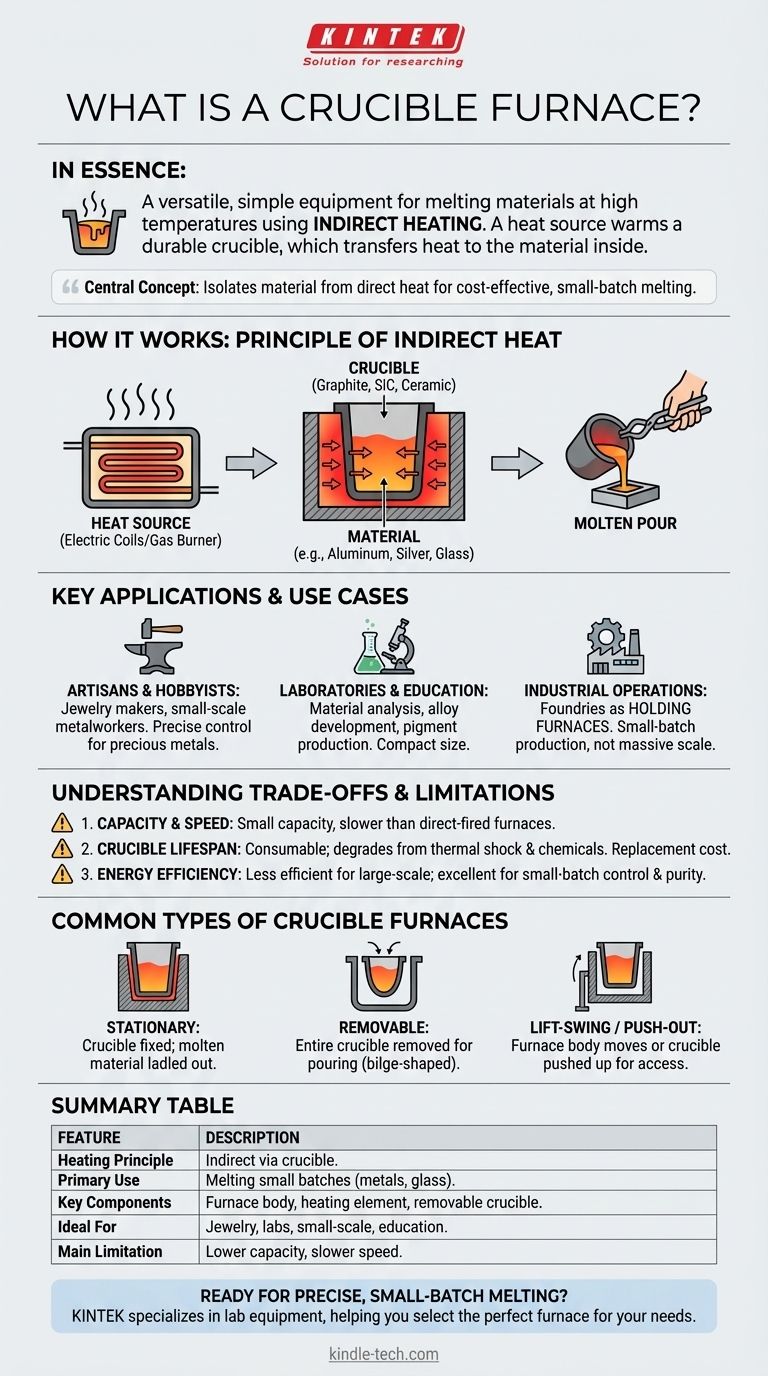
In essence, a crucible furnace is a simple and versatile piece of equipment designed for melting materials at high temperatures. It operates on the principle of indirect heating, where a heat source—typically electric or gas—warms a durable container called a crucible, which in turn transfers that heat to the material placed inside it until it becomes molten.
The central concept to grasp is that a crucible furnace isolates the material being melted from the direct heat source. This simplicity makes it a cost-effective and highly adaptable tool for small-batch melting of a wide variety of materials, from metals to glass.

How a Crucible Furnace Works: The Principle of Indirect Heat
A crucible furnace's design is straightforward, focusing on efficiently transferring energy to a contained material. Its operation revolves around two primary components.
The Core Components: Crucible and Heat Source
The system consists of a furnace body made from refractory (heat-resistant) materials. Inside, a heating element (electric coils or a gas burner) generates high temperatures.
The most critical component is the crucible, a cup- or pot-shaped container that sits inside the furnace. Crucibles are made from materials like graphite, silicon carbide, or ceramic to withstand extreme thermal stress.
The Step-by-Step Melting Process
The process is direct and effective. First, the material to be melted (e.g., aluminum, silver, glass) is placed inside the crucible.
The furnace is then activated, and the heating element raises the temperature of the chamber. This heat is absorbed by the crucible and conducted inward, melting the contents.
Once the material is fully molten, it can be poured into a mold. In many designs, the crucible itself is removed from the furnace with tongs to perform the pour.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The versatility and range of sizes make crucible furnaces suitable for many different environments, from workshops to industrial facilities.
For Artisans and Hobbyists
Small, often electric, tabletop crucible furnaces are extremely popular among jewelry makers and small-scale metalworkers. Their ease of use and precise temperature control are ideal for working with precious metals.
For Laboratories and Education
In scientific and educational settings, these furnaces are used for material analysis, alloy development, and pigment production. Their compact size makes them a perfect fit for lab work and vocational training.
For Industrial Operations
While not suited for massive-scale melting, larger crucible furnaces serve vital roles in foundries. They are often used as holding furnaces to keep a small batch of metal molten and ready for casting or for small, specialized production runs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly useful, crucible furnaces are not the solution for every melting task. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Capacity and Speed
Crucible furnaces are inherently small-capacity devices. They are not efficient for melting large volumes of metal compared to direct-fired furnaces. The indirect heating process can also be slower.
Crucible Lifespan
The crucible is a consumable item. It degrades over time due to thermal shock and chemical reactions with the molten material. The cost and downtime associated with replacing crucibles are operational factors to consider.
Energy Efficiency
For large-scale melting, the energy required to heat the furnace chamber and then the crucible is less efficient than heating the material directly. Their efficiency shines in small-batch applications where control and purity are more important than sheer volume.
Common Types of Crucible Furnaces
Furnace designs vary based on how the molten material is handled, which directly impacts workflow and safety.
Stationary Furnaces
In the simplest design, the crucible remains fixed inside the furnace. Molten material must be ladled out, which is suitable for holding applications or when working with smaller quantities.
Removable Crucible Furnaces
These are the most common type for casting. They allow the entire crucible to be removed from the furnace for pouring. The crucibles are often bilge-shaped (like a barrel) to be securely gripped by specialized tongs.
Lift-Swing and Push-Out Designs
These are two common mechanisms for removable crucible furnaces. A Lift-Swing furnace allows the furnace body itself to be lifted and swung away, leaving the crucible accessible. A Push-Out furnace uses a mechanism to push the crucible up and out of the furnace body from below.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate furnace depends entirely on your specific objective, scale, and material.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist metalworking or jewelry: A compact electric tabletop furnace offers the best combination of safety, precise control, and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is a laboratory or small-scale production: A gas-powered or induction furnace with a removable crucible provides greater flexibility and faster heating cycles for various materials.
- If your primary focus is holding a small amount of molten metal at temperature: A simple, stationary crucible furnace is a reliable and cost-effective solution.
By understanding its function as a simple, indirect heating tool, you can effectively leverage the crucible furnace for controlled, high-quality melting.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Indirect heating via a crucible container. |
| Primary Use | Melting small batches of metals, glass, and other materials. |
| Key Components | Furnace body, heating element (electric/gas), and a removable crucible. |
| Ideal For | Jewelry making, laboratories, small-scale production, and educational use. |
| Main Limitation | Lower capacity and slower melting speed compared to large-scale industrial furnaces. |
Ready to achieve precise, small-batch melting in your lab or workshop?
The controlled, indirect heating of a crucible furnace is ideal for applications where material purity and precise temperature control are paramount. Whether you're developing new alloys, creating jewelry, or need a reliable holding furnace, choosing the right equipment is critical for your results and safety.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible furnace for your specific material and workflow requirements, ensuring you get the performance and durability you need.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the right melting solution for your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















