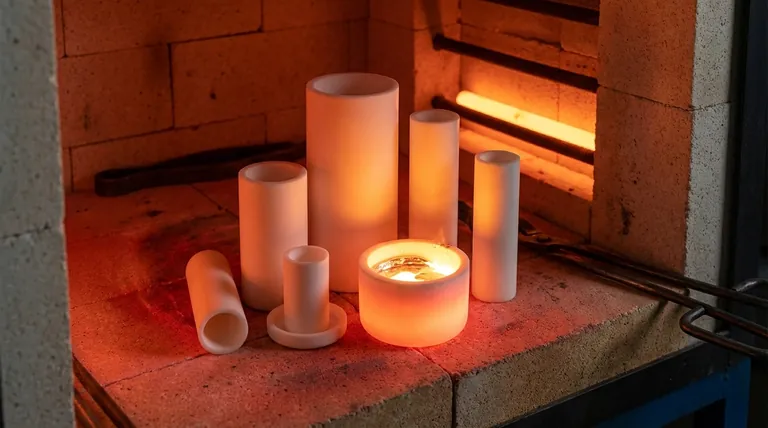
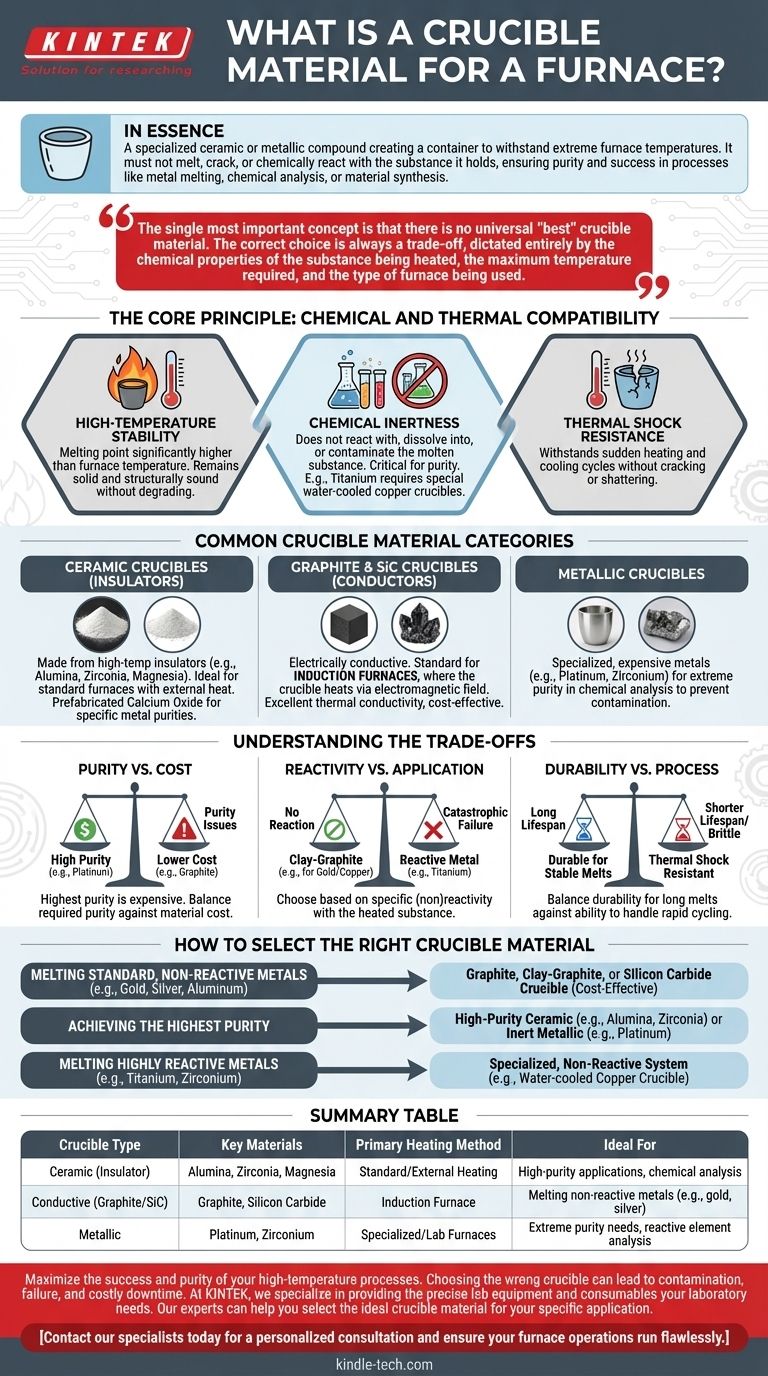
In essence, a crucible material is a specialized ceramic or metallic compound used to create a container that can withstand extremely high temperatures inside a furnace. The material is chosen specifically so it does not melt, crack, or chemically react with the substance it holds, ensuring the purity and success of processes like metal melting, chemical analysis, or material synthesis.
The single most important concept is that there is no universal "best" crucible material. The correct choice is always a trade-off, dictated entirely by the chemical properties of the substance being heated, the maximum temperature required, and the type of furnace being used.
The Core Principle: Chemical and Thermal Compatibility
The fundamental job of a crucible is to act as a stable, inert barrier. This requires a material that meets several demanding criteria.
High-Temperature Stability
A crucible's primary characteristic is a melting point significantly higher than the operating temperature of the furnace. The material must remain solid and structurally sound without degrading.
Chemical Inertness
The crucible material should not react with, dissolve into, or otherwise contaminate the molten metal or chemical compound it contains. This is critical for maintaining the purity of the final product. For example, highly reactive metals like titanium require special water-cooled copper crucibles that completely prevent any reaction.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Furnace processes often involve rapid heating and cooling cycles. A good crucible material must be able to withstand these sudden temperature changes without cracking or shattering.
Common Crucible Material Categories
Crucibles are generally grouped by their composition and properties, which makes them suitable for different heating methods and applications.
Ceramic Crucibles (Insulators)
These are made from high-temperature insulating materials like alumina, zirconia, or magnesium oxide. Because they are electrical insulators, they are ideal for standard furnaces where heat is applied externally. Prefabricated calcium oxide crucibles are a specialized ceramic type used to improve the purity of certain metals.
Graphite & Silicon Carbide Crucibles (Conductors)
Graphite and silicon carbide are electrically conductive. This property makes them the standard choice for induction furnaces, where the crucible itself is heated by an electromagnetic field. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and are relatively cost-effective.
Metallic Crucibles
For specialized applications, crucibles are made from metal. In laboratory settings requiring extreme purity for chemical analysis, very inert and expensive metals like platinum or zirconium are used to prevent any sample contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible material involves balancing competing factors. An ideal choice for one application can be a complete failure in another.
Purity vs. Cost
Materials that offer the highest purity, like platinum, are exceptionally expensive. Graphite is affordable but can introduce carbon into a melt, which is undesirable for certain alloys. You must weigh the required purity of your final product against the material cost.
Reactivity vs. Application
A clay-graphite crucible is perfect for melting gold or copper, but it would fail catastrophically if used to melt a reactive metal like titanium. The material must be chosen based on its specific (non)reactivity with the substance being heated.
Durability vs. Process
Some materials are extremely durable for long melts at stable temperatures but may be too brittle to handle the thermal shock of rapid cycling. Others may handle thermal shock well but have a shorter overall lifespan.
How to Select the Right Crucible Material
Your choice should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is melting standard, non-reactive metals (e.g., gold, silver, aluminum): A cost-effective graphite, clay-graphite, or silicon carbide crucible is often the best choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity: Select a high-purity ceramic crucible (like alumina or zirconia) or, for analytical purposes, an inert metallic one like platinum.
- If your primary focus is melting highly reactive metals (e.g., titanium, zirconium): You must use a specialized, non-reactive system such as a water-cooled copper crucible to prevent contamination.
Choosing the correct crucible material is a critical engineering decision that directly ensures the integrity and success of your high-temperature work.

Summary Table:
| Crucible Type | Key Materials | Primary Heating Method | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic (Insulator) | Alumina, Zirconia, Magnesia | Standard/External Heating | High-purity applications, chemical analysis |
| Conductive (Graphite/SiC) | Graphite, Silicon Carbide | Induction Furnace | Melting non-reactive metals (e.g., gold, silver) |
| Metallic | Platinum, Zirconium | Specialized/Lab Furnaces | Extreme purity needs, reactive element analysis |
Maximize the success and purity of your high-temperature processes. Choosing the wrong crucible can lead to contamination, failure, and costly downtime. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal crucible material for your specific application, whether you're melting metals, synthesizing materials, or conducting chemical analysis.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and ensure your furnace operations run flawlessly.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C



















