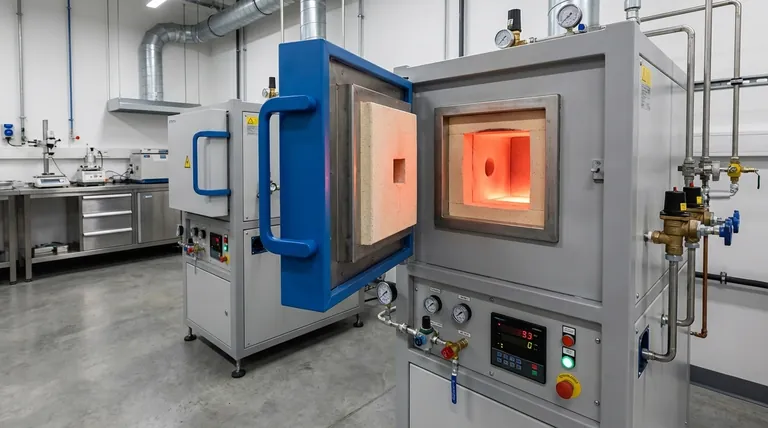
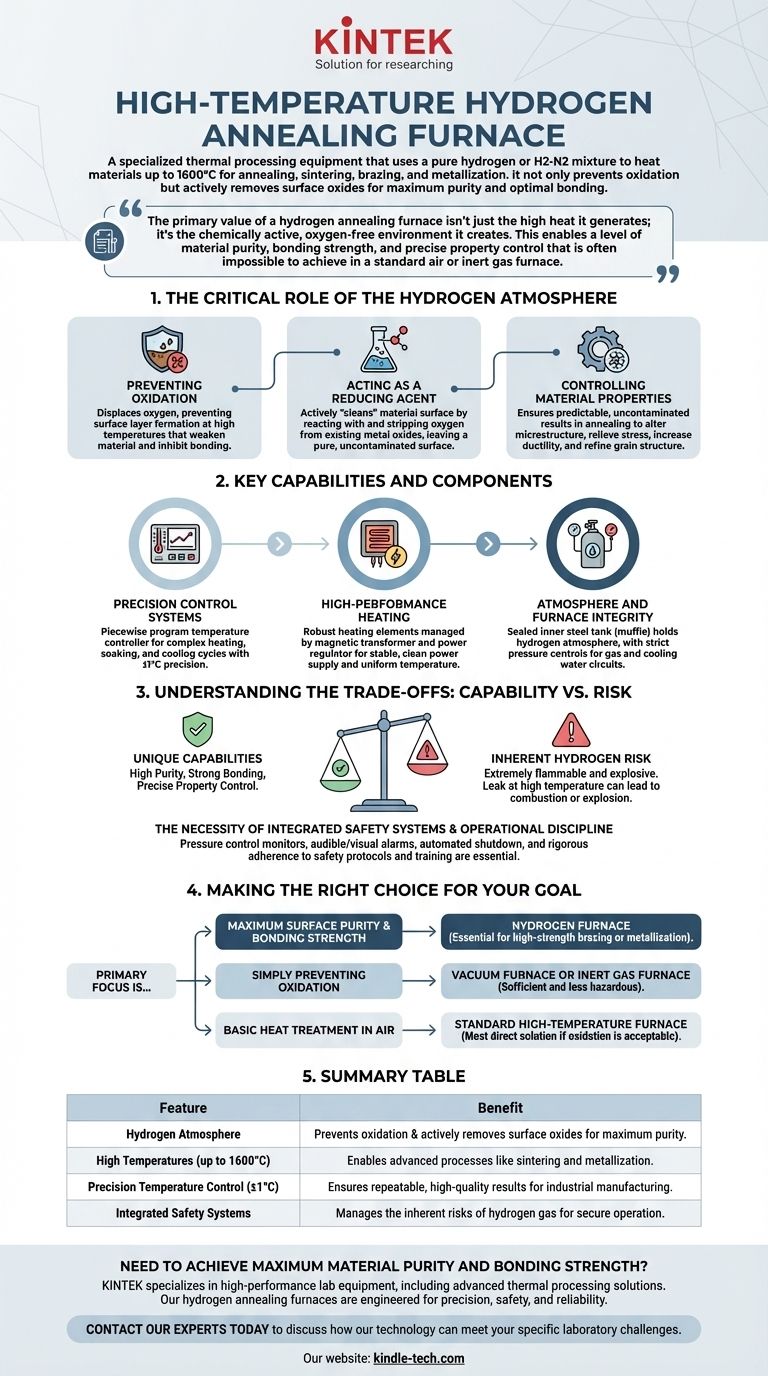
A high-temperature hydrogen annealing furnace is a specialized piece of thermal processing equipment that uses a pure hydrogen or a hydrogen-nitrogen gas mixture as a protective, chemically active atmosphere. It is designed to heat materials to extremely high temperatures, often up to 1600°C, for processes like annealing, sintering, brazing, and metallization. The core purpose of the hydrogen atmosphere is not just to prevent oxidation, but to actively remove existing oxides from a material's surface, ensuring maximum purity and optimal bonding.
The primary value of a hydrogen annealing furnace isn't just the high heat it generates; it's the chemically active, oxygen-free environment it creates. This enables a level of material purity, bonding strength, and precise property control that is often impossible to achieve in a standard air or inert gas furnace.

The Critical Role of the Hydrogen Atmosphere
The defining feature of this furnace is its use of hydrogen gas. This choice is deliberate and central to its function, offering benefits beyond simply preventing contamination.
Preventing Oxidation
At high temperatures, most metals and many ceramics will rapidly react with any available oxygen. This process, known as oxidation, creates a surface layer that can weaken the material, inhibit proper bonding during brazing, or alter its electrical properties. A hydrogen atmosphere displaces all oxygen, creating a protective environment where this cannot occur.
Acting as a Reducing Agent
Unlike inert gases like argon, hydrogen is an active reducing agent. This means it actively "cleans" the material's surface at a chemical level. The hydrogen reacts with metal oxides that may already be present on the component, stripping the oxygen atoms away and leaving behind a pure, uncontaminated surface. This is critical for creating the strongest possible joints in brazing applications.
Controlling Material Properties
The process of annealing is used to alter a material's microstructure, typically to relieve internal stresses, increase ductility, and refine the grain structure. Performing this process in a hydrogen atmosphere ensures the final properties are predictable and uncontaminated by surface reactions, which is especially important in the manufacturing of semiconductors and specialized alloys.
Key Capabilities and Components
These furnaces are complex systems engineered for precision and safety under demanding conditions.
Precision Control Systems
The entire process is governed by a piecewise program temperature controller. This allows operators to define complex heating, soaking, and cooling cycles with extreme accuracy. This precision is vital for achieving repeatable results in industrial manufacturing.
High-Performance Heating
The furnace achieves its high temperatures using robust heating elements. Power is often managed by a magnetic transformer and power regulator, which ensures a stable and clean power supply. This stability is directly linked to the furnace's ability to maintain uniform temperatures, often with a precision of ±1°C.
Atmosphere and Furnace Integrity
The core of the furnace contains a sealed inner steel tank or muffle, which holds the protective hydrogen atmosphere and separates it from the heating elements. The entire system is managed with strict pressure controls for both the gas and the necessary cooling water circuits, ensuring the integrity of the sealed environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Capability vs. Risk
The unique capabilities of a hydrogen furnace come with a significant operational responsibility. The primary trade-off is leveraging a highly effective but potentially hazardous gas.
The Inherent Risk of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is extremely flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. A leak in the furnace chamber or gas supply lines at high operating temperatures could lead to a spontaneous combustion or explosion. This is the single greatest risk associated with this technology.
The Necessity of Integrated Safety Systems
Because of this risk, hydrogen furnaces are equipped with extensive safety interlocks. These include pressure control monitors for the water and gas circuits, audible and visual alarms, and automated shutdown procedures. These systems are not optional features; they are essential for safe operation.
The Demand for Strict Operational Discipline
Operating this equipment requires rigorous adherence to safety protocols. Regular inspection of the furnace seal, gas lines, and electrical systems is mandatory. Operators must be thoroughly trained to understand the risks and execute both normal and emergency procedures correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a thermal process depends entirely on the material requirements and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface purity and bonding strength: A hydrogen furnace is essential for applications like high-strength brazing or metallization, where an oxide-free surface is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is simply preventing oxidation: A vacuum furnace or a furnace using an inert gas (like argon) may be a sufficient and less hazardous alternative.
- If your primary focus is basic heat treatment in air: For processes like simple stress relief or hardening where surface oxidation is acceptable or can be removed later, a standard high-temperature furnace is the most direct solution.
Ultimately, choosing a hydrogen annealing furnace is a strategic decision driven by the need for an active, reducing atmosphere to achieve the highest levels of material performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation & actively removes surface oxides for maximum purity. |
| High Temperatures (up to 1600°C) | Enables advanced processes like sintering and metallization. |
| Precision Temperature Control (±1°C) | Ensures repeatable, high-quality results for industrial manufacturing. |
| Integrated Safety Systems | Manages the inherent risks of hydrogen gas for secure operation. |
Need to achieve maximum material purity and bonding strength?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced thermal processing solutions. Our hydrogen annealing furnaces are engineered for precision, safety, and reliability, helping you achieve superior results in applications like brazing, sintering, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our technology can meet your specific laboratory challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do laboratory vacuum or atmosphere furnaces contribute to the anti-oxidation of samples? Achieve Pure Research Results
- What is the function of an atmosphere protection annealing furnace? Optimize CoFe2O4/Fe Magnetic Performance
- How are reducing atmospheres used in the firing of ceramic products? Master Glaze Colors & Clay Chemistry
- What is the role of a high-temperature atmosphere furnace in Alloy X-750 preparation? Achieve Precise Solution Treatment
- How does a Tube Atmosphere Furnace ensure noble metal activity? Key Steps for Preparing Pt/Al2O3 Catalysts
- What role do high-vacuum or atmosphere furnaces play in the annealing of metals? Enhance Material Performance & Purity
- What is a reducing atmosphere? Optimize Material Processing by Preventing Oxidation
- What happens during the annealing process? A Guide to Controlled Softening and Stress Relief



















