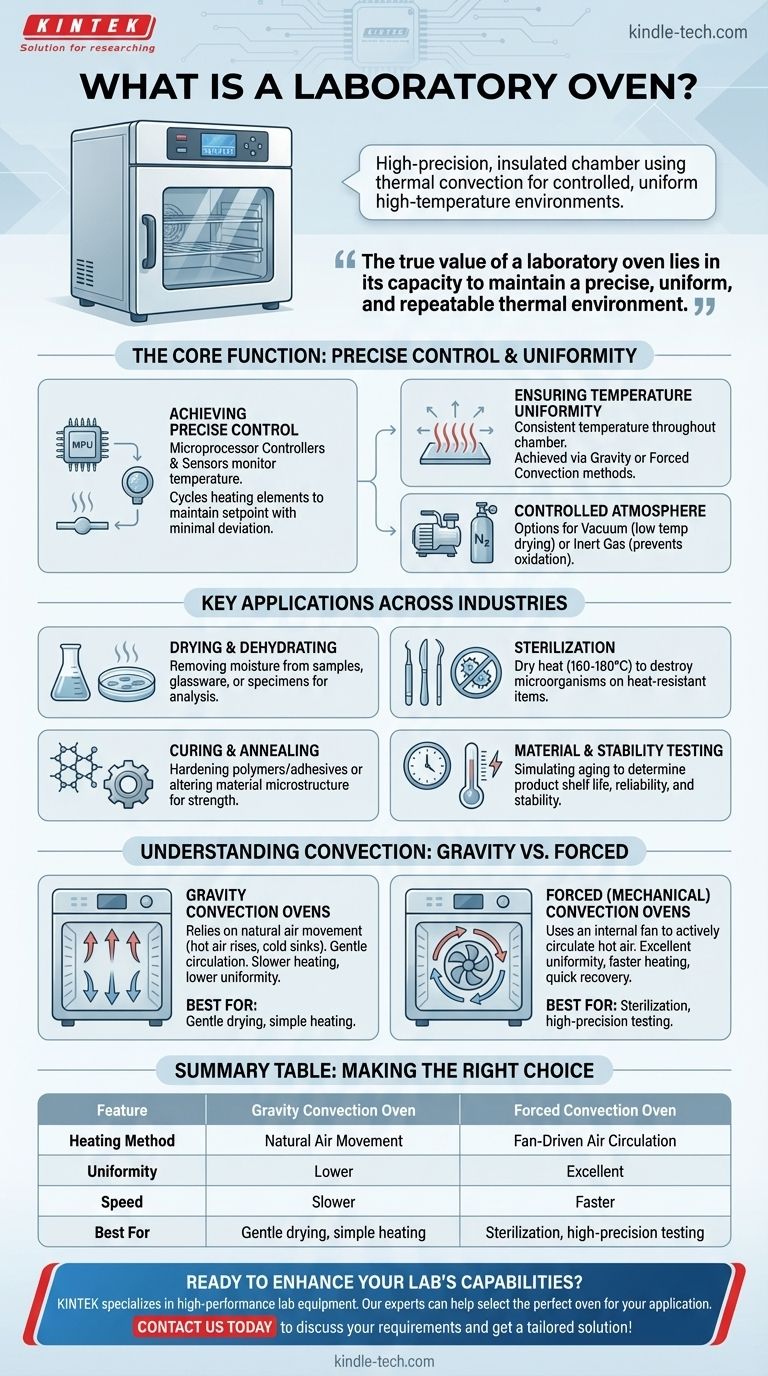
In essence, a laboratory oven is a high-precision, insulated chamber that uses thermal convection to create a controlled and uniform high-temperature environment. Unlike a conventional kitchen oven, its purpose is not to cook food but to perform critical scientific and industrial functions such as drying, sterilizing, curing, and testing materials where temperature accuracy and stability are non-negotiable.
The true value of a laboratory oven lies not just in its ability to generate heat, but in its capacity to maintain a precise, uniform, and repeatable thermal environment, making it an indispensable tool for reliable scientific outcomes.

The Core Function: More Than Just Heat
A lab oven's design is entirely focused on creating a stable and predictable environment. This is achieved through a combination of precise control, uniform heat distribution, and robust construction.
Achieving Precise Temperature Control
Modern lab ovens use sophisticated microprocessor-based controllers and sensors, typically thermocouples. These systems constantly monitor the internal temperature and cycle the heating elements on and off to maintain the setpoint with minimal deviation, often within a fraction of a degree Celsius.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
Temperature uniformity refers to how consistent the temperature is throughout the entire chamber. Uneven heating can ruin an experiment or process. Ovens achieve uniformity primarily through two methods: gravity or forced convection.
The Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
While most ovens operate with ambient air, some advanced models allow for process-specific atmospheres. Vacuum ovens, for example, remove air to dry materials at lower temperatures, protecting heat-sensitive samples. Others can be purged with an inert gas like nitrogen to prevent oxidation.
Key Applications Across Industries
The precise control offered by laboratory ovens makes them essential in a wide range of fields, from microbiology to materials science and manufacturing.
Drying and Dehydrating
This is one of the most common uses. Ovens are used to remove moisture from scientific samples before weighing, to dry laboratory glassware, or to dehydrate botanical or biological specimens for analysis.
Sterilization
Dry heat sterilization is a crucial process for preparing heat-resistant equipment, such as metal instruments and certain types of glassware. Ovens heat items to temperatures like 160-180°C for an extended period to destroy all microorganisms.
Curing and Annealing
In materials science and manufacturing, ovens are used to cure polymers, adhesives, and composites, causing a chemical reaction that hardens the material. They are also used for annealing, a heat treatment that alters a material's microstructure to increase ductility and reduce hardness.
Material and Stability Testing
Manufacturers use lab ovens to simulate the effects of time and temperature on their products. This accelerated aging helps determine a product's shelf life, component reliability, and overall stability under thermal stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Gravity vs. Forced Convection
The method of heat circulation is the most significant differentiator between oven types and directly impacts performance and cost.
Gravity Convection Ovens
These ovens rely on the natural movement of air—hot air rises and cooler, denser air sinks. This gentle circulation is ideal for drying fine powders or materials that could be disturbed by a fan. However, they heat up more slowly and have poorer temperature uniformity compared to forced-air models.
Forced (Mechanical) Convection Ovens
These models use an internal fan to actively circulate hot air throughout the chamber. This results in excellent temperature uniformity, faster heating, and quicker recovery after the door is opened. They are the standard for applications requiring high precision, like sterilization and most material testing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct oven requires a clear understanding of your primary goal. The choice between convection types and other features depends entirely on the sensitivity and requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is drying delicate powders or simple heating: A gravity convection oven provides a gentle, cost-effective solution where absolute uniformity is not critical.
- If your primary focus is rapid drying, sterilization, or testing requiring high uniformity: A forced convection oven is essential for its speed and temperature consistency across the chamber.
- If your primary focus is working with heat-sensitive materials or removing solvents: A vacuum oven is the necessary choice to enable drying at lower temperatures and prevent oxidation.
Ultimately, choosing the right laboratory oven is an investment in the repeatability and reliability of your results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Gravity Convection Oven | Forced Convection Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Gentle drying, simple heating | Sterilization, high-precision testing |
| Heating Method | Natural air movement | Fan-driven air circulation |
| Uniformity | Lower | Excellent |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? The right laboratory oven is critical for achieving precise, repeatable results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with a range of high-performance ovens. Our experts can help you select the perfect model for your specific application, whether it's for drying, sterilization, or material testing. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance
- Why is a forced-air drying oven required for ZnS powder? Protect Sintered Ceramics from Cracking
- Why is a laboratory-grade forced air drying oven required for alloy chip moisture analysis? Ensure Data Precision



















