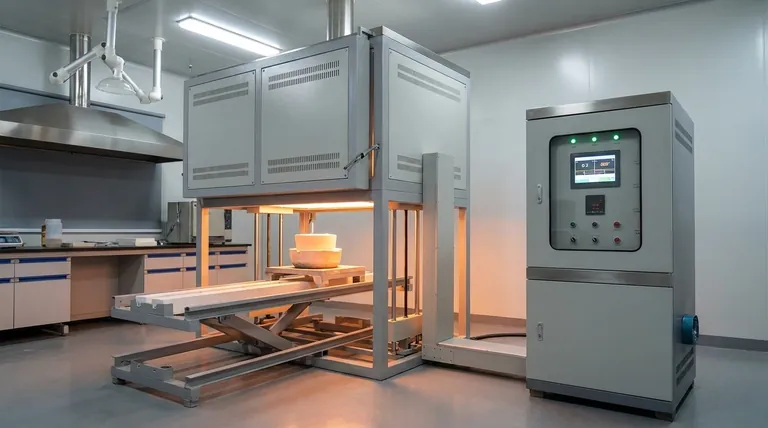
At its core, a muffle furnace is used to determine the composition of a sample by subjecting it to extreme temperatures. It excels at burning away all combustible and volatile components to precisely measure the amount of non-volatile, non-combustible material—such as ash—that remains. This process, known as gravimetric analysis or loss-on-ignition, is fundamental in quality control, materials science, and chemical analysis.
The true value of a muffle furnace isn't just its high heat, but its ability to provide that heat within a controlled, isolated chamber. This "muffle" prevents sample contamination, making the furnace an indispensable tool for both determining a material's inorganic content and for transforming its physical properties.

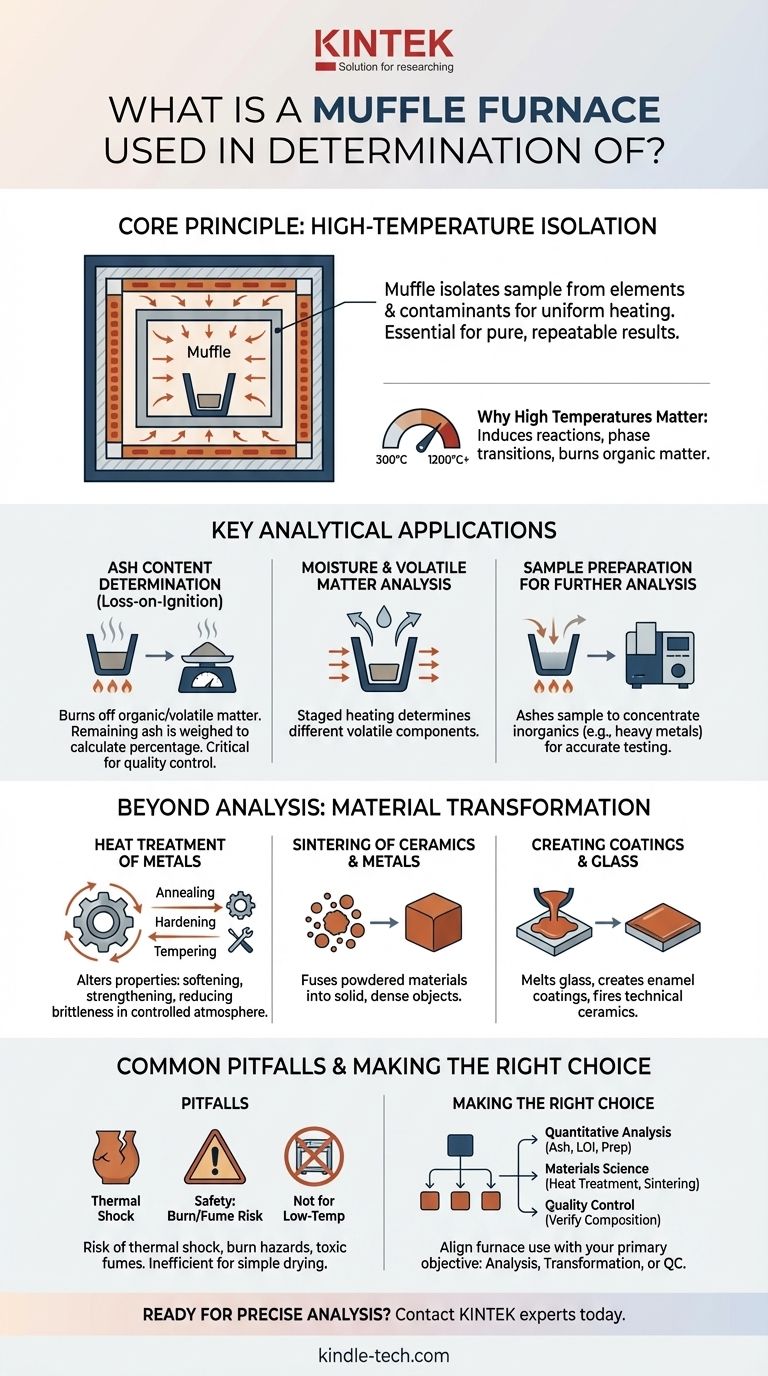
The Core Principle: High-Temperature Isolation
A muffle furnace is more than just a powerful oven. Its unique design is central to its function in both analytical chemistry and materials science.
What is a "Muffle"?
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's inner chamber, which isolates the sample being heated from direct contact with the heating elements and any contaminants from combustion.
This design ensures that the sample is heated uniformly by radiation and convection, not by direct flame or electrical interference. This isolation is critical for achieving pure, repeatable results.
Why High Temperatures Matter
Muffle furnaces operate at extremely high temperatures, typically ranging from 300°C to 1200°C (572°F to 2192°F) or even higher.
These temperatures are necessary to induce chemical reactions, phase transitions, or to completely burn away organic matter, which would not be possible in a standard laboratory oven.
Key Applications in Determination and Analysis
The primary analytical use of a muffle furnace is to find out what a sample is made of by separating its components based on their reaction to heat.
Ash Content Determination
This is the most common analytical application. A sample of known weight is placed in the furnace and heated until all organic and volatile substances have been burned off.
The remaining material, or ash, is then weighed. The difference in weight allows for the precise calculation of the ash percentage, a critical quality metric in industries from food science to coal analysis. This is also known as loss-on-ignition.
Moisture and Volatile Matter Analysis
By using a staged heating process, a muffle furnace can determine different components. A lower temperature step can drive off moisture, while subsequent higher temperatures burn off other volatile compounds.
This allows for a more detailed breakdown of a sample's composition beyond just simple ash content.
Sample Preparation for Further Analysis
In fields like environmental science and water quality analysis, a muffle furnace is used to prepare samples for further testing.
By ashing a sample, analysts can remove interfering organic material, concentrating the inorganic analytes (like heavy metals) for more accurate measurement by other instruments.
Beyond Analysis: Material Transformation
While essential for determination, muffle furnaces are also workhorses for creating and modifying materials. The principle of controlled, high-temperature heating is the same, but the goal is different.
Heat Treatment of Metals
In metallurgy, muffle furnaces are used for processes like annealing (softening metal), hardening (increasing strength), and tempering (reducing brittleness). The controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation on the metal's surface.
Sintering of Ceramics and Metals
Sintering is the process of heating powdered materials to just below their melting point. This fuses the particles together to form a solid, dense object. This technique is fundamental to producing technical ceramics and certain metal parts.
Creating Coatings and Glass
The high, consistent temperatures in a muffle furnace are perfect for melting glass, creating enamel coatings on metal, and firing technical ceramics.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool that requires proper use and understanding of its limitations.
Not for Low-Temperature Applications
Using a muffle furnace for simple drying below 300°C is inefficient. A standard laboratory or convection oven is more appropriate and energy-efficient for these tasks.
Risk of Thermal Shock
The rapid temperature changes a muffle furnace can produce may cause certain materials, especially large ceramic objects, to crack or shatter. Controlled heating and cooling rates are essential.
Safety is Paramount
Operating at extreme temperatures, these furnaces pose significant burn risks. Furthermore, the combustion of samples can release toxic fumes, requiring the furnace to be placed under a ventilation hood or in a well-ventilated area.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, consider the primary objective of your work.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Use the muffle furnace to accurately determine ash content, loss-on-ignition, and to prepare inorganic samples for further elemental testing.
- If your primary focus is materials science: Use it for the heat treatment of metals, sintering of powdered materials, and testing the thermal properties of new compounds.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Employ the furnace to verify the composition of raw materials, such as the filler content in polymers or the purity of chemical ingredients.
Understanding the muffle furnace's role as a high-temperature isolation tool empowers you to perform precise material analysis and transformation with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Ash Content Determination | Burn off organic/volatile matter | Weight of remaining ash (Loss-on-Ignition) |
| Moisture & Volatile Matter Analysis | Staged heating to drive off components | Percentage of different volatile components |
| Sample Preparation | Remove organic material for inorganic analysis | Concentration of inorganic analytes |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, hardening, tempering metals | Altered material properties (strength, brittleness) |
| Sintering | Fuse powdered materials into solid objects | Density and structural integrity |
Ready to achieve precise material analysis and transformation? KINTEK's muffle furnaces provide the controlled high-temperature environment essential for accurate ash determination, loss-on-ignition testing, and material sintering. Our lab equipment ensures contamination-free results for your quality control and research needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of laboratory muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What precautions should you take while using a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe High-Temperature Processing in Your Lab
- How do you cool down a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety with the Correct Procedure
- Does casting change material properties? Understand the Microstructural Impact on Performance
- What is the working principle of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating



















