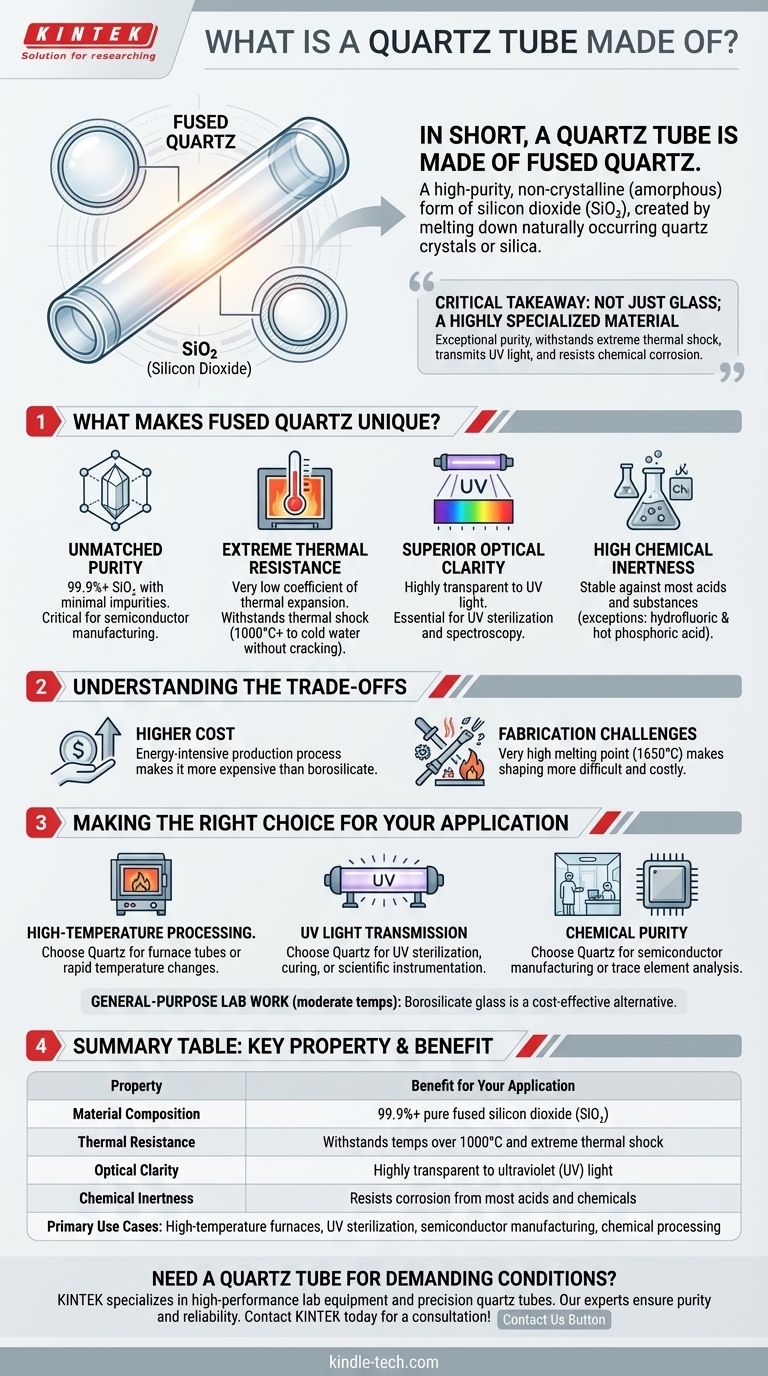
In short, a quartz tube is made of fused quartz. This is a high-purity, non-crystalline (amorphous) form of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), created by melting down naturally occurring quartz crystals or silica. Unlike standard glass, it is composed almost entirely of this single ingredient, which gives it a unique set of properties essential for demanding technical applications.
The critical takeaway is that a quartz tube is not just a type of glass; it is a highly specialized material. Its value comes from its exceptional purity and ability to withstand extreme thermal shock, transmit ultraviolet light, and resist chemical corrosion where conventional materials would fail.
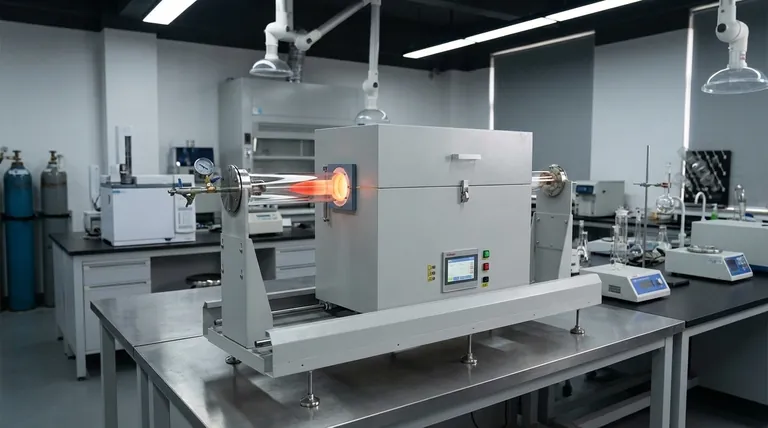

What Makes Fused Quartz Unique?
The choice of fused quartz is deliberate and driven by properties that are impossible to achieve with standard glass, such as borosilicate. These characteristics stem directly from its simple and pure chemical structure.
Unmatched Purity
A quartz tube is one of the purest materials available for industrial and scientific use. It is typically composed of 99.9%+ silicon dioxide (SiO₂) with minimal impurities.
This high purity is critical in applications like semiconductor manufacturing, where even trace amounts of contaminants can ruin microchips.
Extreme Thermal Resistance
Fused quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it barely expands or contracts when its temperature changes dramatically.
You can heat a quartz tube to over 1000°C and then plunge it into cold water without it cracking. This resistance to thermal shock is one of its most important features, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace tubes and lab equipment.
Superior Optical Clarity
Unlike most types of glass, fused quartz is highly transparent to ultraviolet (UV) light. Standard glass blocks most UV wavelengths.
This property makes quartz essential for applications like UV water sterilization lamps, UV curing processes, and various scientific instruments that rely on UV spectroscopy.
High Chemical Inertness
Fused quartz is chemically very stable and does not react with most acids, water, or neutral substances. The only notable exceptions are hydrofluoric acid and hot phosphoric acid.
This resistance to corrosion makes it an excellent choice for containers and tubing used to handle aggressive chemicals in laboratory settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, fused quartz is not the default choice for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Cost
The process of melting and purifying natural quartz crystal into a usable form is energy-intensive and complex. As a result, quartz tubing is significantly more expensive than tubes made from borosilicate or other standard glasses.
Fabrication Challenges
Fused quartz has a very high melting point (around 1650°C), making it more difficult and costly to shape and work with than conventional glass. This limits the complexity of shapes that can be easily manufactured and increases the cost of custom fabrication.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the demands of your specific task.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing: Quartz is the superior choice for furnace tubes or any application involving rapid, extreme temperature changes.
- If your primary focus is UV light transmission: Quartz is non-negotiable for applications like UV sterilization, curing, or scientific instrumentation that requires UV transparency.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity: Quartz is essential for semiconductor manufacturing, trace element analysis, and other fields where contamination must be avoided at all costs.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work at moderate temperatures: Borosilicate glass is often a more cost-effective and perfectly suitable alternative.
Ultimately, choosing a quartz tube is a decision to invest in unparalleled performance for conditions where other materials simply cannot operate.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Your Application |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | 99.9%+ pure fused silicon dioxide (SiO₂) |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands temperatures over 1000°C and extreme thermal shock |
| Optical Clarity | Highly transparent to ultraviolet (UV) light |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from most acids and chemicals |
| Primary Use Cases | High-temperature furnaces, UV sterilization, semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing |
Need a Quartz Tube for Demanding Conditions?
Choosing the right material is critical for your lab's success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision quartz tubes designed for extreme thermal and chemical environments. Our quartz tubes ensure the purity and reliability your applications demand.
Let our experts help you select the perfect solution for your specific needs. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry



















