In essence, a sintered element is a solid component created by compressing a powdered material—such as metal, ceramic, or plastic—and heating it to just below its melting point. This process causes the individual powder particles to fuse together on an atomic level, forming a strong, rigid structure. The defining characteristic of a sintered element is that its density and porosity can be precisely engineered for specific applications.
The core concept to grasp is that sintering builds a solid object from the ground up, particle by particle, without ever melting the material. This unique "solid-state" process gives engineers precise control over the material's final structure, creating components with properties like controlled porosity that are often impossible to achieve with traditional casting or machining.
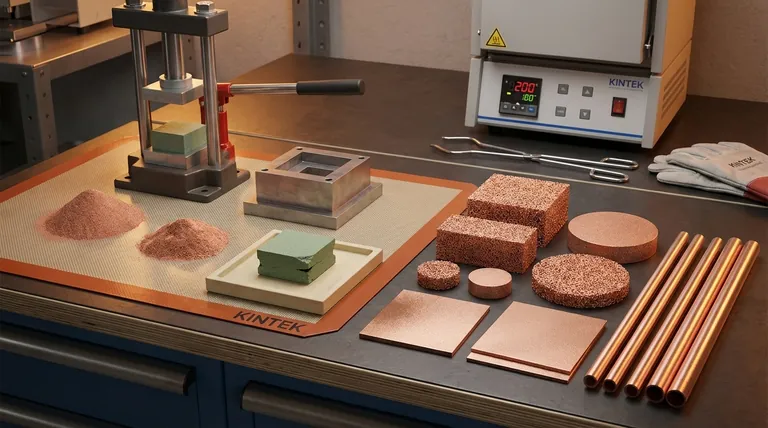
How Sintering Transforms Powder into a Solid
The creation of a sintered element is a multi-stage process that relies on pressure and thermal energy to fundamentally change the nature of a powdered material.
The Starting Point: Powder and a Mold
The process begins with a fine powder of the chosen material. This powder is carefully loaded into a die or mold that has the negative shape of the final part.
Step 1: Compaction (The "Green" State)
Immense pressure is applied to the powder within the mold. This compaction forces the particles into close contact, creating a fragile, weakly bonded part that is often called a "green compact". This part holds its shape but has very little structural strength.
Step 2: The Furnace (Atomic Diffusion)
The green compact is carefully removed from the mold and placed into a high-temperature furnace. It is heated to a specific temperature that is hot enough to excite the atoms but remains below the material's melting point.
The Fusion Mechanism
At this elevated temperature, a phenomenon called atomic diffusion occurs. Atoms from individual particles migrate across the boundaries to their neighbors, effectively welding the particles together on a microscopic level. Any temporary binders used during compaction are burned away, and the part shrinks and densifies into a final, solid component.
The Defining Characteristic: Engineered Porosity
Unlike in cast or forged metals where porosity is considered a defect, in sintered elements, it is often a key design feature.
Porosity by Design, Not by Flaw
Because the part is built from individual particles, a network of microscopic pores remains in the final structure. The key is that the size and distribution of these pores can be controlled with remarkable precision.
Controlling Pore Size and Density
By adjusting the initial powder size, the compaction pressure, and the temperature and duration of the sintering process, manufacturers can dictate the final density of the part. This allows for the creation of everything from nearly solid components to highly porous, filter-like structures.
Common Applications of Porosity
This engineered porosity is the basis for many applications. Sintered elements are used as filters, where their controlled pore network allows fluids to pass through while trapping contaminants. They are also used for self-lubricating bearings, where the pores are impregnated with oil that is released during operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintered element requires understanding both its powerful advantages and its inherent limitations.
The Advantage: Complex Shapes and Material Blends
Sintering excels at producing complex, net-shape parts with high precision, dramatically reducing or eliminating the need for costly secondary machining. It also allows for the creation of parts from materials or material combinations that cannot be alloyed through melting.
The Advantage: Hardness and Wear Resistance
The final sintered part is typically very hard and resistant to wear, making these elements ideal for gears, bearings, and other components subjected to friction.
The Limitation: Inherent Porosity and Strength
While strong, a sintered part is rarely as strong as a fully dense component made from forged or wrought metal. The residual porosity, however small, can be a point of weakness, potentially making the part more brittle and less resistant to high-impact loads.
The Limitation: Tooling Costs and Size
The dies and molds required for the compaction stage are expensive to produce. This makes sintering most cost-effective for high-volume production runs where the initial tooling cost can be amortized over many thousands of parts. The process is also typically limited to small and medium-sized components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is filtration or self-lubrication: Sintering is the ideal choice, as it is one of the few processes that allows you to engineer the exact porosity your application requires.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex, high-volume part cost-effectively: Sintering is an excellent candidate, as it produces near-net-shape components that minimize material waste and machining labor.
- If your primary focus is absolute maximum strength and impact resistance: A forged or fully machined component from a solid billet is likely a more suitable choice, as it avoids the inherent porosity of a sintered part.
By understanding the principles of sintering, you can leverage its unique capabilities to solve engineering challenges that other manufacturing methods cannot address.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Powder is compacted and heated below melting point. | Creates complex, net-shape parts with minimal waste. |
| Key Characteristic | Engineered Porosity | Can be designed for filtration or self-lubrication. |
| Primary Advantage | Material and Shape Flexibility | Ideal for hard-to-machine materials and intricate designs. |
| Ideal For | High-volume production of small to medium parts. | Cost-effective for large runs after initial tooling investment. |
Need a precise, high-performance component for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including custom sintered elements. Our expertise in materials science allows us to create components with the exact properties—like controlled porosity for filters or self-lubricating bearings—that your laboratory or production process requires.
We help you leverage the unique advantages of sintering to solve complex engineering challenges, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a custom sintered solution can benefit your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Foam
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of copper foam? Unlock High-Performance Thermal and Electrical Solutions
- What are the proper storage conditions for nickel and copper foam? A Guide to Preserving Performance
- What are the factors that affect heat transfer? Master the Key Variables for Optimal Thermal Performance
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- What role does convection play in heat transfer? Understanding Heat Movement in Fluids













