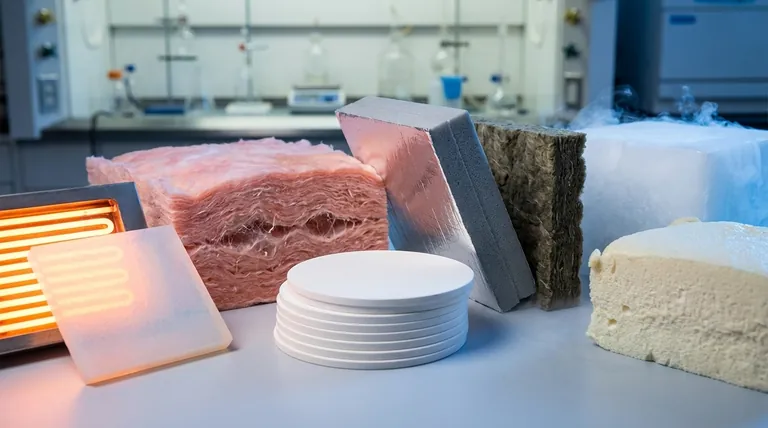
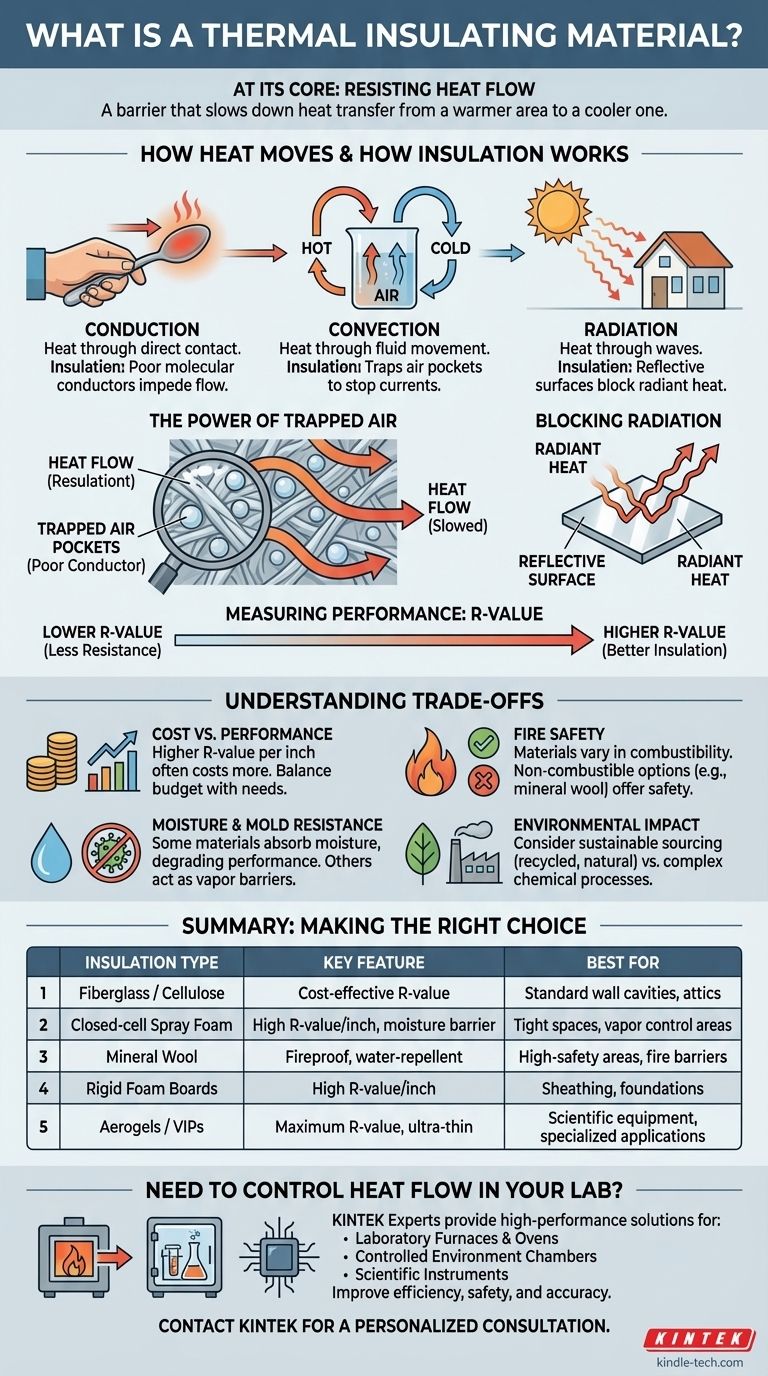
At its core, a thermal insulating material is a substance designed to resist the flow of heat. Its primary purpose is not to generate cold or warmth, but to act as a barrier that slows down heat transfer from a warmer area to a cooler one. Common examples range from the fiberglass in your attic and the foam in a coffee cup to the high-tech aerogels used by NASA.
The effectiveness of an insulator is not about the material itself, but about its structure. Most insulation works by trapping pockets of gas (usually air), which is a very poor conductor of heat, thereby preventing heat from moving through it efficiently.

How Heat Moves: The Problem Insulation Solves
To understand how an insulator works, you must first understand the three ways heat travels. Every insulating material is engineered to combat one or more of these transfer mechanisms.
Conduction: Heat Through Touch
Conduction is heat transfer through direct molecular contact. Think of the handle of a metal spoon getting hot when you leave it in a cup of tea.
Materials with tightly packed molecules, like metals, are excellent conductors. Insulators are the opposite; they are poor conductors because their molecular structure makes it difficult for heat energy to pass from one molecule to the next.
Convection: Heat Through Movement
Convection is heat transfer through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). This is why warm air rises and cool air sinks, creating a convection current.
A material can be a poor conductor, but if it allows air to move freely through it, heat will be carried away by convection. This is the primary mechanism that most common insulators are built to stop.
Radiation: Heat Through Waves
Radiation is heat transfer through electromagnetic waves, like the warmth you feel from the sun or a campfire. It doesn't require a medium to travel through.
Shiny, reflective surfaces are effective at blocking radiant heat transfer. This is why you see radiant barriers, often with a foil-like surface, used in attics in hot climates.
How Insulators Actually Work
An insulating material's power comes from its ability to disrupt the three forms of heat transfer, primarily by leveraging a simple principle: air is a terrible conductor of heat.
The Power of Trapped Air
The vast majority of insulating materials, like fiberglass, mineral wool, and cellulose, are not dense solids. They are composed of a matrix of fine fibers that trap countless tiny pockets of air.
By trapping the air, the material prevents heat transfer via convection. Since the air itself is a poor conductor, and the fibers provide a long, difficult path for conduction, heat transfer is slowed dramatically. A thick winter coat works on the exact same principle.
Blocking Radiation
Some insulation, like rigid foam boards or radiant barriers, incorporates a reflective surface. This foil layer reflects thermal radiation, adding another layer of defense against heat transfer, which is particularly effective against the sun's heat.
Measuring Performance: The R-Value
An insulator's effectiveness is measured by its R-value, which indicates its resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the better the material's insulating performance. This value is determined by the material's composition, thickness, and density.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an insulating material isn't just about picking the highest R-value. Several practical factors create a series of trade-offs that must be considered for any application.
Cost vs. Performance
Generally, a higher R-value per inch comes with a higher price tag. Materials like aerogel offer incredible R-values in a very thin profile but are prohibitively expensive for most applications. In contrast, fiberglass offers a good balance of cost and performance for residential construction.
Moisture and Mold Resistance
Some insulation types, like loose-fill cellulose, can absorb and hold moisture, which severely degrades their R-value and can lead to mold growth. Closed-cell spray foam, on the other hand, acts as a vapor barrier and is highly resistant to water.
Fire Safety
Fire resistance is a critical safety consideration. Mineral wool and fiberglass are naturally non-combustible. In contrast, foam plastics (like EPS or XPS) are combustible and must be covered with a fire-resistant barrier, such as drywall, to be used safely in a building.
Environmental Impact
The production of insulating materials can have a significant environmental footprint. Some products, like cellulose (made from recycled paper) or cork, are valued for their sustainable sourcing. Others, like spray foams, are derived from petroleum and involve complex chemical processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" insulator is entirely dependent on the specific goal of your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective home energy efficiency: Materials like fiberglass batts or blown-in cellulose offer the best R-value for the lowest cost and are ideal for standard wall cavities and attics.
- If your primary focus is performance in a tight space: Closed-cell spray foam or rigid foam boards provide a high R-value per inch, making them suitable for areas where you cannot afford to lose space.
- If your primary focus is fire and moisture safety: Mineral wool is an excellent choice, as it is non-combustible, water-repellent, and offers solid thermal and acoustic insulation.
- If your primary focus is specialized high-tech applications: Materials like vacuum insulated panels (VIPs) or aerogels are used when maximum thermal resistance is needed in the thinnest possible profile, such as in scientific equipment or refrigeration.
Ultimately, a thermal insulator is a strategically engineered material designed to control how and where heat moves.
Summary Table:
| Insulation Type | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass / Cellulose | Cost-effective R-value | Standard wall cavities, attics |
| Closed-cell Spray Foam | High R-value per inch, moisture barrier | Tight spaces, areas needing vapor control |
| Mineral Wool | Fireproof, water-repellent | High-safety areas, fire barriers |
| Rigid Foam Boards | High R-value per inch | Sheathing, foundations |
| Aerogels / VIPs | Maximum R-value, ultra-thin | Scientific equipment, specialized applications |
Need to Control Heat Flow in Your Lab?
The right thermal insulation is critical for maintaining precise temperatures, ensuring experiment integrity, and protecting sensitive lab equipment. The experts at KINTEK understand the unique thermal management challenges faced by laboratories.
We provide high-performance insulating materials and solutions tailored for:
- Laboratory Furnaces & Ovens: Maximize efficiency and safety.
- Controlled Environment Chambers: Ensure temperature stability.
- Scientific Instruments: Protect sensitive components from heat transfer.
Let us help you select the ideal insulation to improve your lab's energy efficiency, safety, and experimental accuracy.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation on our lab equipment and consumables!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Ball Valve Seat
People Also Ask
- Which of the following is used in furnace to withstand high temperature? Key Materials for Extreme Heat
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- What is the primary purpose of using alumina sintering plates? Ensure Purity for R1/3Zr2(PO4)3 Samples
- What is the function of alumina setter plates for LATP? Protect Material Purity & Prevent Adhesion
- What are the typical properties of high-alumina (Al2O3) refractories? Enhance Performance with High-Temp Resilience



















