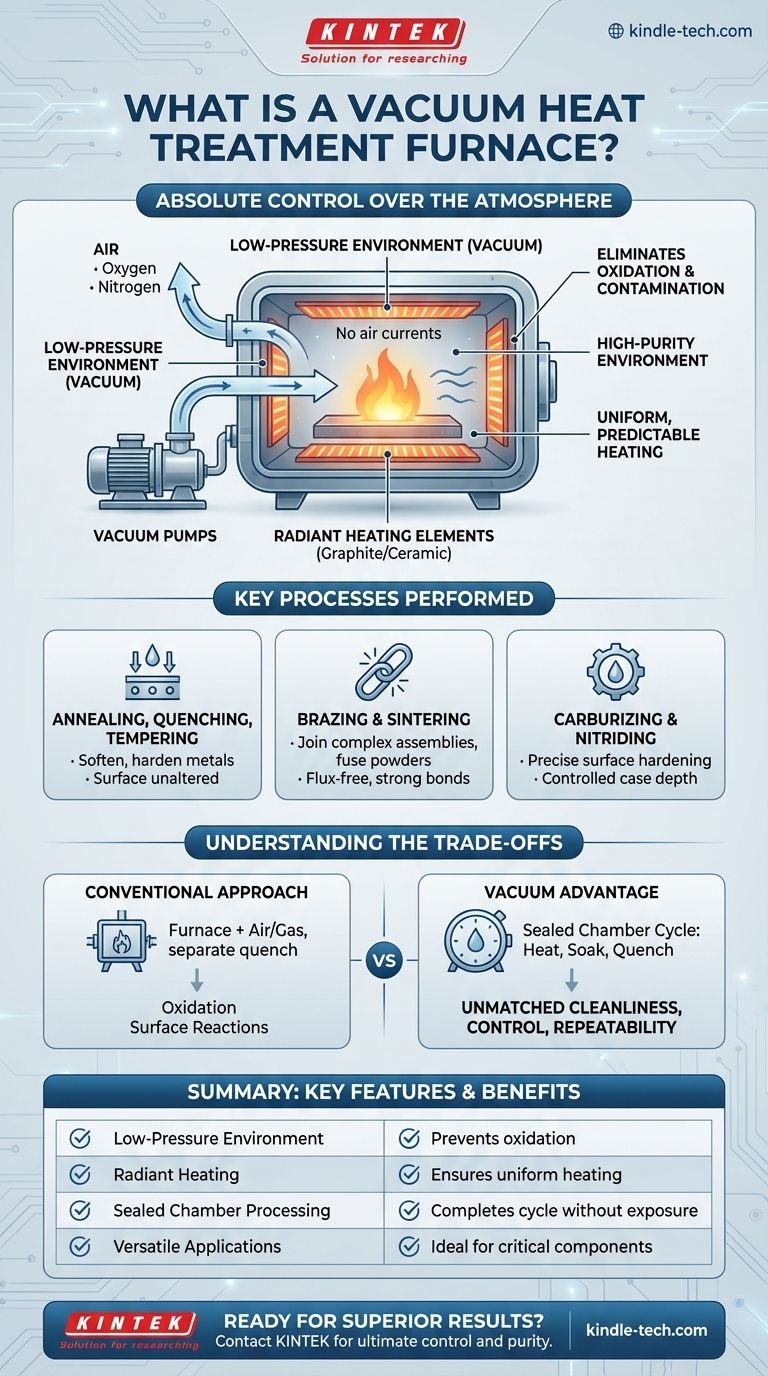
In essence, a vacuum heat treatment furnace is a highly controlled thermal processing system that operates under a low-pressure environment. It consists of a sealed chamber connected to powerful vacuum pumps that remove air—specifically oxygen and nitrogen—before heating a material. This process prevents surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization, ensuring the treated component emerges with a clean, bright finish and superior metallurgical properties.
The true value of a vacuum furnace is not just its ability to heat materials, but its power to create an exceptionally pure and stable environment. This control eliminates atmospheric contamination, leading to predictable, high-quality results that are often impossible to achieve with conventional methods.

The Core Principle: Absolute Control Over the Atmosphere
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is its ability to manipulate the environment where heat treatment occurs. This provides a level of precision that fundamentally changes the outcome of the process.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
By removing oxygen and other reactive gases, a vacuum furnace creates a chemically inert environment. This prevents the formation of an oxide layer (scale) on the material's surface during heating.
The result is a component with a bright, clean surface that often requires no subsequent cleaning or finishing. This is critical for high-value parts in industries like aerospace, medical, and high-performance tooling.
Achieving a High-Purity Environment
The process begins by placing the workload into a sealed chamber. A system of vacuum pumps then evacuates the atmosphere to a specific low pressure, measured in units like Torr or millibar.
This environment is considered a "vacuum," meaning it is substantially below normal atmospheric pressure.
Ensuring Precision Heating
Once the vacuum is established, heat is applied using internal heating elements, often made of graphite or specialized ceramic composites.
Because there is almost no air, heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation, not convection. This eliminates disruptive air currents and allows for extremely uniform heating across the entire workpiece, ensuring consistent and predictable results.
Key Processes Performed in a Vacuum Furnace
A vacuum furnace is not limited to a single function; its controlled environment makes it one of the most versatile tools in modern metallurgy.
Annealing, Quenching, and Tempering
These fundamental processes are used to soften metals, increase their hardness, or improve their toughness. Performing them in a vacuum ensures the material's surface chemistry is unaltered, preserving its integrity.
Brazing and Sintering
Vacuum brazing is a superior method for joining complex assemblies, as the clean environment ensures the filler metal flows perfectly without the use of corrosive fluxes.
Sintering—the process of fusing powdered materials together with heat—also benefits immensely from the vacuum environment, which prevents contamination and produces stronger, purer final parts.
Carburizing and Nitriding
While seemingly counterintuitive, processes that add elements to a surface (like carbon or nitrogen) can also be performed with extreme precision in a vacuum.
This is known as low-pressure carburizing or nitriding. The vacuum first purges all contaminants, and then a precise amount of process gas is introduced, allowing for exceptional control over the case depth and surface hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Vacuum vs. Conventional
While vacuum technology offers significant advantages, it is important to understand how it compares to traditional atmospheric furnaces.
The Conventional Approach
Conventional heat treatment typically involves heating a part in a furnace open to the air or filled with a protective gas.
The part is then quenched (rapidly cooled) by moving it to a separate tank of oil, water, or salt. This exposure to air and quenching fluids inevitably leads to oxidation and surface reactions.
The Vacuum Advantage
A vacuum furnace completes the entire cycle—heating, soaking, and quenching (often with high-pressure inert gas)—within the same sealed chamber.
This integrated process provides unmatched cleanliness, control, and repeatability. There is no risk of atmospheric interference at any stage, guaranteeing a higher-quality end product.
Key Considerations
The primary benefit of a vacuum furnace is the superior quality of the output. However, the equipment is generally more complex and has a higher initial investment cost compared to basic atmospheric furnaces. The decision depends entirely on the required quality and performance of the final component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment method requires matching the technology to the desired outcome for the material.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish and maximum material integrity: A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and decarburization, especially for critical components in the aerospace, medical, or tool and die industries.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies with clean, strong bonds: Vacuum brazing provides a flux-free process with superior filler metal flow and joint quality.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose hardening where post-process cleaning is acceptable: A conventional atmospheric furnace can be a more cost-effective solution for less critical applications.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize control, cleanliness, and the metallurgical purity of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low-Pressure Environment | Prevents oxidation & surface contamination |
| Radiant Heating | Ensures uniform, predictable heating |
| Sealed Chamber Processing | Completes heating and quenching without atmospheric exposure |
| Versatile Applications | Ideal for annealing, brazing, sintering, and low-pressure carburizing |
Ready to achieve superior results for your critical components?
A vacuum heat treatment furnace from KINTEK provides the ultimate control and purity for your laboratory or production needs. Whether you are working in aerospace, medical device manufacturing, or high-performance tooling, our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a solution tailored to your application.
We specialize in helping laboratories like yours enhance material integrity and achieve pristine surface finishes. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can transform your heat treatment processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















