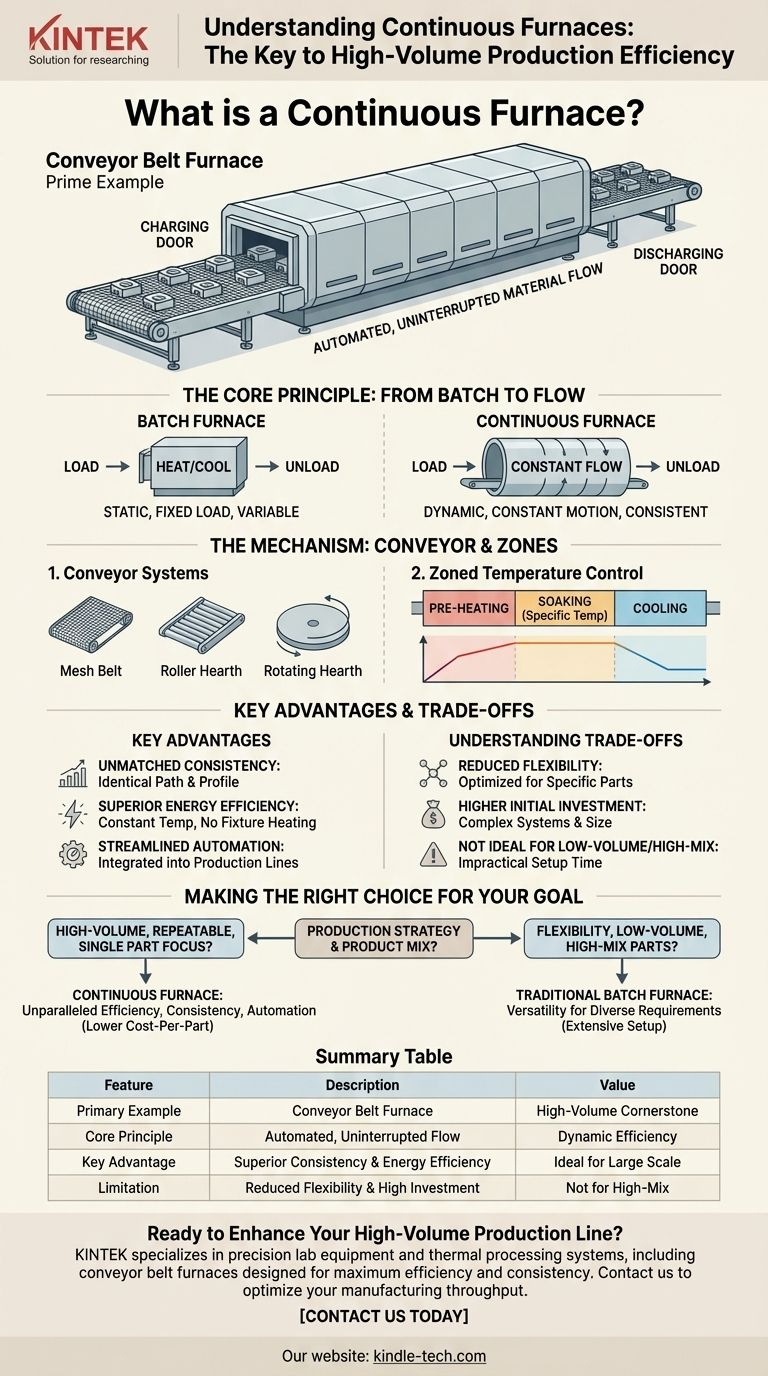
A prime example of a continuous furnace is the conveyor belt furnace, a cornerstone of modern high-volume manufacturing. In this system, products are placed on a continuously moving belt—often made of wire mesh—that transports them through a long, tunnel-like chamber. This process ensures every single part is subjected to the exact same temperature profile, achieving a level of consistency that is difficult to match with other methods.
The defining characteristic of a continuous furnace is not its heat source, but its automated, uninterrupted material flow. This design sacrifices the flexibility of processing varied, small batches to gain superior efficiency and repeatability for large-scale, uniform production.

The Core Principle: From Batch to Flow
The fundamental shift from a traditional batch furnace to a continuous one is the move from a static process to a dynamic one. It's the difference between baking cookies on a tray you put in and take out, versus a production line where cookies are constantly moving through an oven.
What Defines a "Continuous" Process?
In a continuous furnace, the material is always in motion. The components are loaded at a charging door, transported through the furnace at a constant, controlled speed, and removed at a discharging door.
This contrasts sharply with a batch furnace, where a fixed load of material is placed inside, the door is closed, the furnace heats and cools, and the entire batch is removed at once.
The Role of the Conveyor System
The mechanism for moving the parts is central to the furnace's design. While a mesh belt is common, other systems exist to suit different products and temperatures.
These can include roller hearths, where parts are moved along by powered rollers, or rotating hearths, which use a large, circular, rotating floor to move components through the heat zones.
Zoned Temperature Control
A key advantage of the tunnel-like structure is the ability to create multiple, distinct temperature zones. A part can move sequentially through a pre-heating zone, a soaking zone (where it's held at a specific temperature), and finally, one or more cooling zones.
This precise, multi-stage thermal profile is critical for sophisticated heat treatment processes and ensures every part receives the identical, optimal treatment.
Key Advantages in High-Volume Operations
The design of a continuous furnace is entirely optimized for the demands of automated, large-scale production lines.
Unmatched Consistency and Uniformity
Because every component follows the exact same path and time-temperature profile, the final product quality is exceptionally consistent. This eliminates the process variations that can occur in batch operations, where parts in the center of a load may heat differently than those on the edges.
Superior Energy Efficiency
Continuous furnaces operate at a constant temperature, avoiding the energy-intensive cycles of heating up and cooling down required by batch furnaces.
Furthermore, they often eliminate the need for heavy racks, baskets, or fixtures to hold the parts. Heating only the product, not the extra hardware, results in significant energy savings.
Streamlined Automation and Throughput
These furnaces are designed to be integrated directly into a production line. Parts can flow from a previous manufacturing step, through the furnace, and onto the next stage with minimal human intervention. This maximizes throughput and reduces operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, continuous furnaces are not a universal solution. Their specialized nature comes with clear limitations.
Reduced Flexibility
A continuous furnace is typically optimized for a specific part or a narrow range of similar products. Changing the temperature profile, belt speed, and zone settings for a completely different product can be complex and time-consuming, leading to significant downtime.
Higher Initial Investment
The sophisticated conveyor systems, multi-zone controls, and sheer size of continuous furnaces mean they represent a much larger upfront capital investment compared to simpler, more versatile batch furnaces.
Not Ideal for Low-Volume or High-Mix Production
If your operation involves heat-treating many different types of parts in small quantities, a continuous furnace is impractical. The setup time required for each new part would negate any efficiency gains.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision between a continuous and a batch furnace hinges entirely on your production strategy and product mix.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production of a single part: A continuous furnace offers unparalleled efficiency, consistency, and automation that will lower your cost-per-part.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for low-volume, high-mix parts: A traditional batch furnace provides the versatility needed to handle diverse product requirements without extensive setup changes.
Ultimately, understanding your production volume and product mix is the key to selecting the most effective thermal processing technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Example | Conveyor Belt Furnace |
| Core Principle | Automated, uninterrupted material flow through temperature zones |
| Key Advantage | Superior consistency and energy efficiency for large-scale production |
| Ideal For | High-volume, uniform part manufacturing |
| Limitation | Reduced flexibility for low-volume or high-mix production |
Ready to enhance your high-volume production line with a continuous furnace solution? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and thermal processing systems, including conveyor belt furnaces designed for maximum efficiency and consistency. Our experts can help you select the ideal furnace to optimize your manufacturing throughput and reduce operational costs. Contact us today to discuss your specific production needs and discover the KINTEK advantage!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity



















