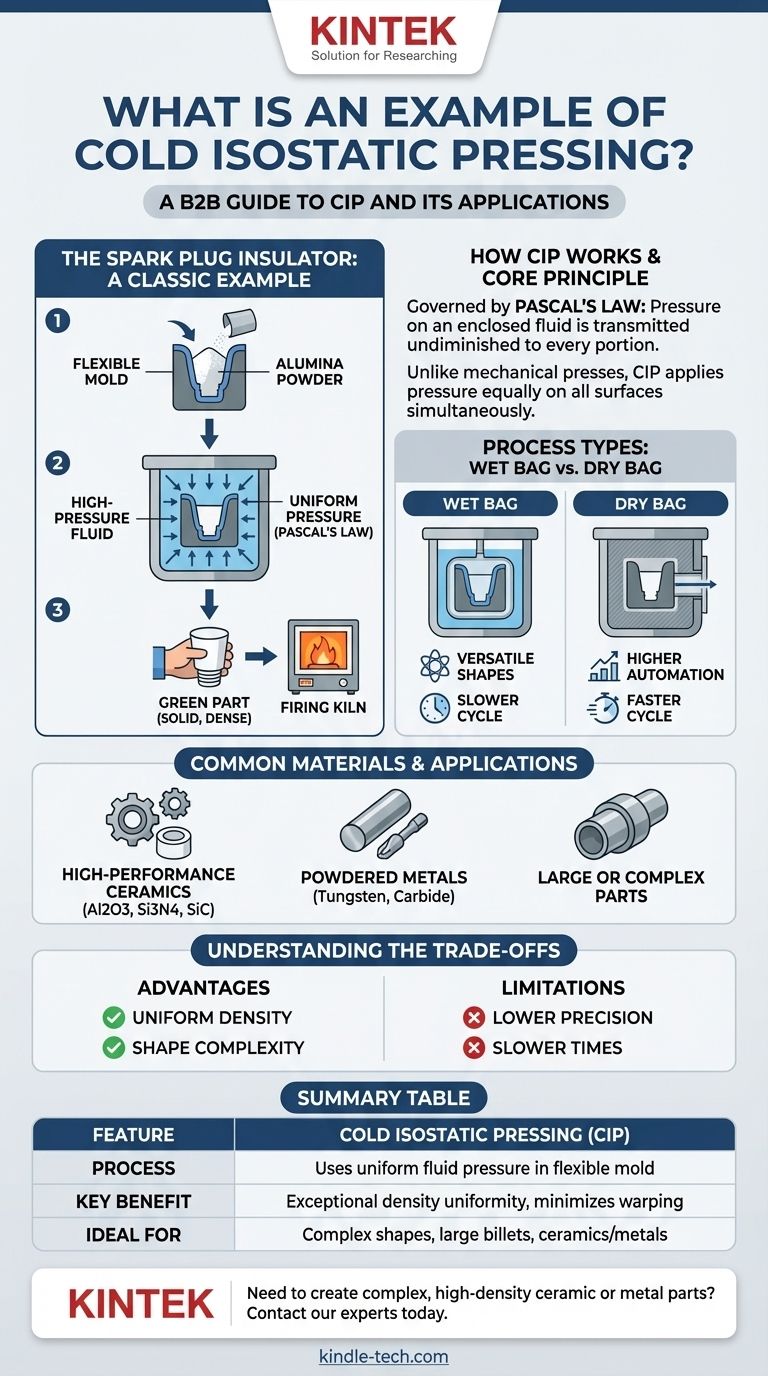
A classic example of cold isostatic pressing (CIP) is the manufacturing of the white ceramic insulator for a spark plug. In this process, fine alumina powder is loaded into a flexible mold, which is then submerged in a high-pressure fluid. This uniform pressure compacts the powder into a dense, solid "green" part that is strong enough to be handled before it undergoes final firing in a kiln.
Cold isostatic pressing is not merely a shaping method; it is a powder consolidation technique. Its primary purpose is to use uniform, fluid-based pressure to create components with exceptionally consistent density, which is critical for the performance and reliability of parts made from ceramic or metal powders.

How Cold Isostatic Pressing Works
Cold isostatic pressing, also known as hydrostatic pressing, is a method for compacting powders into a solid mass before subsequent processing like sintering or machining. It relies on a fundamental principle of physics to achieve its unique results.
The Core Principle: Pascal's Law
The process is governed by Pascal's Law, which states that pressure exerted on an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
Unlike a traditional mechanical press that applies force from one or two directions, CIP surrounds the part with a pressurized liquid. This ensures pressure is applied equally on all surfaces simultaneously.
The "Wet Bag" vs. "Dry Bag" Process
There are two primary methods for performing CIP:
- Wet Bag: The powder-filled, sealed, flexible mold is directly immersed in the pressurizing fluid inside the pressure vessel. This method is highly versatile for various shapes and sizes but is typically slower due to manual loading and unloading.
- Dry Bag: The flexible mold is integrated into the pressure vessel itself. The powder is placed inside this permanent membrane, and the fluid pressurizes the exterior of the membrane. This approach allows for higher automation and faster cycle times.
Why It's Called a "Rubber Press"
The term "rubber press" is sometimes used because the process relies on a flexible, rubber-like mold or bag. This mold is what separates the powder from the pressurizing fluid and translates the hydrostatic pressure into a compacting force on the powder within.
Common Materials and Applications
CIP is chosen when uniform density is more critical than the initial dimensional accuracy of the pressed part. It is particularly effective for materials that are difficult to compact using other methods.
High-Performance Ceramics
This is a primary application area for CIP. Powders like alumina (Al2O3), silicon nitride (Si3N4), and silicon carbide (SiC) are compacted to form high-strength components, turbocharger rotors, and bearing balls.
Powdered Metals and Alloys
CIP is used to form solid billets from powdered metals. Tungsten rods, carbide cutting tools, and high-alloy ferrous billets are often created with CIP. Sometimes, it is an intermediate step before a final hot isostatic pressing (HIP) cycle.
Large or Complex Parts
The process is ideal for parts that are too large or have a geometry too complex for conventional uniaxial die pressing. This includes large tubes, blocks, and specialized industrial tooling components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No manufacturing process is perfect for every scenario. Choosing CIP requires understanding its distinct advantages and limitations.
Advantage: Uniform Density
This is the most significant benefit. By eliminating the friction from die walls found in uniaxial pressing, CIP produces parts with virtually no density variation. This uniformity minimizes warping and cracking during the final sintering (firing) stage.
Advantage: Shape Complexity
Because the pressure is hydrostatic, it can effectively compact complex concave and convex shapes, creating parts that would be impossible to make in a rigid die.
Limitation: Lower Dimensional Precision
The "green" parts produced by CIP do not have the tight dimensional tolerances of parts made in a precision-machined die. The final shape is often achieved through machining the part after it is pressed or, more commonly, after it is sintered.
Limitation: Slower Cycle Times
Compared to the high-speed nature of automated die compaction, CIP—especially the wet bag method—is a more batch-oriented and slower process, making it less suitable for very high-volume production of simple parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct powder consolidation method depends entirely on the material, the complexity of the part, and your production requirements.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum uniform density in a complex ceramic part: CIP is the ideal method for creating a consistent "green" body to ensure strength and prevent failure during sintering.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing very large components from powdered metal: CIP provides a practical way to form large, dense billets that are impossible to create with traditional die compaction.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, high-volume production of simple shapes: A traditional uniaxial press is likely a more cost-effective and faster solution.
Ultimately, understanding CIP allows you to select the right powder consolidation technique to ensure the integrity and performance of your final component.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses uniform fluid pressure to compact powders in a flexible mold |
| Key Benefit | Exceptional density uniformity, minimizing warping/cracking |
| Common Materials | Alumina, silicon nitride, powdered metals (tungsten, carbide) |
| Ideal For | Complex shapes, large billets, high-performance ceramics |
| Limitation | Lower initial dimensional precision vs. die pressing |
Need to create complex, high-density ceramic or metal parts with uniform consistency?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for powder consolidation techniques like cold isostatic pressing. Whether you're developing spark plug insulators, turbocharger rotors, or specialized tooling, our expertise ensures you achieve the material integrity and performance your applications demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your manufacturing process and deliver reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- What is a cold isostatic press? Achieve Uniform Powder Compaction for Complex Parts
- What are the disadvantages of powder metallurgy? Key Limitations in Strength and Size
- What is the difference between sintering and pressing? A Guide to Powder Metallurgy Processes
- How big is the isostatic pressing market? A Deep Dive into the $1.2B+ Advanced Manufacturing Enabler



















