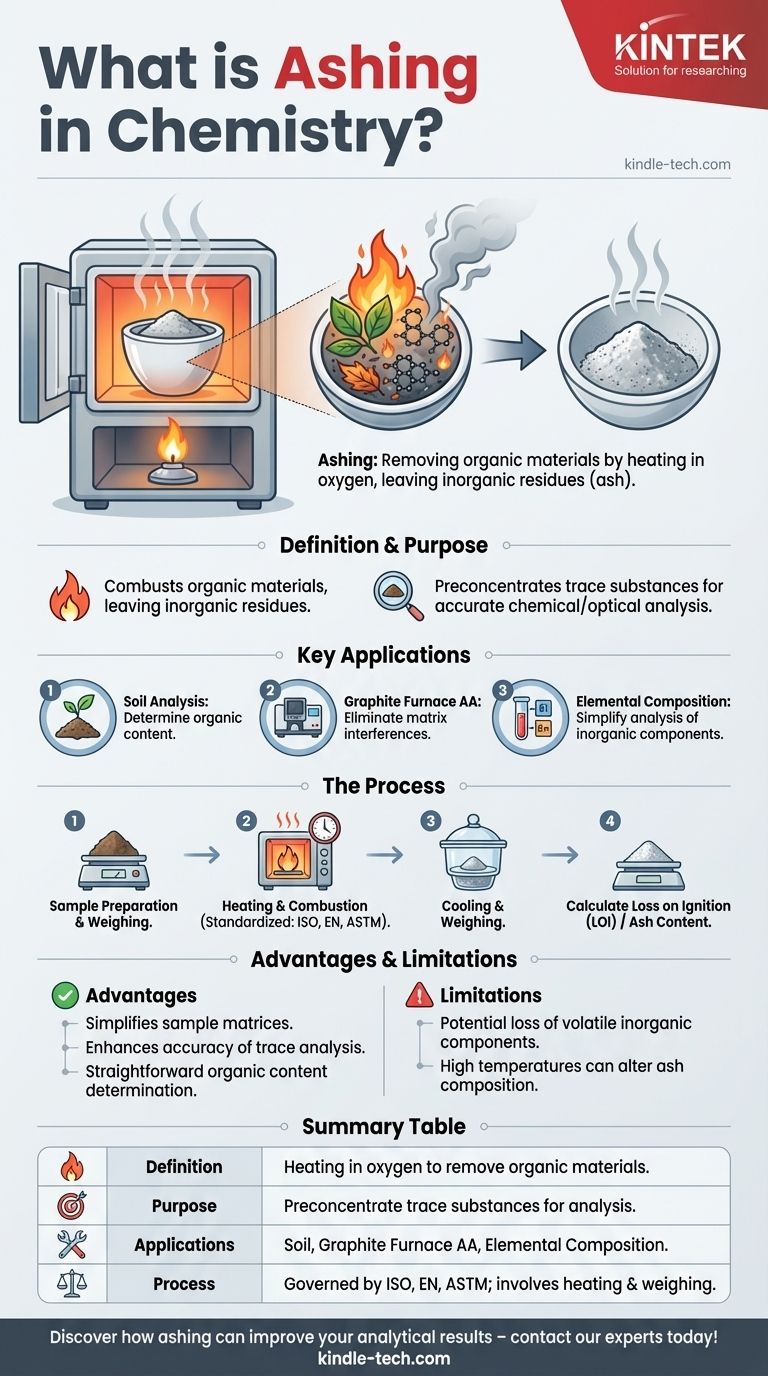
Ashing in chemistry is a process used to remove organic materials from a sample by heating it in the presence of oxygen, leaving behind inorganic, non-combustible residues known as ash. This technique is widely used in analytical chemistry for preconcentration of trace substances, enabling more accurate analysis of inorganic components through methods like chromatography or spectroscopy. Ashing is also employed in soil analysis to determine organic content and in graphite furnace atomic absorption (AA) programs to eliminate matrix interferences. The process is often standardized by international protocols like ISO, EN, or ASTM, with applications including Loss on Ignition (LOI) measurements.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition and Purpose of Ashing:
- Ashing is a mineralization process that involves heating a sample in the presence of oxygen to combust organic materials, leaving behind inorganic residues (ash).
- The primary purpose is to preconcentrate trace substances for subsequent chemical or optical analysis, such as chromatography or spectroscopy.
-
Applications of Ashing:
- Soil Analysis: Ashing is used to determine the organic content of soil by comparing the mass before and after the process.
- Graphite Furnace AA: In atomic absorption spectroscopy, ashing removes matrix constituents that could interfere with the measurement of the analyte.
- Elemental Composition Analysis: By removing organic materials, ashing simplifies the analysis of inorganic components in a sample.
-
Process of Ashing:
- Samples are heated in air until they combust, oxidizing organic compounds and leaving behind non-combustible inorganic residues.
- The process is often governed by international standards (e.g., ISO, EN, ASTM) to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Specific objectives, such as Loss on Ignition (LOI), involve weighing samples before and after ashing to measure mass reduction.
-
Importance in Analytical Chemistry:
- Ashing is a critical step in preparing samples for accurate analysis, particularly when dealing with complex matrices.
- It enhances the sensitivity and precision of analytical techniques by removing interfering substances.
-
Standardization and Protocols:
- The ashing process is often standardized to ensure reproducibility and reliability across different laboratories.
- Protocols may specify temperature, duration, and other parameters to achieve consistent results.
-
Advantages of Ashing:
- Simplifies sample matrices, making it easier to analyze inorganic components.
- Enhances the accuracy of trace element analysis by removing organic interferences.
- Provides a straightforward method for determining organic content in materials like soil.
-
Limitations and Considerations:
- The process may result in the loss of volatile inorganic components if not carefully controlled.
- High temperatures can sometimes alter the composition of the ash, requiring careful calibration and validation of results.
By understanding the principles and applications of ashing, chemists and analysts can effectively use this technique to improve the accuracy and reliability of their analytical results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Heating a sample in oxygen to remove organic materials, leaving inorganic ash. |
| Purpose | Preconcentrate trace substances for accurate chemical or optical analysis. |
| Applications | Soil analysis, graphite furnace AA, elemental composition analysis. |
| Process | Governed by ISO, EN, or ASTM standards; involves heating and weighing samples. |
| Advantages | Simplifies matrices, removes interferences, and determines organic content. |
| Limitations | Potential loss of volatile components; high temperatures may alter ash. |
Discover how ashing can improve your analytical results—contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of a laboratory oven in MnO2-GAC synthesis? Optimize Your Catalyst Preparation
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the importance of precise programmed temperature control in a high-temperature furnace? Master Co-Sintering
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play during the re-austenitization of 17-4 PH? Transform SLM Performance



















