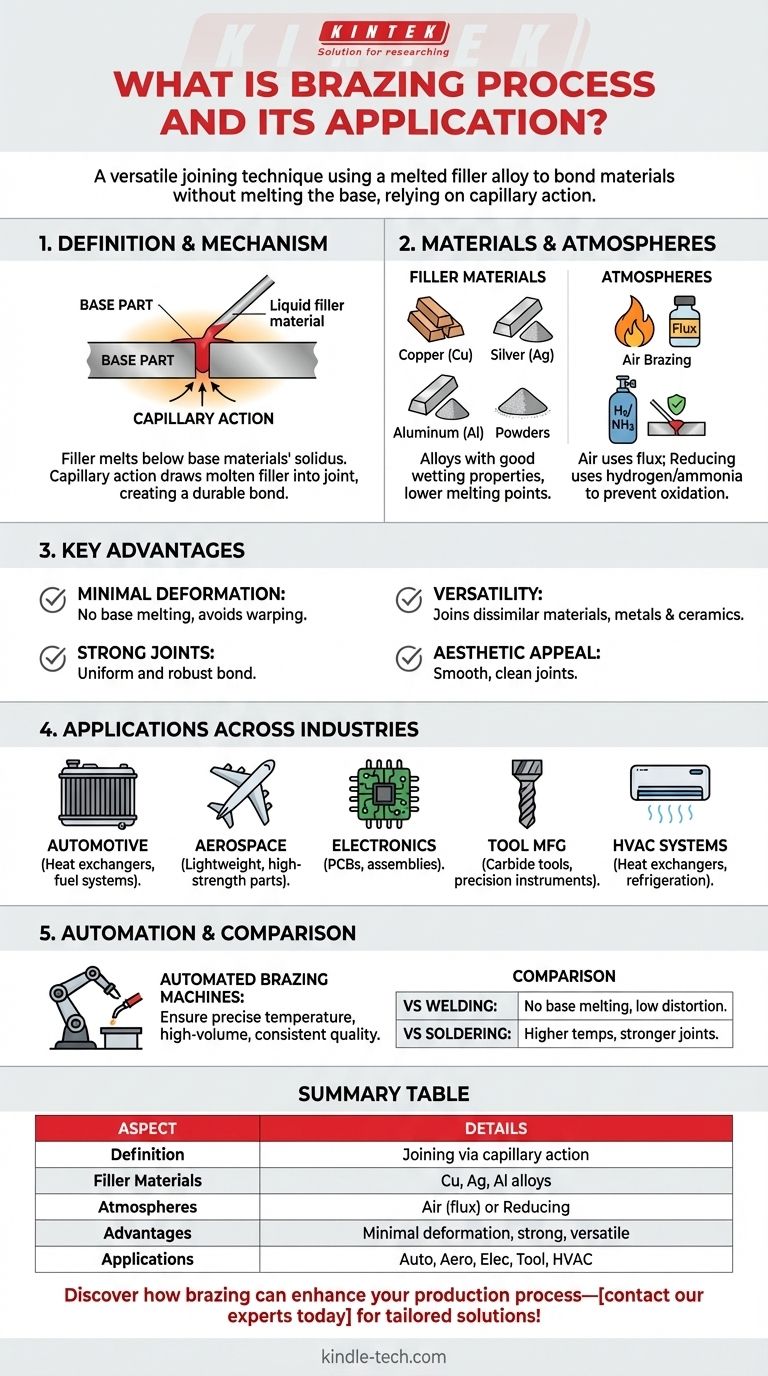
The brazing process is a versatile and widely used joining technique that involves melting a filler material (typically an alloy) to bond two or more metal or ceramic components. Unlike welding, brazing does not melt the base materials, allowing for minimal deformation and strong, aesthetically pleasing joints. The process relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler into the gaps between the parts, creating a durable bond. Brazing is suitable for joining similar or dissimilar materials, including metals and ceramics, and is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and tool manufacturing. It is particularly effective for precision, complex, and multi-material components.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition and Mechanism of Brazing:
- Brazing is a joining process where a filler material, with a lower melting point than the base materials, is melted and flowed into the joint using capillary action.
- The base materials are heated to a temperature above the filler's liquidus but below their solidus, ensuring they remain solid while the filler melts and bonds the parts.
-
Filler Materials:
- The filler material is typically an alloy, such as copper, silver, or aluminum-based alloys, chosen based on the application and the materials being joined.
- The filler must have good wetting properties to ensure proper flow and adhesion to the base materials.
-
Types of Brazing Atmospheres:
- Air Brazing: Conducted in open air with the use of fluxes to prevent oxidation and promote filler flow.
- Reducing Atmosphere Brazing: Often performed in environments like pure hydrogen or dissociated ammonia to minimize oxidation and improve joint quality.
-
Advantages of Brazing:
- Minimal Deformation: Since the base materials do not melt, brazing avoids warping or distortion, making it ideal for precision components.
- Strong Joints: The capillary action ensures a uniform and robust bond.
- Versatility: Suitable for joining dissimilar materials, including metals and ceramics.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Produces smooth, clean joints that are visually appealing.
-
Applications of Brazing:
- Automotive Industry: Used for joining components like radiators, heat exchangers, and fuel systems.
- Aerospace: Ideal for lightweight and high-strength joints in aircraft components.
- Electronics: Commonly used in printed circuit boards and electronic assemblies.
- Tool Manufacturing: Effective for joining carbide tools and other precision instruments.
- HVAC Systems: Used in heat exchangers and refrigeration systems.
-
Automated Brazing Machines:
- Modern brazing processes often utilize automated machines to ensure precise temperature control and consistent results.
- These machines are particularly beneficial for high-volume production and applications requiring repeatable quality.
-
Comparison to Other Joining Methods:
- Brazing vs. Welding: Unlike welding, brazing does not melt the base materials, reducing the risk of distortion and enabling the joining of dissimilar materials.
- Brazing vs. Soldering: Brazing typically uses higher temperatures and stronger filler materials than soldering, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
-
Process Considerations:
- Joint Design: Proper joint design is critical to ensure capillary action and strong bonding.
- Surface Preparation: Surfaces must be clean and free of contaminants to achieve optimal adhesion.
- Temperature Control: Precise heating is essential to melt the filler without damaging the base materials.
By understanding these key points, a purchaser of equipment or consumables for brazing can make informed decisions about the materials, processes, and machinery required for their specific applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Joining process using a filler material melted via capillary action. |
| Filler Materials | Copper, silver, or aluminum-based alloys with good wetting properties. |
| Atmosphere Types | Air brazing (with fluxes) or reducing atmosphere (e.g., hydrogen). |
| Advantages | Minimal deformation, strong joints, versatility, and aesthetic appeal. |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, electronics, tool manufacturing, HVAC systems. |
| Automation | Automated machines ensure precise temperature control and consistent results. |
| Comparison | Differs from welding (no base material melting) and soldering (higher temps). |
Discover how brazing can enhance your production process—contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds



















