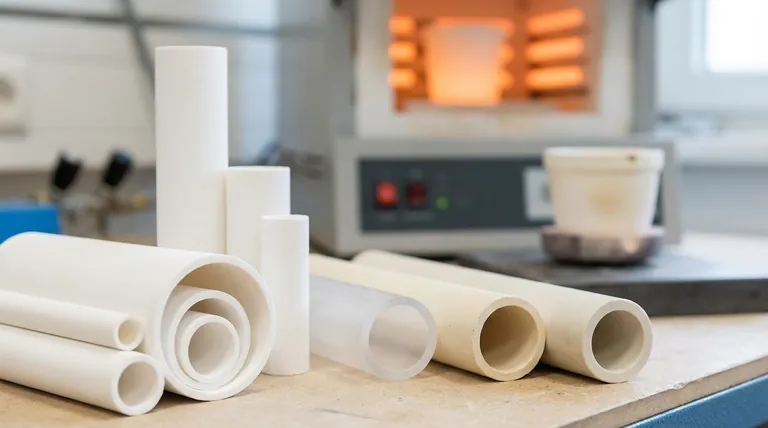
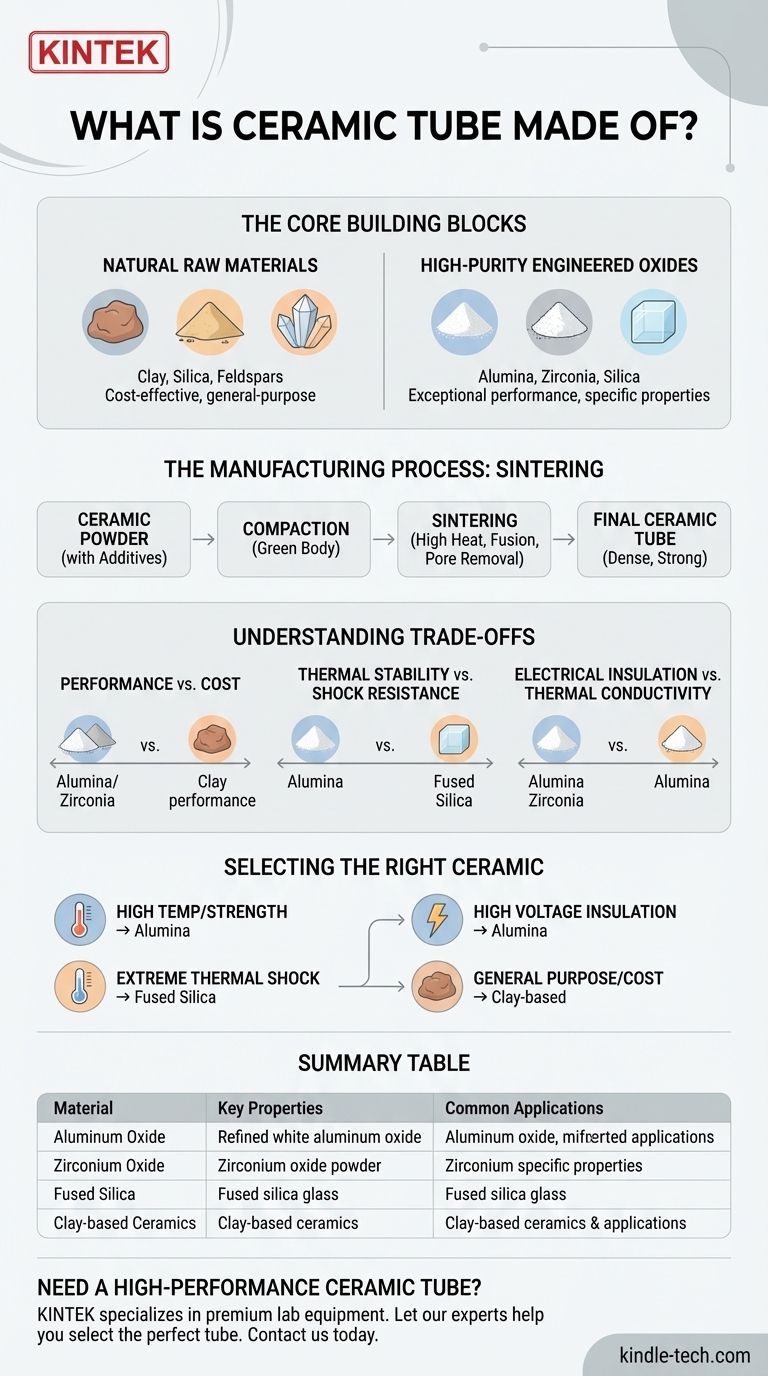
At their core, ceramic tubes are made from inorganic, non-metallic materials, primarily natural minerals like clay and silica, or highly refined synthetic powders like aluminum oxide and zirconium oxide. These raw materials are formed into the desired tube shape and then fired at extremely high temperatures in a process called sintering, which fuses the particles together to create a hard, dense, and durable final product.
The specific material used to create a ceramic tube is not arbitrary; it is carefully selected to achieve a desired performance characteristic. The choice is always a balance between the application's demands—such as heat resistance, electrical insulation, or chemical inertness—and the overall cost.

The Core Building Blocks: From Clay to Pure Oxides
The term "ceramic" covers a wide range of materials. They can be broadly categorized into two groups: those derived from natural, mixed minerals and those engineered from high-purity synthetic compounds.
Natural Raw Materials
For many general-purpose applications, ceramic tubes are made from naturally occurring minerals. These are often cost-effective and provide excellent all-around properties.
The most common materials in this group include clay, silica (from quartz or sand), and feldspars. These materials are blended, mixed with water, formed, and fired to create a strong ceramic body.
High-Purity Engineered Oxides
When an application demands exceptional performance, manufacturers turn to refined, man-made powders. These are typically metal oxides with very few impurities.
Aluminum Oxide (Alumina) is the most common high-performance ceramic. It is prized for its excellent high-temperature stability, high dielectric strength (electrical insulation), and resistance to wear and chemical attack.
Zirconium Oxide (Zirconia) is another advanced ceramic, known for its exceptional toughness, high-temperature stability, and low thermal conductivity.
Silicon Dioxide (Silica), in its pure, fused form, is used for applications requiring extreme thermal shock resistance and a very low coefficient of thermal expansion.
The Manufacturing Process: Turning Powder into a Solid
The properties of a ceramic tube are defined not just by its chemical composition but also by how it is manufactured. The key step is sintering.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal treatment process. A fine ceramic powder is first compacted into the desired tube shape and then heated to a high temperature, but one that is below its melting point.
At this temperature, the individual particles of the powder begin to fuse, bonding together at their contact points. This process eliminates the pores between particles, resulting in a dense, solid, and mechanically strong object.
The Role of Additives
During manufacturing, other materials are often added to the primary ceramic powder to aid in the process.
Organic additives, such as binders, are used to hold the powder together in its "green" or unfired state, making it easier to form. These additives burn out completely during the high-temperature firing.
Other inorganic materials, like lime or iron oxide, may be added in small amounts to modify the sintering temperature or to impart specific final properties, such as color.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Material Choice Matters
Selecting the correct ceramic material is a critical engineering decision driven by a series of trade-offs. The ideal material for a furnace liner is likely different from one used for an electrical standoff.
Performance vs. Cost
This is the most fundamental trade-off. Natural, clay-based ceramics are significantly less expensive than high-purity, engineered oxides like Zirconia. The added cost of an engineered ceramic is only justified when its superior performance—such as higher operating temperature or greater strength—is a strict requirement.
Thermal Stability and Shock Resistance
All ceramics perform well at high temperatures, but they differ in their ability to handle rapid temperature changes (thermal shock). Materials like Fused Silica are exceptional in this regard, while some high-purity Alumina grades can be more sensitive to sudden heating or cooling.
Electrical Insulation vs. Thermal Conductivity
Most ceramics are excellent electrical insulators. However, some materials, like Alumina, combine high electrical resistivity with reasonably good thermal conductivity, making them ideal for dissipating heat from electronic components. Others, like Zirconia, are thermal insulators, which is ideal for containing heat within a furnace.
Selecting the Right Ceramic for Your Application
Understanding the base materials and their properties allows you to choose the right tube for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature furnace or kiln components: Choose a high-purity Aluminum Oxide (Alumina) tube for its excellent thermal stability and strength.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation in a high-voltage environment: A high-purity Alumina is an outstanding choice due to its high dielectric strength.
- If your primary focus is extreme thermal shock resistance: A Fused Quartz or Fused Silica tube is the best option for its near-zero thermal expansion.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose or cost-sensitive project: A mullite or other clay-based ceramic tube will provide a reliable, economical solution.
By understanding that a ceramic tube's composition directly dictates its function, you can confidently select the precise material to ensure your project's success.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide (Alumina) | High thermal stability, excellent electrical insulation, wear-resistant | High-temperature furnace tubes, electrical insulators |
| Zirconium Oxide (Zirconia) | Exceptional toughness, low thermal conductivity | High-stress environments, thermal barriers |
| Fused Silica | Extreme thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion | Applications with rapid temperature changes |
| Clay-based Ceramics | Cost-effective, good general properties | General-purpose, economical projects |
Need a high-performance ceramic tube for your lab? The right material is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including ceramic tubes made from Alumina, Zirconia, and more, tailored to your specific needs for high-temperature stability, electrical insulation, or chemical resistance.
Let our experts help you select the perfect tube for your application.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- High Temperature Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Protective Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the material used in high temperature furnace? Selecting the Right Ceramic for Extreme Heat
- What is the role of corundum tubes in oxygen permeation testing? Ensure Integrity for Bi-doped Membranes
- What is the heating rate for alumina tubes? A Variable Schedule to Prevent Thermal Shock
- What is the primary function of an Alumina (Al2O3) tube in LLZTO sintering? Optimize Your Thermal Processing



















