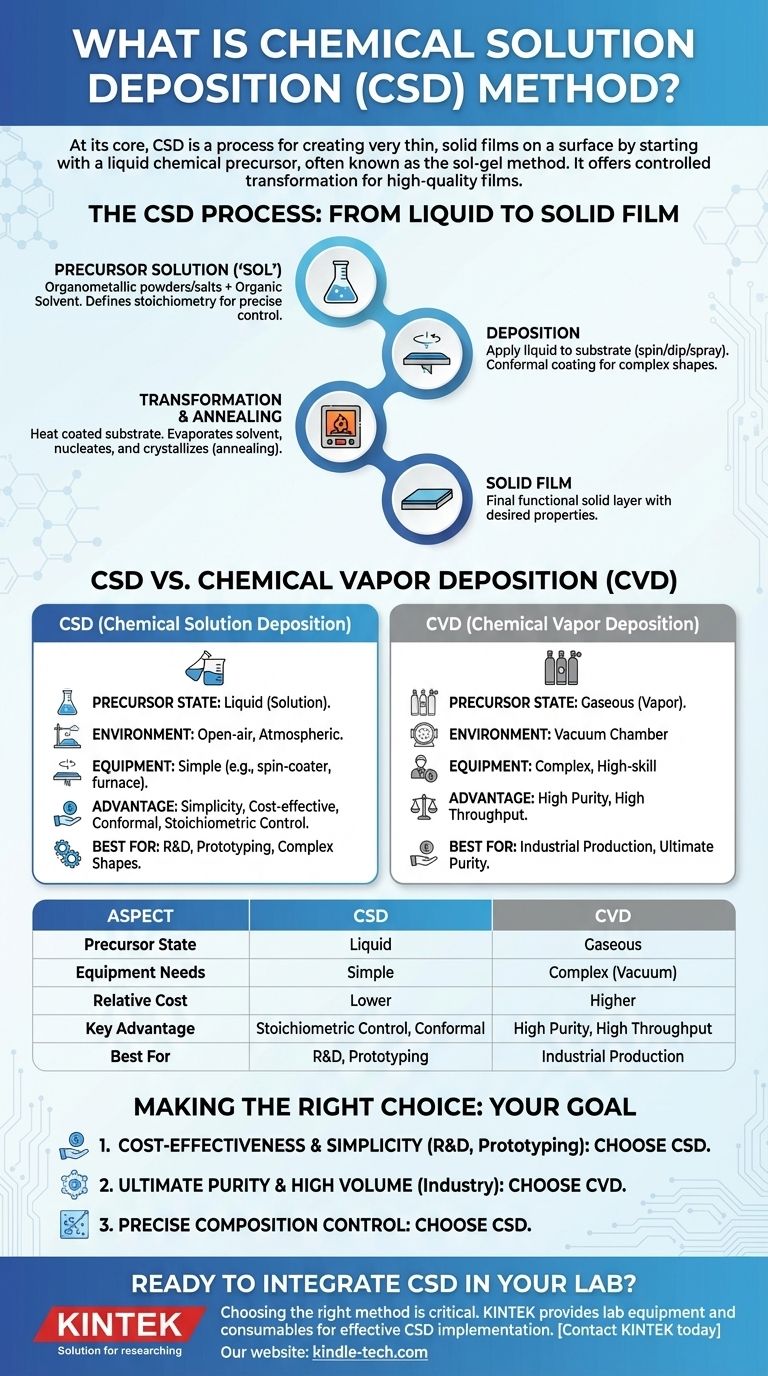
At its core, Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) is a process for creating very thin, solid films on a surface by starting with a liquid chemical precursor. This method involves applying the liquid solution onto a substrate and then using a chemical or thermal process to transform it into the desired solid material. CSD is often referred to by one of its most common variations: the sol-gel method.
The central principle of CSD is the controlled transformation of a specially designed liquid solution into a high-quality solid film. It stands out as a simpler, more accessible, and often less expensive alternative to complex, vacuum-based deposition techniques.
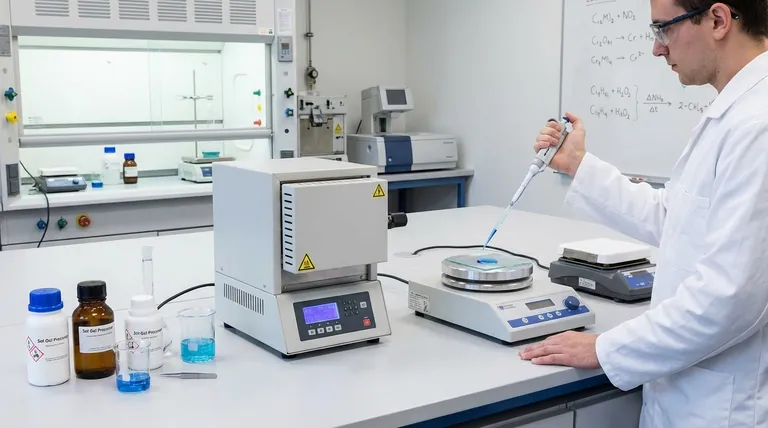

How CSD Works: From Liquid to Solid Film
The elegance of CSD lies in its straightforward, multi-step process that moves from a liquid state to a final, functional solid layer.
The Precursor Solution (The "Sol")
The process begins with a chemical "cocktail" called a precursor solution, or "sol." This is typically made by dissolving organometallic powders or salts into an organic solvent.
The composition of this liquid is critical, as it directly dictates the exact atomic ratio, or stoichiometry, of the final solid film. This gives scientists precise control over the material's properties.
The Deposition Step
Once the solution is prepared, it is applied to a substrate—the base material being coated. This can be done using various simple techniques like spin-coating, dip-coating, or spraying.
The goal of this step is to cover the substrate with a uniform, thin layer of the liquid precursor. The "conformal" nature of liquids allows CSD to easily coat complex or irregular shapes.
The Transformation and Annealing
After deposition, the coated substrate is heated. This serves two purposes: first, it evaporates the solvent, and second, it initiates a chemical reaction.
During this transformation, nucleation (the formation of tiny initial crystal seeds) and subsequent crystal growth occur. This converts the liquid layer into a solid film, often an amorphous or gel-like state. A final, higher-temperature heating step, known as annealing, is typically used to crystallize the film and achieve the desired final properties.
CSD vs. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A Key Distinction
CSD is often compared to Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), but they operate on fundamentally different principles.
State of the Precursor
The most significant difference is the state of the starting material. CSD uses a liquid precursor, whereas CVD uses a gaseous precursor.
Process Environment and Complexity
CSD can often be performed in an open-air, atmospheric environment with relatively simple equipment like a spin-coater and a furnace.
CVD, in contrast, requires a sophisticated vacuum chamber to contain the reactive gases and is a more complex, high-skill process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technical process, CSD has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for specific applications.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit of CSD is its simplicity and low cost. It does not require expensive vacuum systems, making it highly accessible for research and development.
It also offers excellent control over chemical stoichiometry and can easily coat large or non-flat surfaces with a uniform, conformal film.
Potential Limitations
The quality of a CSD film is highly dependent on the purity of the precursor chemicals and the precise control of the heating and annealing stages.
Solvents or chemical residues can sometimes remain as impurities in the final film if not burned off correctly. The process can also be slower for creating very thick films compared to some other methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on your project's priorities, budget, and desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and process simplicity: CSD is an outstanding choice, especially for lab-scale research, prototyping, and coating complex shapes.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and high-volume industrial throughput: CVD is often the preferred method, despite its higher equipment cost and complexity.
- If your primary focus is precise control over material composition: CSD provides exceptional stoichiometric control directly from the initial liquid solution.
Ultimately, understanding the trade-off between CSD's liquid-phase simplicity and other methods' unique capabilities is key to achieving your material engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor State | Liquid (Solution) | Gaseous (Vapor) |
| Equipment Needs | Simple (e.g., spin-coater, furnace) | Complex (Vacuum chamber required) |
| Relative Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Key Advantage | Excellent stoichiometric control, conformal coating | High purity, high throughput |
| Best For | R&D, prototyping, complex shapes | Industrial production, ultimate purity |
Ready to Integrate CSD into Your Lab Workflow?
Choosing the right deposition method is critical for your research and development success. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need to implement Chemical Solution Deposition techniques effectively.
Whether you're setting up a new lab or optimizing an existing process, our expertise can help you achieve precise, cost-effective thin film coatings.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your material engineering projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Variable Speed Peristaltic Pump
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure in the CVD process? Mastering Control for Superior Film Quality
- What is vacuum deposition method? A Guide to High-Performance Surface Coatings
- Which method is used to deposit insulating thin films? Choose the Right Technique for Your Application
- What is the process gas for sputtering? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition with the Right Gas
- What are the methods of CVD deposition? Choosing the Right Energy Source for Your Thin Film
- What role does a vacuum Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system play in the production of large-area graphene films?
- How does DC sputtering work? A Guide to Conductive Thin-Film Deposition
- What is a major disadvantage of the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process? Overcoming Safety and Thermal Challenges


















