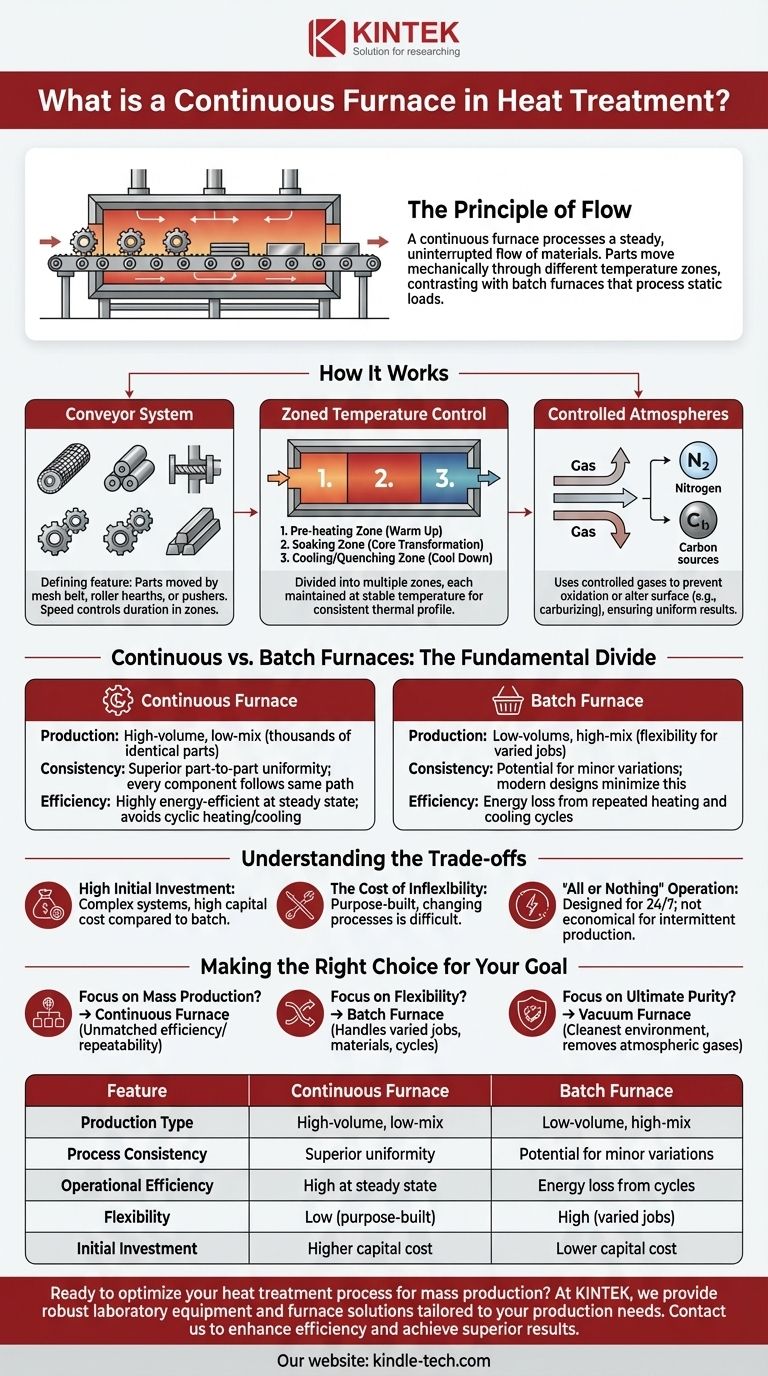
In heat treatment, a continuous furnace is an industrial system designed to process a steady, uninterrupted flow of materials. Parts are moved mechanically through different chambers set at specific temperatures, allowing for a consistent and high-volume production cycle. This stands in direct contrast to a batch furnace, which processes a single, static load of material at a time.
The core distinction is not about temperature or atmosphere, but about production philosophy. Continuous furnaces are built for mass production and consistency, while batch furnaces are built for flexibility and varied workloads.

How Continuous Furnaces Work: The Principle of Flow
A continuous furnace operates like an assembly line for heat treatment. Instead of placing parts in a box that gets heated and cooled, the parts themselves move through different environments.
The Conveyor System
The defining feature of a continuous furnace is its material handling system. Parts are transported through the furnace on a conveyor.
Common types include mesh belt conveyors for smaller, lightweight parts, roller hearths for heavier plates or bars, or pusher mechanisms that push trays of parts through the furnace. The speed of this conveyor is precisely controlled to determine how long parts spend in each zone.
Zoned Temperature Control
A continuous furnace is not one single temperature. It is divided into multiple distinct zones, each maintained at a stable temperature.
A typical sequence includes a pre-heating zone, a soaking zone where the core metallurgical transformation occurs, and a cooling or quenching zone. This design ensures every part experiences the exact same thermal profile, leading to exceptional process consistency.
Controlled Atmospheres
Like other advanced furnaces, continuous systems use controlled atmospheres to protect or intentionally alter the surface of the material.
Gases like nitrogen prevent oxidation, while reactive gases are used for processes like carburizing, where carbon is diffused into the steel's surface. The key advantage here is that the atmosphere in each zone can be held constant, ensuring uniform results across thousands of parts.
Continuous vs. Batch Furnaces: The Fundamental Divide
Choosing between a continuous and a batch furnace is a strategic decision based on production volume, part variety, and operational goals.
Production Volume and Part Mix
Continuous furnaces are the clear choice for high-volume, low-mix production. They are ideal for manufacturing thousands of identical fasteners, bearings, or stampings per hour.
Batch furnaces excel in low-volume, high-mix environments. A commercial heat treater, for example, uses batch furnaces to handle different jobs from various clients, each with unique specifications.
Process Consistency
Continuous furnaces offer superior part-to-part consistency. Since every component follows the same path at the same speed, thermal variations are virtually eliminated.
In a batch furnace, there can be minor temperature differences between parts in the center of the load versus those on the outside, though modern designs minimize this.
Operational Efficiency
Once at a steady state, a continuous furnace is highly energy-efficient. It remains at a constant temperature, avoiding the energy loss from repeated heating and cooling cycles inherent to batch processing.
However, bringing a large continuous furnace up to temperature from a cold start is a slow and energy-intensive process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the continuous furnace model is not universally applicable. Its efficiency comes with significant constraints.
The High Initial Investment
Continuous furnaces are complex systems with integrated conveyors and multi-zone controls. This results in a much higher capital cost compared to a simpler batch furnace of similar capacity.
The Cost of Inflexibility
These furnaces are often purpose-built for a specific thermal process and part size. Changing the process—for example, from annealing to hardening—can require significant downtime and re-engineering, if it's possible at all.
"All or Nothing" Operation
Continuous furnaces are designed for 24/7 operation to maintain thermal stability and justify their cost. They are not economical for intermittent production schedules or single-shift operations due to the high energy cost of startup and shutdown.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace technology is about aligning your equipment with your operational and business strategy.
- If your primary focus is mass production of identical parts: A continuous furnace offers unmatched efficiency and repeatability for high-volume manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for varied jobs: A batch furnace provides the agility to handle different part geometries, materials, and heat treatment cycles with minimal changeover time.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity for critical components: A vacuum furnace, which is a type of batch furnace, provides the cleanest environment by removing atmospheric gases entirely.
Understanding this fundamental distinction between continuous flow and static batch processing is the key to optimizing your heat treatment operations.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Continuous Furnace | Batch Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Production Type | High-volume, low-mix | Low-volume, high-mix |
| Process Consistency | Superior part-to-part uniformity | Potential for minor variations |
| Operational Efficiency | High efficiency at steady state | Energy loss from heating/cooling cycles |
| Flexibility | Low (purpose-built) | High (handles varied jobs) |
| Initial Investment | Higher capital cost | Lower capital cost |
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process for mass production?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment, including advanced furnace solutions tailored to your production needs. Whether you require the high-volume consistency of a continuous furnace or the flexibility of a batch system, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your specific application.
Let our specialists help you enhance your operational efficiency and achieve superior metallurgical results. Contact us today to discuss your heat treatment requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















