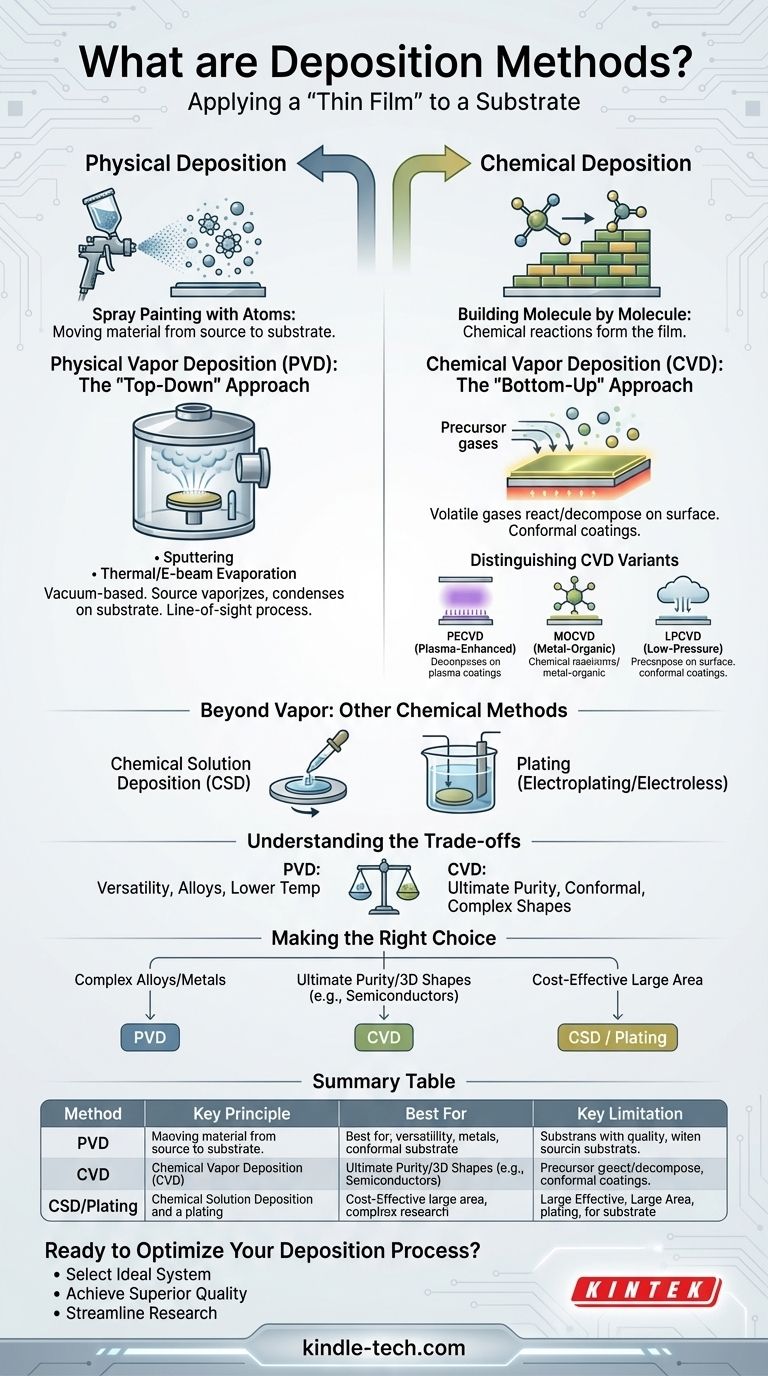
At its core, deposition is the process of applying a thin layer of material—a "thin film"—onto a surface, known as a substrate. These methods are broadly classified into two primary categories: Physical Deposition, where a material is physically moved from a source to the substrate, and Chemical Deposition, where chemical reactions are used to form the film on the substrate's surface.
The choice between deposition methods is not about which is "better," but which is appropriate for the task. Physical methods are like spray painting with atoms, offering versatility, while chemical methods are like building the film molecule by molecule, offering unparalleled purity and precision.
The Two Pillars of Deposition: Physical vs. Chemical
The fundamental distinction between deposition techniques lies in how the film material arrives and forms on the substrate. This difference dictates the properties of the final film, the equipment required, and the types of materials you can deposit.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): The "Top-Down" Approach
Physical Vapor Deposition encompasses a set of vacuum-based techniques where a solid or liquid source material is vaporized and then transported to the substrate, where it condenses to form the thin film.
Think of it as creating a fine mist of atoms or molecules inside a vacuum chamber that evenly coats any surface in its path. Because it is a physical line-of-sight process, there are no chemical changes to the source material itself.
Common PVD methods include sputtering, thermal evaporation, and e-beam evaporation.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The "Bottom-Up" Approach
Chemical Vapor Deposition uses volatile precursor gases that react or decompose on the substrate's surface to create the desired film. The film is literally built from the atoms supplied by these gases.
This is more akin to building a crystalline structure brick by brick. Because the film is formed by a chemical reaction at the surface, CVD can produce highly uniform (conformal) coatings that cover even complex, three-dimensional shapes without gaps.
This high precision is why CVD is a dominant method in the semiconductor industry.
Distinguishing Key CVD Variants
The basic CVD process has been adapted for different needs, leading to several variants:
- Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): Uses a plasma to energize the precursor gases, allowing deposition to occur at much lower temperatures. This is critical for temperature-sensitive substrates.
- Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD): Employs metal-organic compounds as precursors, which is essential for manufacturing complex compound semiconductors used in LEDs and lasers.
- Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD): Operating at reduced pressure improves film uniformity and reduces unwanted gas-phase reactions, leading to higher-purity films.
Beyond Vapor: Exploring Other Chemical Methods
While PVD and CVD are the main vapor-based techniques, the "Chemical Deposition" category is broader. It also includes methods that use liquid precursors instead of gases.
Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD)
CSD involves applying a liquid precursor solution (often a "sol-gel") to a substrate, typically through spinning, dipping, or spraying. The substrate is then heated to evaporate the solvent and initiate chemical reactions that form the final solid film.
Plating (Electroplating and Electroless)
Plating is a long-established chemical method where a substrate is submerged in a chemical bath. An electrical current (electroplating) or an autocatalytic chemical reaction (electroless plating) causes dissolved metal ions to deposit onto the substrate's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right deposition method requires balancing the need for film quality, material compatibility, and cost.
When to Choose PVD
PVD excels at depositing materials that are difficult or impossible to create with chemical precursors, such as specific metal alloys or compounds. The processes can often be run at lower temperatures than traditional CVD, and the equipment can be highly versatile. However, its line-of-sight nature can make it difficult to uniformly coat complex shapes.
When to Choose CVD
CVD is the clear choice when the highest purity and conformality are required. Its ability to perfectly coat intricate topographies makes it indispensable for manufacturing integrated circuits. The main drawbacks are the high process temperatures (for some variants) and the cost and potential hazards of the precursor gases.
The Niche for Liquid Methods
CSD and plating offer a significant advantage in cost and simplicity, as they do not require expensive high-vacuum systems. They are excellent for coating large areas or when the absolute highest purity is not the primary concern. Film quality and uniformity, however, may not match what is achievable with vapor-based methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision will be guided by the specific requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is versatility and depositing complex alloys or elemental metals: PVD is often the most direct and effective method.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and uniform coverage on complex 3D shapes (like in semiconductors): CVD provides unparalleled precision and conformity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating on a large scale without vacuum requirements: Chemical solution methods like plating or CSD are strong contenders.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the deposition technique that aligns perfectly with your material, substrate, and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Principle | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Physical transfer of material in a vacuum | Versatility, complex alloys, lower temperatures | Line-of-sight coating, uneven complex shapes |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Chemical reaction on substrate surface | Ultimate purity, conformal 3D coatings (e.g., semiconductors) | High temperatures, costly precursor gases |
| Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) / Plating | Liquid precursor application or chemical bath | Cost-effective large-area coating, no vacuum needed | Lower film uniformity and purity vs. vapor methods |
Ready to Optimize Your Deposition Process?
Choosing the right deposition method is critical for achieving the perfect thin film for your application. Whether you need the versatility of PVD, the precision of CVD, or the cost-effectiveness of solution methods, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your lab's unique needs.
Let KINTEK help you:
- Select the ideal deposition system for your materials and substrates
- Achieve superior film quality with our advanced lab equipment
- Streamline your research or production with reliable, high-performance solutions
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our deposition solutions can enhance your work. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a plasma furnace? Unlocking Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- What is the role of a laboratory constant temperature drying oven in anaerobic digestion? Precision TS Analysis
- What is an example of a continuous furnace? Discover the Conveyor Belt Furnace for High-Volume Production
- What are the advantages of reactive sputtering? Achieve Precise Control Over Compound Thin Films
- What are the conditions for fast pyrolysis? Achieve Maximum Bio-Oil Yield from Biomass
- What are the basics of thin films? Master the Technology Behind Modern Electronics and Coatings
- What are the different types of melting process? From Smelting to Suspension for Ultimate Purity
- What is the controversy with carbon nanotubes? The Asbestos-Like Health Risks Explained



















