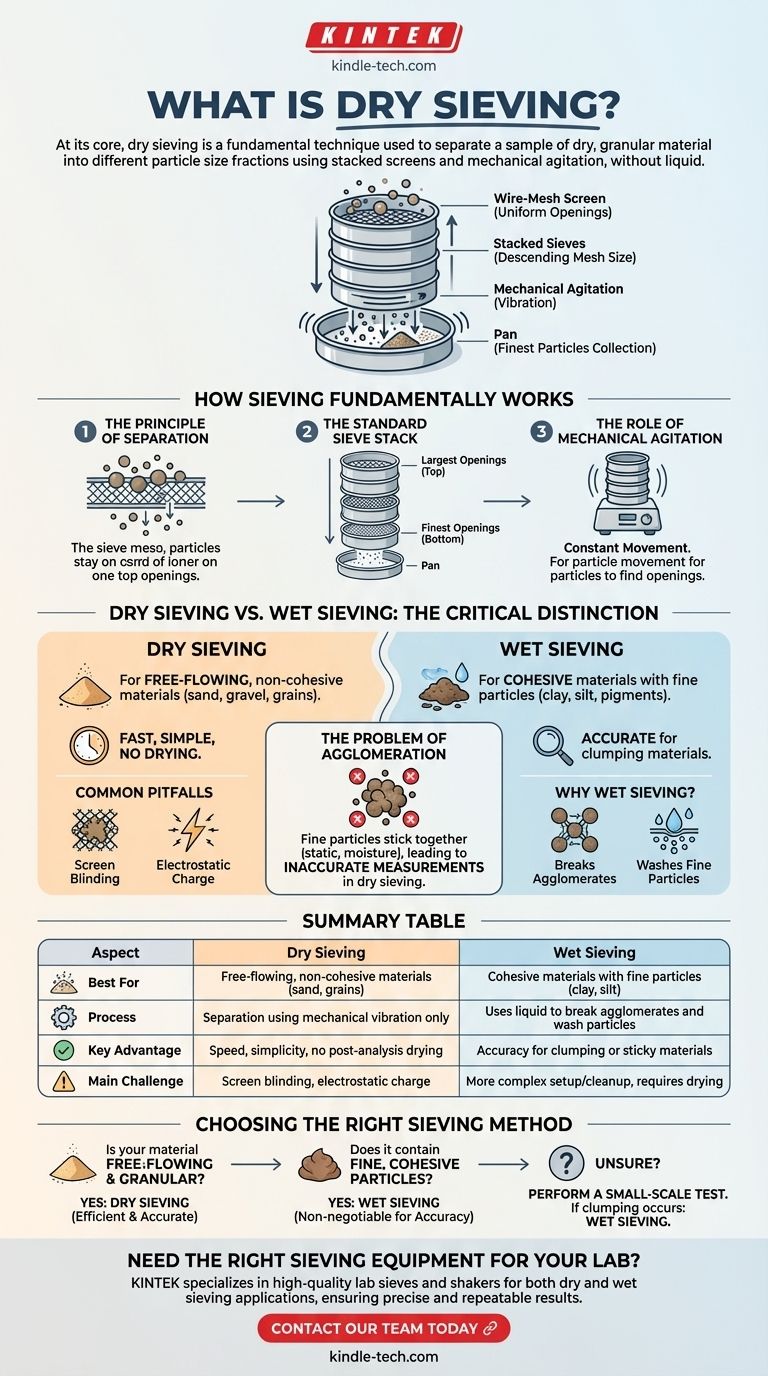
At its core, dry sieving is a fundamental technique used to separate a sample of dry, granular material into different particle size fractions. The process involves passing the material through a series of stacked screens, or sieves, each with a specific mesh size, using mechanical shaking or vibration to facilitate the separation without the use of any liquid.
The choice between dry and wet sieving is not a matter of preference, but a necessary decision dictated by the physical properties of your material. The goal is to ensure particles can move freely and be separated accurately, and the primary obstacle is whether those particles tend to stick together.
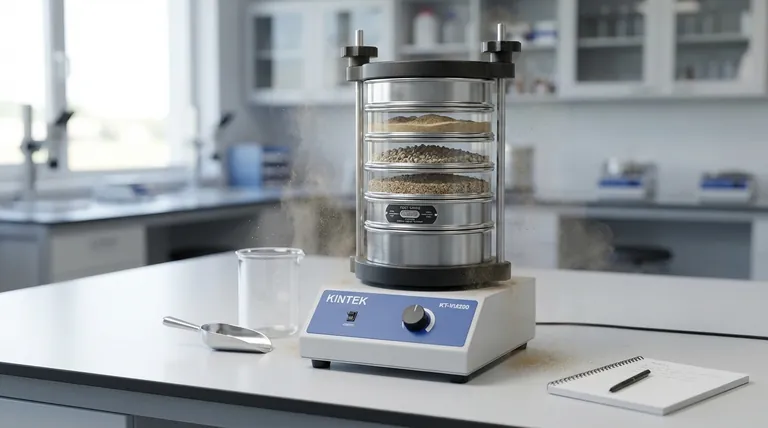

How Sieving Fundamentally Works
Sieving is one of the oldest and most common methods of particle size analysis. The principles are straightforward but crucial for achieving reliable results.
The Principle of Separation
The process relies on a wire-mesh screen with precisely measured uniform openings. When a sample is placed on the sieve, particles smaller than the openings pass through, while larger particles are retained on the mesh surface.
The Standard Sieve Stack
For a detailed analysis, multiple sieves are stacked in a column. The sieve with the largest mesh openings is placed at the top, and the mesh size progressively decreases in each subsequent sieve down the stack. A solid pan is placed at the very bottom to collect the finest particles.
The Role of Mechanical Agitation
Simply placing a sample on a sieve is not enough. The stack is placed in a mechanical shaker that vibrates or taps the sieves. This agitation ensures particles are constantly moving, giving each one an opportunity to find an opening and pass to the next level.
Dry Sieving vs. Wet Sieving: The Critical Distinction
Understanding when to use a liquid—and when not to—is the key to accurate particle analysis.
What is Dry Sieving?
Dry sieving is the default method for materials that are free-flowing and do not clump together. This includes materials like dry sand, gravel, grains, and many non-cohesive powders. The entire process is performed on a dry sample, making it fast and relatively simple.
When Wet Sieving Becomes Necessary
According to the reference materials, wet wash sieving is required when a liquid, typically water, is needed to help particles pass through the screen. This is essential for materials where very fine particles, like clay and silt, adhere to larger particles.
The liquid serves two purposes: it breaks the bonds holding the particles together (agglomerates) and helps wash the now-separated fine particles through the mesh.
The Problem of Agglomeration
Fine particles can stick to each other and to larger particles due to forces like static electricity or moisture content. If you attempt to dry sieve such a material, these clumps will behave like larger individual particles, leading to a highly inaccurate measurement. They will be retained on a sieve with larger openings, skewing the results to show a coarser distribution than reality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each method has clear advantages and is suited for different situations. Choosing the wrong one compromises your results.
The Simplicity of Dry Sieving
Dry sieving is generally faster, requires less setup, and has a simpler cleanup. Crucially, the sample does not need to be dried after the analysis, which saves significant time and energy, preventing a major bottleneck in the workflow.
The Accuracy of Wet Sieving
For materials prone to clumping, dry sieving is not a valid option. Wet sieving is the only way to ensure that fine particles are properly separated and measured. While it adds steps like washing, liquid handling, and post-analysis drying, this complexity is necessary for accurate and repeatable results.
Common Pitfalls in Dry Sieving
Even with suitable materials, issues can arise. Screen blinding occurs when particles of a certain size become lodged in the mesh openings, blocking other particles from passing through. Additionally, very fine, dry powders can develop electrostatic charges during shaking, causing them to cling to the sieve frames and distort the final weight measurements.
Choosing the Right Sieving Method
Your decision must be based on a clear understanding of your material's physical behavior.
- If your material is free-flowing and granular (like sand, grain, or plastic pellets): Dry sieving is the most efficient and direct method for accurate analysis.
- If your material contains fine, cohesive particles (like soil with clay, aggregates with silt, or certain powdered pigments): Wet sieving is non-negotiable to break up agglomerates and achieve a true particle size distribution.
- If you are unsure about your material's properties: Perform a small-scale test. If you observe clumping or a significant amount of dust that clings to surfaces, wet sieving is the safer and more reliable choice.
Ultimately, matching the sieving method to the material's properties is the only way to ensure your particle size data is reliable and truly representative.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Dry Sieving | Wet Sieving |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Free-flowing, non-cohesive materials (sand, grains) | Cohesive materials with fine particles (clay, silt) |
| Process | Separation using mechanical vibration only | Uses liquid to break agglomerates and wash particles |
| Key Advantage | Speed, simplicity, no post-analysis drying | Accuracy for clumping or sticky materials |
| Main Challenge | Screen blinding, electrostatic charge | More complex setup and cleanup, requires drying |
Need the Right Sieving Equipment for Your Lab?
Accurate particle size analysis starts with reliable equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and shakers designed for both dry and wet sieving applications, ensuring precise and repeatable results for materials like soils, aggregates, powders, and grains.
Let our experts help you select the perfect sieving solution for your specific needs. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What is the operating procedure of a sieve shaker? Master Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- Which Cannot be separated by sieving? Understanding the Limits of Particle Size Separation
- What is the maximum sieving deviation permitted? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Precision Limits
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of sieve analysis? A Guide to Cost-Effective Particle Sizing



















