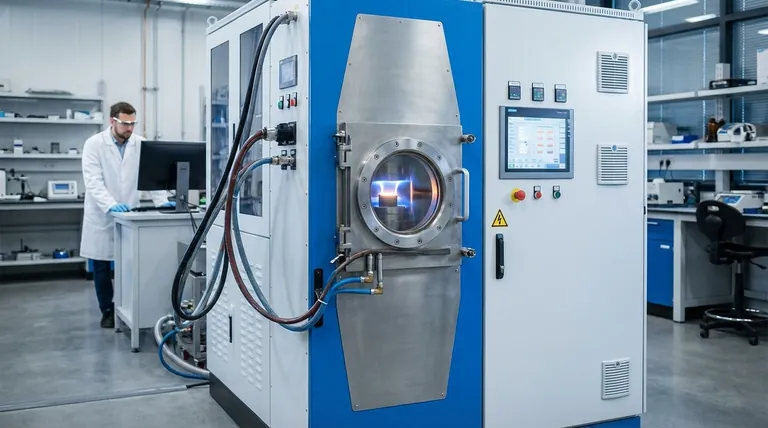
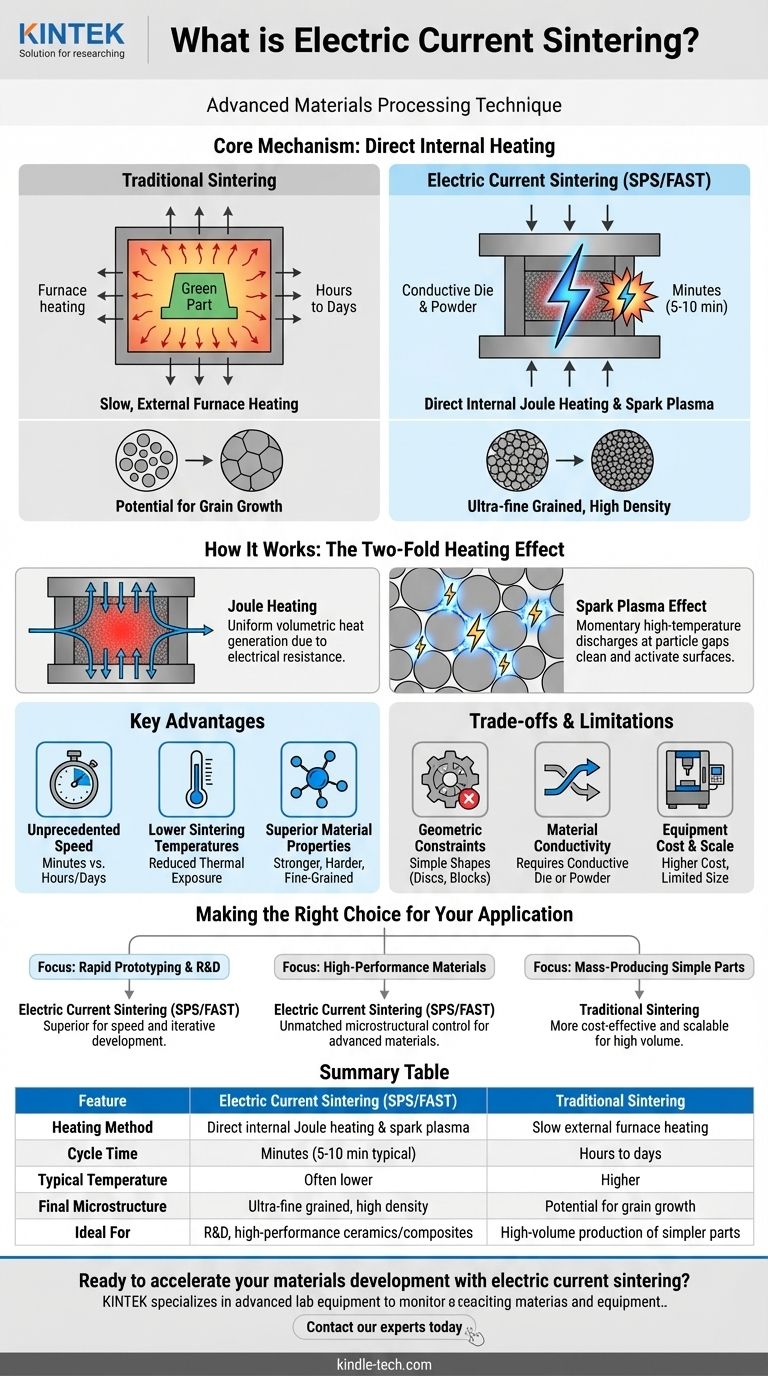
Electric current sintering is an advanced materials processing technique that uses a high-amperage, low-voltage electrical current passed directly through a powder compact to heat and consolidate it. Unlike traditional sintering, which relies on slow, external heating in a furnace, this method generates heat internally and instantaneously. This direct heating mechanism, combined with applied pressure, enables materials to be densified into a solid state with unprecedented speed.
The core innovation of electric current sintering is its heating method. By using electricity as a direct and internal heat source, it dramatically shortens processing times from hours to minutes, often resulting in materials with superior density and finer microstructures compared to those made by conventional methods.

From Traditional Furnaces to Direct Current
To understand the value of electric current sintering, it's essential to first understand the conventional process it improves upon.
The Conventional Sintering Process
Traditional sintering involves placing a loosely compacted powder part, known as a "green part," into a high-temperature furnace.
Heat is slowly transferred from the furnace atmosphere to the part. Over a long period—often many hours or even days—the particles heat up and fuse together at their contact points, gradually eliminating the porous spaces between them.
The Limitation: Time and Energy
This conventional method is effective but slow and energy-intensive. The long exposure to high temperatures can also lead to undesirable grain growth, where smaller grains merge into larger ones, which can degrade the final material's mechanical properties.
How Electric Current Sintering Works: The Core Mechanism
Electric current sintering, most commonly known as Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) or Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST), fundamentally changes the heating dynamic.
The Setup: A Conductive Die
The powdered material is loaded into a conductive die, typically made of graphite. This entire assembly is placed between two electrodes within a press. Mechanical pressure is applied to the powder throughout the process.
The Key Step: Applying Pulsed Current
Instead of an external furnace, a powerful pulsed direct current (DC) is passed through the electrodes and into the conductive die and the powder itself. This creates intense, rapid heating through two primary effects.
Effect 1: Joule Heating
As the current flows through the die and powder, their natural electrical resistance generates uniform, volumetric heat. This is the same principle (Joule heating) that makes an electric stove burner glow red.
Effect 2: The "Spark Plasma" Effect
On a microscopic level, the pulsed current creates momentary high-temperature spark discharges in the gaps between powder particles. This generates a localized plasma that cleans and activates the particle surfaces, stripping away contaminants and promoting atomic diffusion for exceptionally efficient bonding.
Key Advantages of Electric Current Sintering
The unique heating mechanism of SPS/FAST delivers several transformative benefits over traditional methods.
Unprecedented Speed
Sintering cycles that take 8-24 hours in a conventional furnace can be completed in 5-10 minutes. This massive increase in throughput is critical for research and development as well as specialized production.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
Because the heating is so efficient and localized at the particle surfaces, the required overall temperature to achieve full density is often lower than in traditional sintering.
Superior Material Properties
The combination of rapid heating and lower temperatures suppresses grain growth. This allows for the creation of ultra-fine-grained, fully dense materials that are stronger, harder, and more durable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Despite its advantages, electric current sintering is not a universal solution. It comes with specific constraints that must be considered.
Geometric Constraints
The process requires a rigid die, which typically limits the final part geometry to simple shapes like discs, cylinders, and blocks. Producing complex, three-dimensional parts is very difficult.
Material Conductivity
For the process to work most efficiently, either the powder material or the die must be electrically conductive. While non-conductive materials like some ceramics can be sintered by letting the conductive die heat them, it is less efficient than direct heating of the powder.
Equipment Cost and Scale
SPS machines are complex and significantly more expensive than conventional furnaces. They are also generally limited in size, making them ideal for high-value, smaller components rather than large-scale bulk production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct sintering method depends entirely on your project's goals, materials, and economic constraints.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or materials research: Electric current sintering is the superior choice for its speed, allowing for dozens of experimental iterations in the time it takes for one conventional run.
- If your primary focus is producing high-performance, fine-grained materials: The microstructural control offered by SPS is unmatched, making it ideal for creating advanced ceramics, composites, and alloys with optimal properties.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing simple, low-cost metal parts: Traditional powder metallurgy (press-and-sinter) remains more cost-effective and scalable for high-volume manufacturing where peak performance is not the only consideration.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of electric current sintering empowers you to select the most effective tool for creating advanced materials with precisely tailored properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Current Sintering (SPS/FAST) | Traditional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct internal Joule heating & spark plasma | Slow external furnace heating |
| Cycle Time | Minutes (5-10 min typical) | Hours to days |
| Typical Temperature | Often lower | Higher |
| Final Microstructure | Ultra-fine grained, high density | Potential for grain growth |
| Ideal For | R&D, high-performance ceramics/composites, rapid prototyping | High-volume production of simpler parts |
Ready to accelerate your materials development with electric current sintering?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including sintering solutions for research and high-performance material production. Our expertise can help you achieve faster cycle times and superior material properties for your advanced ceramics, composites, and alloys.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our sintering technology can benefit your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum hot pressing furnace precision influence SiC/Ti composites? Master Interface Quality for Peak Strength
- What critical processing conditions does a vacuum hot-pressing furnace provide? Master Graphite & Copper Manufacturing
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace contribute to high-density Cr-50 wt% Si alloys? Achieve Superior Densification
- How temperature control affects Ti-Al composites? Master Vacuum Hot Pressing for Superior Microstructures
- How do graphite molds and flexible graphite paper function in ZrB2–SiC–TaC sintering? Optimize Your Hot-Pressing Process
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace facilitate nanocrystalline structures? Enhance Fe–Cu–Ni–Sn–VN Composite Hardness
- What does a vacuum press do? Achieve Perfect, Uniform Clamping for Laminates & Composites
- Why is it essential to maintain a high vacuum state during hot press sintering? Optimize SiCp/2024Al Quality



















