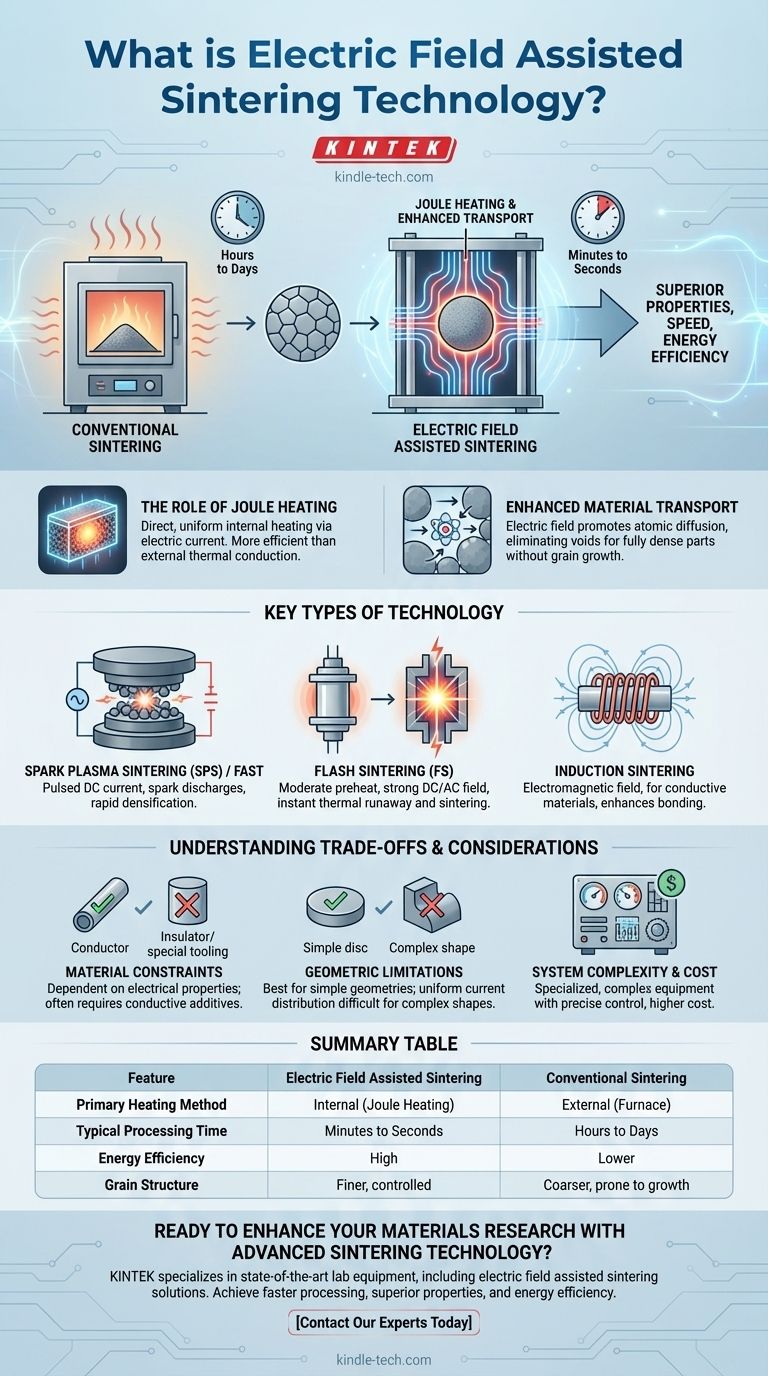
At its core, electric field assisted sintering is a category of advanced manufacturing processes that uses an electric current or field to dramatically accelerate the consolidation of powdered materials into a dense, solid object. Unlike traditional methods that rely solely on external heat over long periods, these techniques apply electrical energy directly to the material, enabling sintering at lower temperatures and in a fraction of the time. Key examples of this technology include Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) and Flash Sintering (FS).
The fundamental advantage of electric field assisted sintering is its ability to achieve superior material properties—such as higher density and finer grain structures—with remarkable speed and energy efficiency compared to conventional furnace-based methods.

The Core Principle: Why Use an Electric Field?
Traditional sintering is akin to baking in a conventional oven; heat slowly soaks in from the outside. Electric field assisted techniques are more like using a microwave or induction cooktop, delivering energy directly and rapidly where it's needed most.
The Role of Joule Heating
The primary mechanism in many of these techniques is Joule heating. When an electric current is passed through the powdered material (and the surrounding mold), its electrical resistance causes it to heat up internally and uniformly.
This direct, internal heating is far more efficient than relying on slow thermal conduction and radiation from external heating elements in a traditional furnace.
Enhanced Material Transport
Beyond simple heating, the electric field also promotes the movement of atoms between the powder particles. This enhanced atomic diffusion is critical for eliminating the voids between particles and achieving a fully dense final part, often without the undesirable grain growth seen in high-temperature conventional sintering.
Key Types of Electric Field Assisted Sintering
While they share a common principle, different techniques apply the electric field in unique ways to achieve specific outcomes.
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) / Field Assisted Sintering (FAST)
SPS, also known as FAST, is the most established of these technologies. It works by sending a pulsed Direct Current (DC) through a graphite die containing the powder compact.
This process is believed to generate spark discharges or plasma in the gaps between powder particles, which cleans the particle surfaces and activates them for bonding. The combination of intense Joule heating and plasma effects results in extremely rapid densification.
Flash Sintering (FS)
Flash Sintering is a newer, even faster technique. A component is first heated to a moderate temperature in a furnace, after which a strong DC or AC electric field is applied.
This triggers a phenomenon known as thermal runaway, where the material's electrical conductivity rapidly increases, causing a sudden, intense burst of sintering that can fully densify a ceramic part in mere seconds.
Induction Sintering
Though sometimes categorized separately, induction sintering also uses an electromagnetic field. It is primarily used for metallic and conductive materials, where it enhances the bonding of solid particles and compresses voids to achieve high density.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, these technologies are not a universal replacement for all sintering applications. Objectivity requires acknowledging their specific limitations.
Material Constraints
The effectiveness of these techniques is highly dependent on the electrical properties of the material being processed. They are most directly applicable to conductive and semi-conductive materials. Sintering electrical insulators often requires specialized tooling or conductive additives.
Geometric and Scale Limitations
Most commercial SPS/FAST systems are best suited for producing relatively simple geometries, such as discs and blocks. Complex, three-dimensional shapes can be challenging to process due to difficulties in achieving a uniform current distribution.
System Complexity and Cost
The equipment required for electric field assisted sintering is more complex and expensive than a conventional furnace. It demands precise control over electrical parameters, pressure, and atmosphere, requiring specialized operator knowledge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate sintering method depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material or component.
- If your primary focus is developing novel, high-performance materials: Electric field assisted sintering is ideal, as it preserves the fine-grained microstructures essential for superior mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is speed and energy efficiency for suitable materials: Techniques like SPS/FAST offer a dramatic reduction in processing time and energy consumption compared to conventional methods.
- If your primary focus is densifying materials that are difficult to sinter conventionally: The combination of heat, pressure, and electrical effects can consolidate powders that would otherwise require extreme temperatures and pressures.
Ultimately, these techniques offer engineers and scientists an unparalleled level of control over the material consolidation process, opening the door to a new generation of advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Field Assisted Sintering | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Heating Method | Internal (Joule Heating) | External (Furnace) |
| Typical Processing Time | Minutes to Seconds | Hours to Days |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Lower |
| Grain Structure | Finer, controlled | Coarser, prone to growth |
Ready to enhance your materials research with advanced sintering technology? KINTEK specializes in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment, including solutions for electric field assisted sintering. Our expertise can help you achieve faster processing times, superior material properties, and greater energy efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in material development and consolidation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why evacuate and backfill argon for Al-Cu hot pressing? Secure Strong, Oxide-Free Diffusion Bonds
- What is the primary function of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Expert Guide for Ti-22Al-25Nb Fabrication
- What is hot isostatic pressing of castings? Eliminate Internal Porosity for Superior Performance
- What are the benefits of using a Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) furnace compared to cold pressing? Boost LLTO Density
- What is a SPS machine? A Guide to Rapid, High-Performance Material Fabrication
- What is the application of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Integrity for High-Performance Parts
- What are the advantages of using vacuum hot pressing for SiC/Al composites? Achieve Superior Microstructural Control
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) contribute to the densification of LLZA solid-state electrolytes?



















