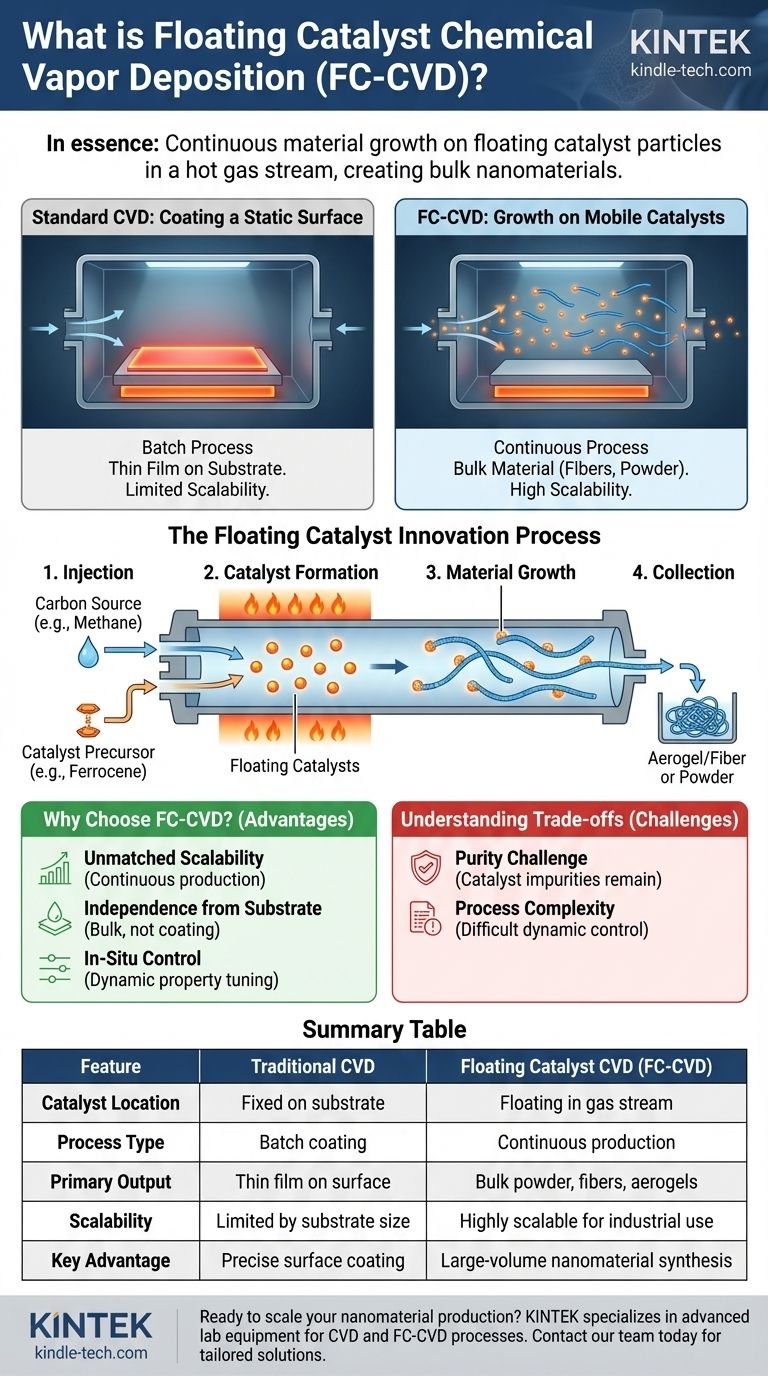
In essence, floating catalyst chemical vapor deposition (FC-CVD) is a specialized manufacturing technique where the material growth occurs on tiny catalyst particles that are actively floating within a hot gas stream. Unlike traditional chemical vapor deposition (CVD) which coats a stationary object, FC-CVD creates the material—most notably carbon nanotubes—within the reaction chamber itself, allowing it to be continuously produced and collected.
The critical distinction of FC-CVD is its method of growth. Instead of depositing a film onto a fixed surface, it uses mobile, gas-phase catalysts to enable continuous, large-scale synthesis of nanomaterials, transforming it from a coating process into a bulk production method.

Understanding the Foundation: Standard CVD
To grasp the innovation of the floating catalyst method, we must first understand the fundamentals of conventional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The Core Principle
Standard CVD is a process used to apply a thin, solid film onto the surface of a substrate or part. It involves placing the part inside a reaction chamber, which is typically under vacuum.
A volatile chemical gas, known as a precursor, is then introduced into the chamber. When heated, this precursor undergoes a chemical reaction or decomposition.
The result of this reaction is a solid material that deposits evenly onto the surface of the part, gradually building a thin and uniform coating.
The Key Components
A traditional CVD system relies on a static relationship between three key elements:
- The Substrate: The stationary workpiece or material being coated.
- The Precursor: The gas that will decompose to form the coating.
- The Heat: The energy source that drives the chemical reaction on the substrate's surface.
The "Floating Catalyst" Innovation
FC-CVD fundamentally changes the relationship between these components by mobilizing the site of material growth.
What is a Catalyst in CVD?
In many CVD reactions, especially for growing materials like carbon nanotubes, a catalyst is required. This is a substance (often a metal like iron, cobalt, or nickel) that enables the precursor gas to efficiently break down and reform into the desired structure.
In traditional CVD, this catalyst is first deposited as a thin layer onto the fixed substrate. Growth only occurs where the catalyst is present on that surface.
From a Fixed to a Floating Catalyst
The "floating catalyst" method eliminates the need for a pre-coated substrate. Instead, the catalyst is introduced directly into the gas stream along with the precursor.
This is typically done by adding a catalyst-containing compound (like ferrocene for an iron catalyst) to the mix of gases entering the hot reactor.
High temperatures cause this compound to decompose, forming nanometer-sized metallic particles. These particles are the "floating catalysts" that are carried along by the gas flow.
The Step-by-Step FC-CVD Process
- A carbon source (like methane or ethanol) and a catalyst precursor (like ferrocene) are injected into a high-temperature tube furnace.
- The heat causes the catalyst precursor to decompose, forming metallic nanoparticles that float in the gas.
- Simultaneously, the carbon source gas decomposes on the surface of these floating nanoparticles.
- The desired material—such as carbon nanotubes—grows directly from these mobile catalyst particles within the gas phase.
- This continuous stream of newly formed material is carried downstream by the gas flow and collected, often as a powder, a tangled "aerogel," or by being spun directly into a fiber or sheet.
Why Choose Floating Catalyst CVD?
FC-CVD is not just a minor variation; it provides distinct advantages that make it the preferred method for certain applications.
Unmatched Scalability
Because the process is continuous rather than batch-based, FC-CVD is exceptionally well-suited for industrial-scale production. Material can be generated constantly as long as precursors are supplied, a feat impossible with substrate-limited methods.
Independence from a Substrate
Growth occurs in the gas phase, not on a surface. This frees the process from the size and geometry limitations of a substrate. The final product is a bulk material, not a surface coating, which opens up entirely new applications like high-strength fibers and conductive films.
In-Situ Control Over Material Properties
By carefully tuning the temperature, gas flow rates, and precursor concentrations, operators can influence the properties of the nanomaterial as it forms. This allows for dynamic control over factors like nanotube diameter or purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its power, FC-CVD introduces its own set of challenges that are critical to understand.
The Challenge of Purity
Since the material grows on catalyst particles, those same particles often become incorporated into the final product as an impurity. Post-processing purification steps are almost always required to remove this residual catalyst, adding cost and complexity.
Process Complexity
Controlling a dynamic, three-dimensional reaction in a flowing gas is inherently more complex than managing a static reaction on a two-dimensional surface. Achieving consistent results requires precise control over numerous interacting variables.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous production of nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes: FC-CVD is often the superior industrial method due to its scalability and bulk output.
- If your primary focus is depositing a precise, uniform thin film onto a specific component (e.g., a silicon wafer): Traditional, substrate-based CVD is the appropriate and more direct choice.
- If your primary focus is research-level synthesis with high control over placement and structure on a surface: Substrate-based methods are generally easier to manage, characterize, and iterate upon.
Ultimately, FC-CVD transforms material synthesis from a surface-coating process into a continuous manufacturing stream for advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional CVD | Floating Catalyst CVD (FC-CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst Location | Fixed on substrate | Floating in gas stream |
| Process Type | Batch coating | Continuous production |
| Primary Output | Thin film on surface | Bulk powder, fibers, aerogels |
| Scalability | Limited by substrate size | Highly scalable for industrial use |
| Key Advantage | Precise surface coating | Large-volume nanomaterial synthesis |
Ready to scale your nanomaterial production? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge research and industrial applications. Whether you're developing carbon nanotube fibers or exploring bulk synthesis methods, our expertise and reliable solutions can accelerate your progress. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs with precision equipment tailored for CVD and FC-CVD processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs



















