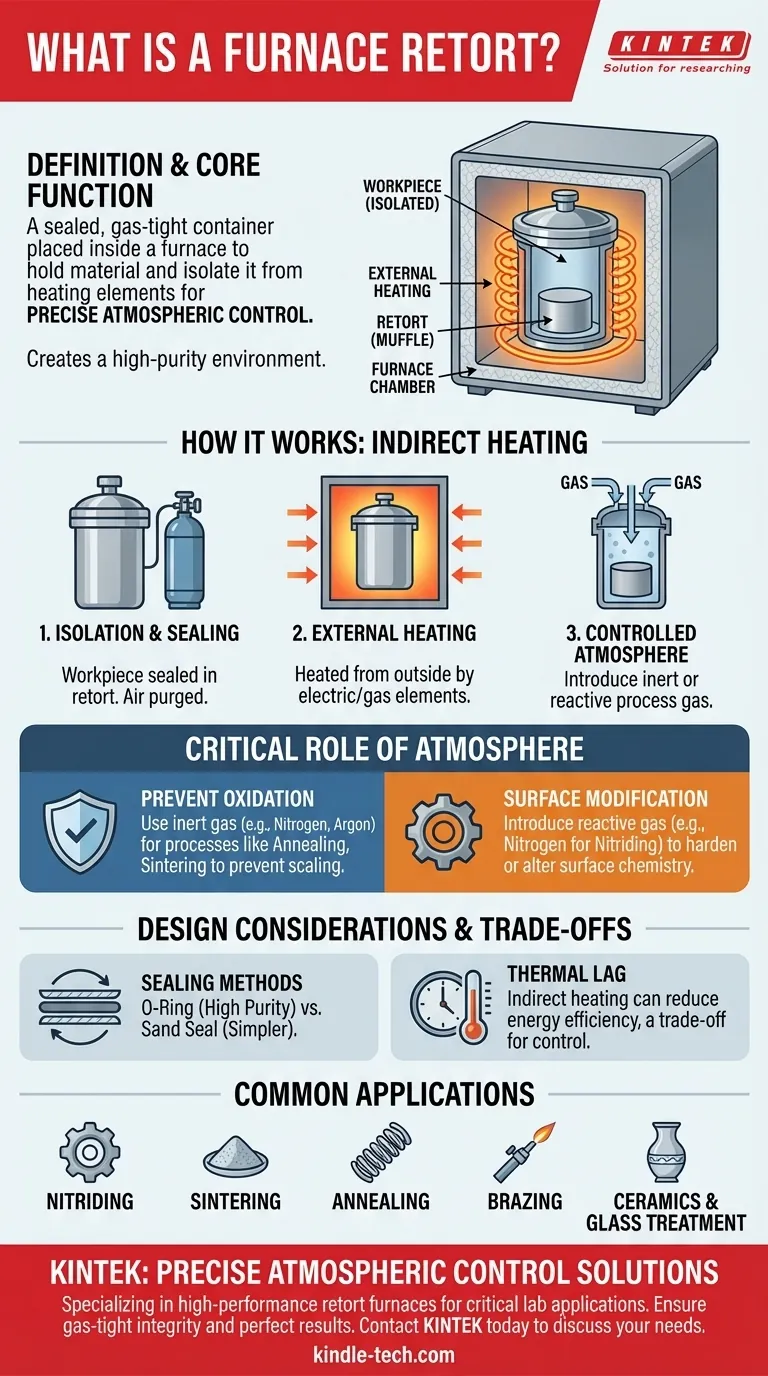
In the context of industrial heat treatment, a furnace retort is a sealed, gas-tight container placed inside a furnace. Its purpose is to hold the material being processed and isolate it from the furnace's heating elements and the external atmosphere. This separation allows for precise control over the atmospheric conditions during the thermal process.
The primary function of a retort is not just to hold material, but to create a high-purity, controlled atmosphere. This isolation is critical for sensitive heat treatment processes where exposure to oxygen or other reactive gases would compromise the integrity and properties of the final product.

How a Retort Furnace Works
A retort furnace operates on a simple but effective principle: indirect heating within a controlled environment. The retort is the central component that makes this possible.
The Core Principle: Isolation
The workpiece is placed inside the retort, which is then sealed to be airtight. The entire retort is then heated externally within the main furnace chamber.
This design creates a distinct inner atmosphere within the retort, separate from the atmosphere of the furnace itself. This inner chamber is often called a muffle.
External Heating
The furnace heats the retort from the outside. This is typically accomplished using either electric resistance heaters or gas burners.
Because the heating elements are outside the retort, byproducts of combustion (in a gas furnace) or contaminants from the elements cannot affect the workpiece.
High-Temperature Construction
Retorts are constructed from materials designed to withstand extreme thermal stress without degrading.
They are typically made from high-temperature resistant steel or specialized nickel-based alloys that maintain their structural integrity and gas-tight properties at elevated temperatures.
The Critical Role of the Atmosphere
The ability to control the atmosphere is the main reason to use a retort furnace. This control enables processes that would otherwise be impossible in a standard furnace.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many heat treatment processes, such as annealing or sintering, require an environment free of oxygen to prevent scaling and oxidation on the material's surface. A retort can be purged of air and filled with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon to create this protective atmosphere.
Introducing a Process Gas
For other processes, the goal is to introduce a specific, reactive gas to chemically alter the surface of the workpiece.
A prime example is nitriding, where nitrogen-rich gas is introduced into the retort to harden the surface of a steel part. The retort contains the process gas and ensures it interacts uniformly with the material.
Understanding the Design and Trade-offs
Retort furnaces come in different configurations, and the choice of design involves specific trade-offs related to process purity and complexity.
Sealing Methods
The method used to seal the retort is critical for atmospheric purity.
A silicone O-ring gasket secured with clamps provides the highest level of gas tightness and is preferred for processes requiring maximum atmospheric purity.
A simpler method is a sand seal, where the retort's lid sits in a trough filled with sand. This is easier to implement but offers a lower degree of sealing performance.
Furnace Orientation
Retort furnaces can be built as horizontal or vertical units. The choice depends on the parts being processed, the factory footprint, and how the material is loaded and unloaded.
Thermal Lag
A key trade-off is thermal efficiency. Because the heat must first transfer through the retort wall to reach the workpiece, these furnaces can have a greater thermal lag and may be less energy-efficient than direct-fired furnaces. However, this is a necessary compromise for achieving atmospheric control.
Common Applications of Retort Furnaces
The versatility of retort furnaces allows them to be used across a wide range of industries and materials.
For Metal Treatment
This is the most common application. Key processes include:
- Nitriding: Surface hardening with nitrogen.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered metals together.
- Tempering & Annealing: Softening metals and relieving internal stresses.
- Soldering & Brazing: Joining metals in a clean, controlled environment.
For Other Industrial Processes
Retort furnaces are also used for processing non-metallic materials, including:
- Shale oil extraction and charcoal development.
- Heat treatment of glass and ceramic components.
- Annealing soft iron shot for use in hunting munitions.
Is a Retort Furnace Right for Your Process?
Choosing the correct furnace type depends entirely on the requirements of your specific thermal process.
- If your primary focus is surface chemistry modification: A retort furnace is essential for processes like nitriding or carburizing where a specific reactive atmosphere is required.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation at high temperatures: A retort provides the necessary inert or vacuum atmosphere for clean annealing, brazing, or sintering.
- If your primary focus is simple heating or stress relief: A direct-fired or standard atmosphere furnace without a retort is often a more cost-effective and energy-efficient solution.
Ultimately, the use of a retort transforms a simple furnace into a precision tool for advanced materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose & Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sealed Container | Isolates workpiece from furnace atmosphere and heating elements. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Enables inert gas or reactive process gas environments. |
| Prevents Oxidation | Protects material integrity during high-temperature processes. |
| External Heating | Heated indirectly, preventing contamination from burners/elements. |
| Common Applications | Nitriding, sintering, annealing, brazing, and more. |
Need precise atmospheric control for your heat treatment processes?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including retort furnaces designed for critical applications like nitriding, sintering, and clean annealing. Our solutions ensure the gas-tight integrity and temperature uniformity you need to protect your materials and achieve perfect results every time.
Let our experts help you select the ideal furnace for your laboratory's needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and discover the right retort furnace for your research or production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes



















