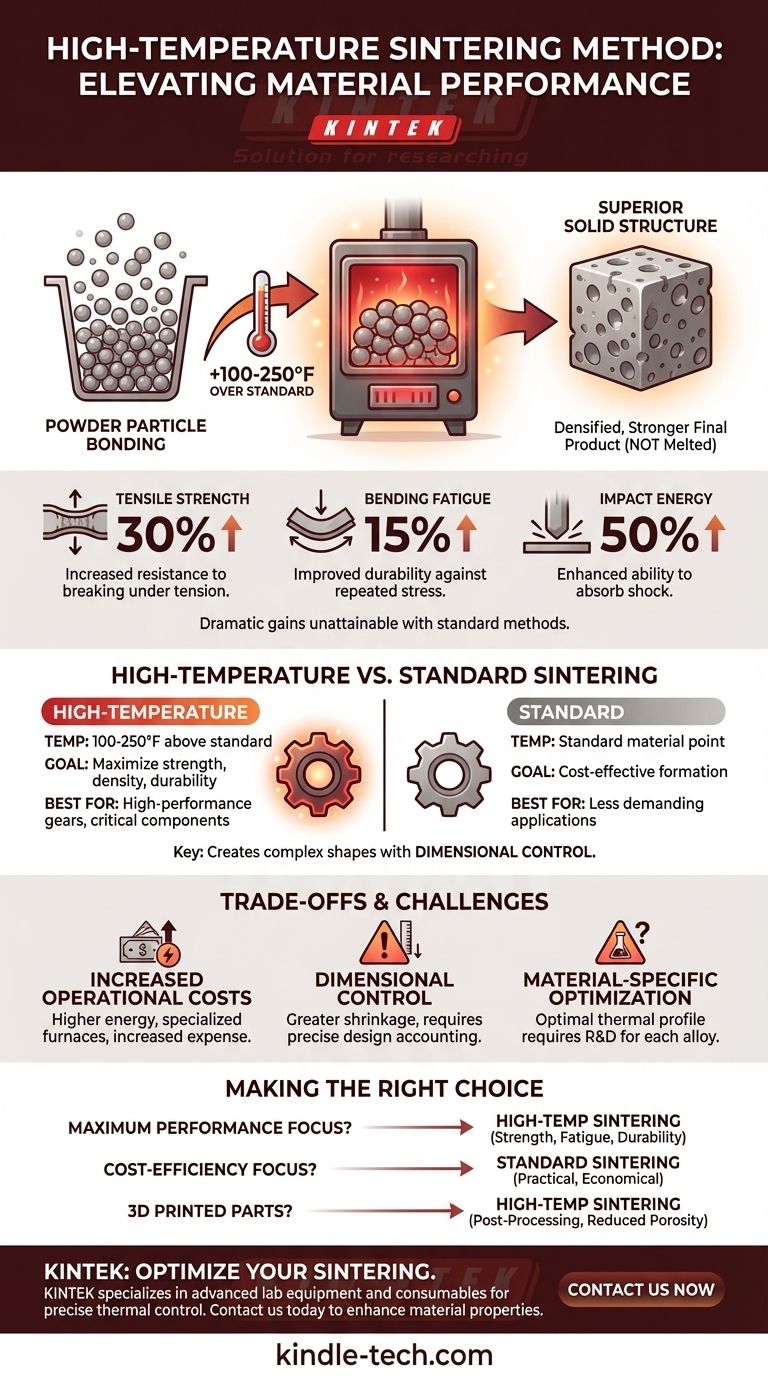
At its core, high-temperature sintering is a manufacturing process that elevates the temperature 100-250°F above the standard sintering point for a given material. For common iron-based metals, this often means heating a part to around 2050°F. This is done not to melt the material, but to create a denser, stronger final product with significantly enhanced physical properties.
The central principle of high-temperature sintering is a strategic trade-off: intentionally increasing energy and equipment costs to achieve superior material characteristics, such as dramatic gains in strength and durability, that are unattainable with standard methods.

The Fundamental Goal: Why Heat It Hotter?
Sintering is a thermal treatment for compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat, but without melting it to the point of liquefaction. High-temperature sintering simply pushes this process further to achieve more dramatic results.
From Powder to Solid Structure
The basic purpose of sintering is to bond individual particles—often a metal or ceramic powder—into a coherent, solid piece. This is especially useful for materials with extremely high melting points, as it bypasses the need to fully melt them.
Achieving Superior Material Properties
The primary driver for using higher temperatures is performance enhancement. This method can yield a 30% increase in tensile strength, a 15% increase in bending fatigue strength, and a 50% increase in impact energy. These are substantial gains that justify the added complexity.
The Role of Reduced Porosity
Heating the material hotter for a longer duration allows the particles to bond more completely. This process significantly reduces the microscopic empty spaces, or porosity, within the material, resulting in a denser and more robust final part.
High-Temperature vs. Standard Sintering
While the principle is the same, the application and outcomes of high-temperature sintering are distinct. It is a specialized process used when standard results are not sufficient for the part's intended function.
Defining the Temperature Difference
As noted, the process involves a deliberate temperature increase of 100-250°F over the material's conventional sintering temperature. This seemingly small change has a profound effect on the material's final atomic structure.
Why Not Just Melt the Material?
The value of sintering lies in creating a solid object from powder without reaching the material's melting point. This allows for the creation of complex shapes with excellent dimensional control, a benefit that would be lost if the material were turned into a liquid. High-temperature sintering operates in a carefully controlled zone that is hotter than normal but still safely below the melting point.
Key Applications
This technique is critical in powder metallurgy for creating high-performance gears, structural components, and other parts that must withstand extreme stress. It is also found in advanced ceramics, 3D printing of custom metal forms, and even in optimizing the performance of materials used in Li-ion batteries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The performance benefits of high-temperature sintering are clear, but they come with practical and financial costs that must be managed.
Increased Operational Costs
The most significant drawback is the expense. Maintaining higher temperatures requires more energy and necessitates the use of more robust, specialized furnaces that can withstand the intense heat, increasing both capital and operational costs.
The Challenge of Dimensional Control
Heating parts hotter can cause them to shrink more than expected. Engineers and manufacturers must carefully account for this increased shrinkage during the design phase to ensure the final component meets precise dimensional specifications.
Material-Specific Optimization
There is no universal "high temperature" for sintering. The optimal thermal profile varies significantly depending on the alloy or material being used. Determining the perfect temperature and duration often requires research and development to achieve the desired properties without causing defects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting high-temperature sintering is a deliberate engineering decision based on the final application's requirements. Use these points as a guide.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance: Choose high-temperature sintering when the part's strength, fatigue resistance, and durability are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency: Standard sintering is the more practical and economical choice for parts in less demanding applications.
- If you are working with 3D printed or complex metal parts: Consider high-temperature sintering as a post-processing step to improve the integrity and reduce the porosity of the final form.
Ultimately, high-temperature sintering is a powerful tool for pushing the boundaries of material performance when the application demands it.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | High-Temperature Sintering | Standard Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 100-250°F above standard point | Standard material-specific point |
| Primary Goal | Maximize strength, density, durability | Cost-effective part formation |
| Strength Increase | Up to 30% tensile, 50% impact energy | Standard material properties |
| Best For | High-performance gears, critical components | Less demanding applications |
Need to achieve superior material performance for your lab or production line?
High-temperature sintering is a specialized process requiring precise thermal control. KINTEK specializes in the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to implement this technique effectively. Our robust sintering furnaces and expert support help you achieve the dramatic gains in strength and durability your projects demand.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your sintering process and enhance your material properties. #Contact Us Now to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Purity



















