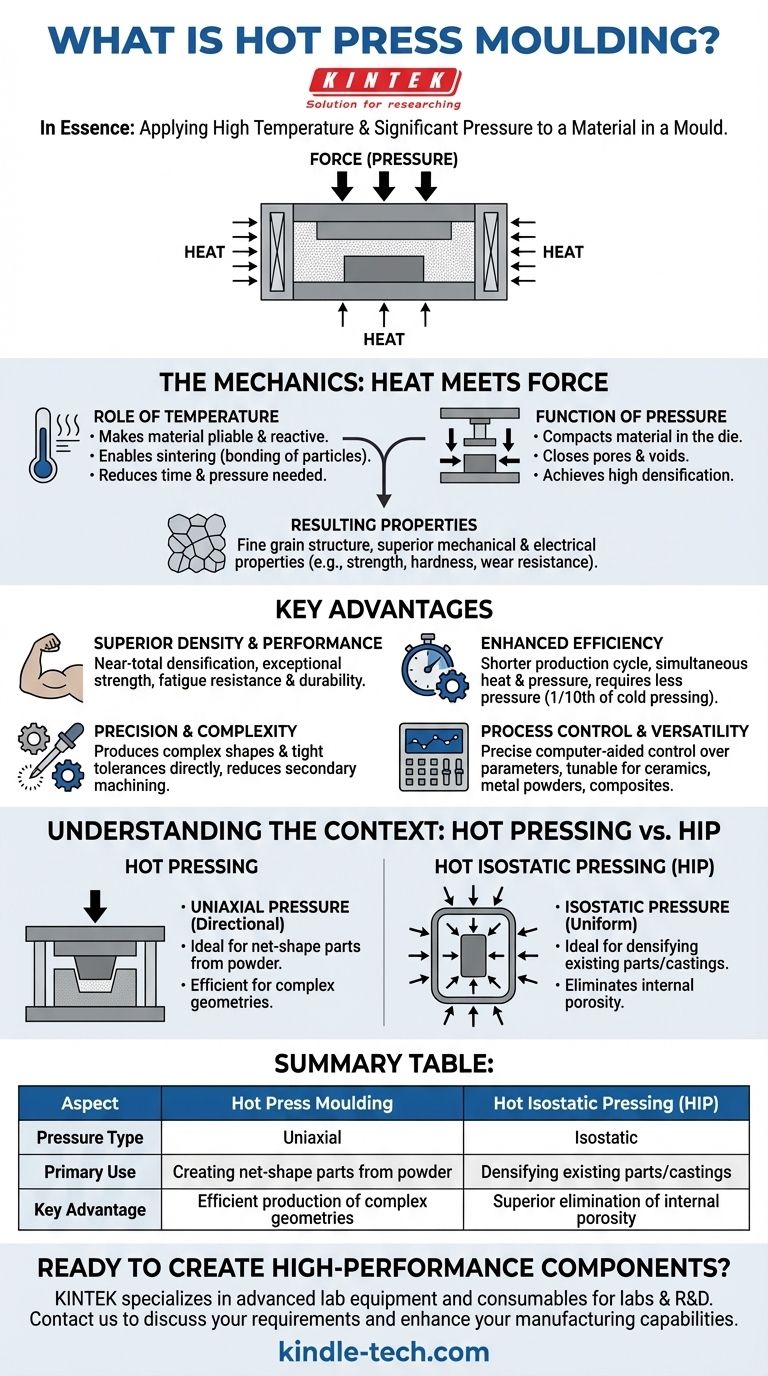
In essence, hot press moulding is a manufacturing process that simultaneously applies high temperature and significant pressure to a material within a mould. This combination of heat, which makes the material more pliable, and force, which compacts it, is used to produce solid, dense parts with enhanced mechanical properties and precise shapes.
The core principle of hot press moulding is to use thermal energy to reduce a material's resistance to deformation while using mechanical force to eliminate internal voids. This synergy allows for the creation of highly dense, strong, and dimensionally accurate components at lower pressures and temperatures than other methods might require.
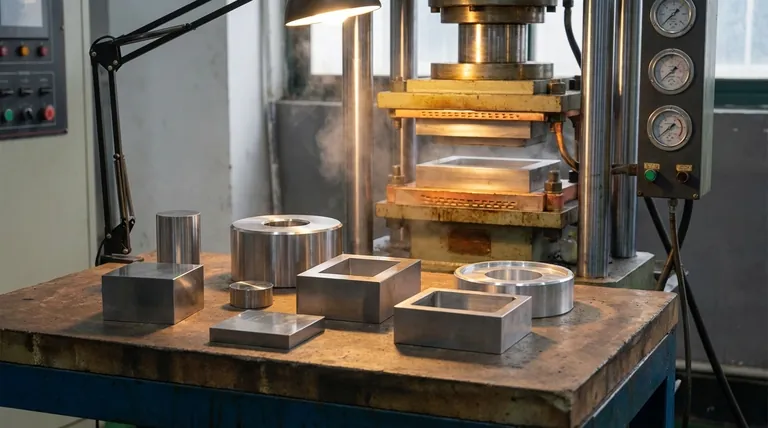

The Mechanics of Hot Pressing: Heat Meets Force
To understand why hot pressing is effective, we must look at the distinct roles that temperature and pressure play in transforming the raw material.
The Role of Temperature
Heat is the catalyst in the hot pressing process. By raising the material's temperature, often in a vacuum or inert gas to prevent oxidation, we make it more plastic and reactive.
This thermal energy allows the individual particles, especially in powdered materials, to soften and bond more readily, a process known as sintering. This reduces the amount of time and pressure needed to form the part.
The Function of Pressure
While heat makes the material workable, pressure provides the directive force. It is applied concurrently to compact the material inside the mould, or die.
This pressure physically forces the material particles together, closing up pores and voids. The result is a highly densified final product, often approaching the material's theoretical maximum density.
The Resulting Properties
The combination of heat and pressure aides mass transfer and inhibits unwanted grain growth within the material's microstructure.
This controlled process yields a final part with a fine grain structure, leading to superior mechanical and electrical properties, such as increased strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
Key Advantages of the Hot Pressing Method
Choosing hot pressing over other manufacturing techniques comes down to a specific set of powerful advantages that are critical for high-performance applications.
Superior Density and Performance
The primary benefit is the ability to achieve near-total densification. By virtually eliminating porosity, the process produces parts with exceptional strength, fatigue resistance, and durability.
Enhanced Efficiency
Compared to cold pressing followed by a separate sintering step, hot pressing is more efficient. The simultaneous application of heat and pressure reduces the required sintering temperature and shortens the overall production cycle time.
Furthermore, because the material is in a thermoplastic state, the process requires significantly less pressure—sometimes only one-tenth of that needed for cold pressing.
Precision and Complexity
Hot press moulding excels at producing products with complex shapes and tight dimensional tolerances directly from the mould. This reduces or eliminates the need for secondary machining, saving time and cost.
Process Control and Versatility
Modern hot press machines offer precise, computer-aided control over temperature, pressure, and timing. This allows for the process to be finely tuned for a wide range of materials, including advanced ceramics, metal powders, and composites.
Understanding the Context: Hot Pressing vs. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot pressing is often discussed alongside a related technology, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). While similar, their methods and primary applications differ significantly.
The Difference in Pressure Application
Hot Pressing typically uses uniaxial pressure, meaning the force is applied from one or two directions by a plunger within a rigid die.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), in contrast, uses isostatic pressure. The part is placed in a pressure vessel, which is then filled with a hot, inert gas (like argon) to apply uniform pressure from all directions simultaneously.
The Difference in Application
Because of its directional pressure, hot pressing is ideal for creating specific, often complex, net-shape parts directly from powder.
HIP is most commonly used to densify pre-existing parts or castings. Its all-encompassing pressure is exceptionally effective at collapsing and eliminating any internal porosity or voids that may have formed during casting or an earlier manufacturing step.
When to Choose Hot Press Moulding
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your material, desired final properties, and production goals.
- If your primary focus is creating a net-shape part with high density and strength directly from a powder: Hot press moulding is an excellent choice for its efficiency and ability to produce complex geometries.
- If your primary focus is eliminating residual internal porosity from an existing casting or pre-formed part: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the more suitable technology due to its use of uniform, gas-based pressure.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing simpler components where maximum density is not the critical factor: A conventional cold pressing and separate sintering process may be more cost-effective.
Ultimately, selecting hot press moulding is a strategic decision to achieve a specific combination of density, strength, and geometric complexity that other methods cannot efficiently deliver.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Press Moulding | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Type | Uniaxial (directional) | Isostatic (uniform from all sides) |
| Primary Use | Creating net-shape parts from powder | Densifying existing parts/castings |
| Key Advantage | Efficient production of complex geometries | Superior elimination of internal porosity |
Ready to Create High-Performance Components?
If you need to produce dense, strong parts with complex shapes directly from powder, hot press moulding could be the ideal solution for your laboratory or production line.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and R&D facilities. Our expertise can help you determine if hot press technology is right for your application and provide the reliable equipment you need to succeed.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What role do graphite mold components play in the vacuum hot pressing of Ti-3Al-2.5V? Optimize Alloy Densification
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What roles do graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Alloy Powder Densification & Precision
- What is the role of high-strength graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing Beryllium? Enhance Densification & Precision



















