In essence, induction brazing is used for manufacturing applications that demand speed, precision, and highly repeatable results, particularly in high-volume production runs. It excels at creating strong, clean joints in a controlled manner for components in the automotive, HVAC, and electromechanical industries, such as joining carbide cutting tips to steel tool shafts.
While many methods can join metal, induction brazing stands apart by offering localized, rapid, and precisely controllable heat. This makes it the preferred choice not just for what is being joined, but for how efficiently and consistently the process must be performed.
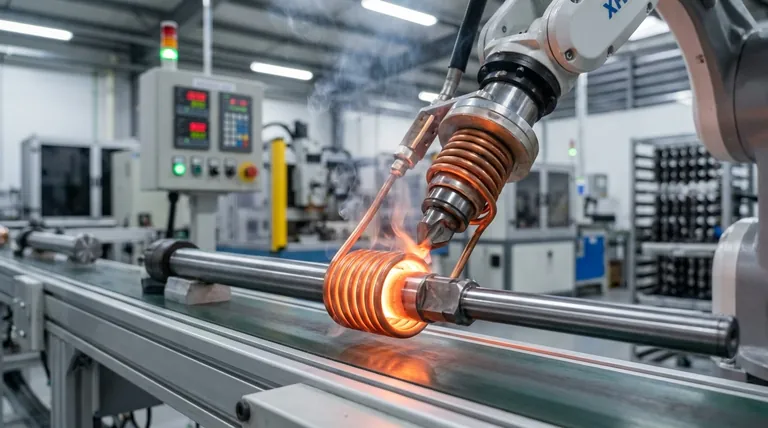

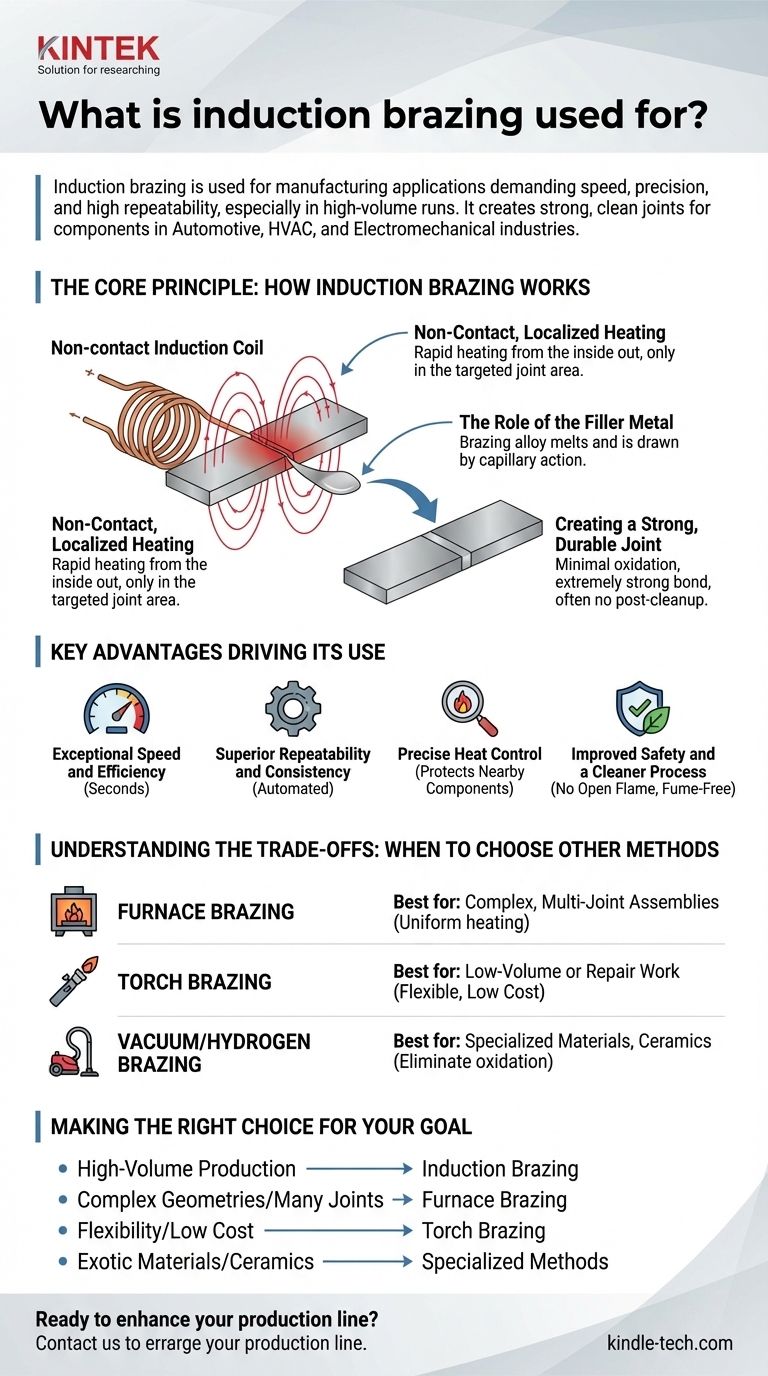
The Core Principle: How Induction Brazing Works
To understand why induction brazing is chosen for specific jobs, you must first understand its fundamental mechanism. It is a highly controlled process that differs significantly from heating with a flame or in a furnace.
Non-Contact, Localized Heating
An induction coil generates a high-frequency magnetic field around the parts to be joined. This field induces an electrical current directly within the metal parts, causing them to heat up rapidly from the inside out.
Crucially, the heat is generated only in the targeted area near the joint, leaving the rest of the assembly unaffected.
The Role of the Filler Metal
A brazing alloy, or filler metal, with a melting point lower than the base metals is placed at the joint. As the induction process heats the base metals, they conduct that heat to the filler, causing it to melt.
The molten filler is then drawn into the gap between the two closely fitted parts by capillary action, creating a perfect metallurgical bond upon cooling.
Creating a Strong, Durable Joint
Because the heating is so fast and precise, there is minimal oxidation or distortion of the base materials. This results in an extremely strong, clean, and durable joint that often requires no post-brazing cleanup.
Key Advantages Driving Its Use
Manufacturers don't choose a process without good reason. Induction brazing's adoption is driven by several key advantages that are critical for modern production environments.
Exceptional Speed and Efficiency
The heating process is incredibly fast, often taking only a few seconds. This makes induction brazing ideal for integration into automated, high-volume production lines where cycle time is a critical factor.
Superior Repeatability and Consistency
Once the parameters (power, time, and coil position) are set, an induction brazing machine produces the exact same result every time. This guarantees uniform quality across thousands of components, a requirement that is difficult to achieve with manual methods.
Precise Heat Control
The ability to heat a very specific area is a major benefit. It prevents heat damage to nearby sensitive components, such as seals, electronics, or other previously brazed joints, and minimizes warping of the parts.
Improved Safety and a Cleaner Process
Unlike torch brazing, induction heating does not involve an open flame. This significantly improves workplace safety and creates a cleaner, fume-free environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Choose Other Methods
Induction brazing is a powerful tool, but it is not the solution for every joining task. Its strengths in one area create limitations in others.
For Complex, Multi-Joint Assemblies: Furnace Brazing
If an assembly has many joints, complex geometry, or joints that are inaccessible to an induction coil, furnace brazing is a better choice. Placing the entire assembly in a controlled-atmosphere furnace ensures all joints are heated uniformly at the same time. This is common for heat exchangers and some aerospace components.
For Low-Volume or Repair Work: Torch Brazing
The setup for induction brazing requires a dedicated machine and custom-fabricated coils, which represents a significant upfront investment. For one-off jobs, prototyping, or field repairs, the flexibility and low cost of manual torch brazing is far more practical.
For Specialized Materials: Vacuum or Hydrogen Brazing
When joining reactive metals or bonding metals to ceramics, oxidation must be completely eliminated. Specialized processes like hydrogen brazing or vacuum brazing are used for these applications, which are common in the medical, research, and high-end electronics fields for devices like X-ray tubes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct brazing method is a strategic engineering decision. Use your primary goal to guide your choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Induction brazing is the clear choice for its unmatched speed, automation potential, and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is complex geometries or many joints: Consider furnace brazing to ensure uniform heating across the entire assembly.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and low initial cost: Torch brazing is the most practical solution for one-off jobs, prototyping, or repairs.
- If your primary focus is joining exotic materials or ceramics: Specialized methods like hydrogen or vacuum brazing are required to meet stringent atmospheric demands.
Ultimately, selecting the right brazing method is a decision based on the specific demands of your materials, production volume, and joint design.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Brazing | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Very Fast (seconds) | High-volume production lines |
| Heat Control | Highly Localized | Protecting sensitive nearby components |
| Consistency | Excellent Repeatability | Automated, uniform quality |
| Joint Strength | Strong, Clean, Durable | Critical automotive & tooling components |
| Alternative Method | Furnace Brazing | Complex assemblies with multiple joints |
| Alternative Method | Torch Brazing | Low-volume, prototyping, or repair work |
Ready to enhance your production line with precise, high-speed brazing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables to meet the demanding needs of modern manufacturing. Whether you're in automotive, HVAC, or electromechanical production, our expertise can help you achieve stronger joints, higher throughput, and consistent quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your brazing process and drive your efficiency forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What is a hydraulic hot press? A Guide to Precision Heat and Pressure for Manufacturing
- What is a hydraulic hot press? Unlock the Power of Heat and Pressure for Advanced Materials
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More



















