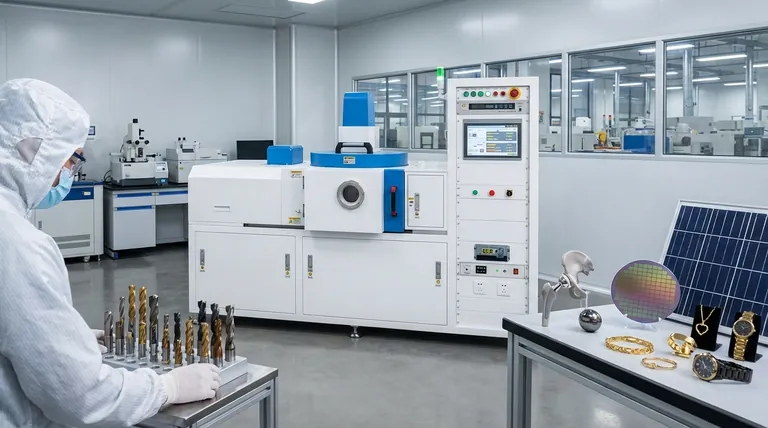
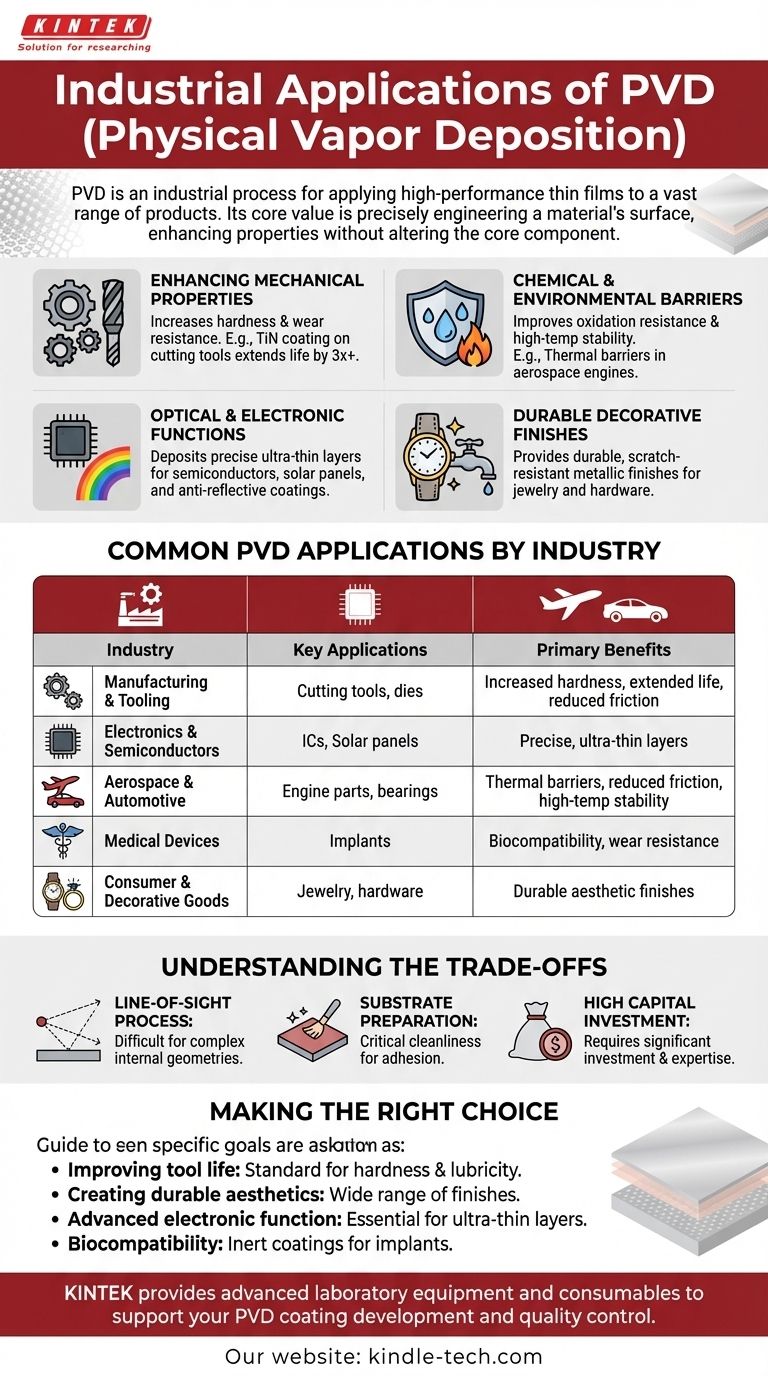
In short, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is an industrial process used to apply high-performance thin films onto a vast range of products. Its applications span from coating cutting tools and medical implants to manufacturing semiconductor devices, solar panels, and creating durable decorative finishes on everyday hardware and jewelry. PVD is the technology of choice wherever a product's surface needs fundamentally different properties than its underlying material.
The core value of PVD is not in a single application, but in its ability to precisely engineer a material's surface. It allows manufacturers to enhance hardness, reduce friction, or change optical and electronic properties without altering the core component.

Why PVD is So Widely Adopted
The versatility of PVD comes from its ability to solve distinct engineering challenges by applying a micro-thin layer of specialized material. This layer becomes an integral part of the final product, providing benefits the base material alone cannot.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
PVD coatings can dramatically increase the hardness and wear resistance of a component's surface. This is critical for items subjected to intense physical stress.
A prime example is coating metalworking tools like drills and end mills with materials like Titanium Nitride (TiN). This reduces friction, allows for higher cutting speeds, and can extend the tool's life by a factor of three or more.
Providing Chemical and Environmental Barriers
PVD films can act as a shield, protecting the substrate from its environment. This includes improving oxidation resistance and providing stability at high temperatures.
In the aerospace industry, PVD is used to apply thermal barrier coatings to engine components, protecting them from extreme heat and ablation. It also creates diffusion barriers that prevent different layers of a material from mixing.
Achieving Specific Optical and Electronic Functions
The process allows for the deposition of extremely thin, pure, and uniform layers, which is essential for modern electronics and optics.
This capability is foundational to manufacturing semiconductor devices and thin-film solar panels. It is also used for creating anti-reflective coatings on glass or specific reflective layers for mirrors and other optical components.
Creating Durable Decorative Finishes
PVD provides a way to apply a brilliant metallic finish that is far more durable than traditional plating. The coating reflects the underlying surface texture, providing a premium luster without needing post-process polishing.
This is why PVD is ubiquitous in products like jewelry, kitchen and bathroom hardware, door handles, and other items where both aesthetics and resistance to scratches and tarnishing are critical.
Common PVD Applications by Industry
While the principles are universal, the specific applications are tailored to the unique demands of each sector.
Manufacturing and Tooling
The most common application is on cutting tools, punches, and forming dies. The goal is simple: increase hardness, reduce friction, and extend operational life.
Electronics and Semiconductors
PVD is indispensable for depositing the conductive and insulating layers required to build integrated circuits, transistors, and other microelectronic components.
Aerospace and Automotive
In addition to thermal barriers, PVD coatings are used on engine parts and bearings to reduce friction and improve efficiency and longevity.
Medical Devices
PVD creates biocompatible coatings for medical implants, such as artificial joints and pacemakers. These inert coatings prevent adverse reactions with the body and improve wear resistance.
Consumer and Decorative Goods
This broad category includes everything from watch cases and jewelry to faucets and lighting fixtures. PVD provides a wide palette of metallic colors that resist fading and wear. It is also used for the thin aluminum layer in food packaging and balloons.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to applying it correctly.
It Is a Line-of-Sight Process
The vaporized coating material travels in a straight line within the vacuum chamber. This means complex internal geometries or hidden surfaces can be very difficult to coat evenly without sophisticated part rotation.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The success of PVD coating is highly dependent on the cleanliness and preparation of the substrate. Any surface contamination will compromise the adhesion and integrity of the film, leading to failure.
It Involves High Capital Investment
PVD coating equipment operates under a high vacuum and requires significant capital investment and technical expertise. This makes it best suited for high-value or high-volume production where the performance benefits justify the cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use PVD should be driven by the specific performance outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is improving tool life and performance: PVD coatings are the industry standard for enhancing the hardness and lubricity of cutting and forming tools.
- If your primary focus is creating a durable, premium aesthetic: PVD provides a wide range of metallic finishes for consumer goods that are highly resistant to scratches and tarnishing.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronic or optical function: PVD is essential for depositing the precise, ultra-thin layers required in semiconductors, sensors, and solar panels.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility or chemical resistance: PVD is used to create inert barrier coatings for medical implants and components exposed to harsh environments.
Ultimately, PVD is the industrial tool of choice for fundamentally upgrading the surface of a material to meet a specific performance demand.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key PVD Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Tooling | Cutting tools, drills, dies | Increased hardness, extended tool life, reduced friction |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Integrated circuits, solar panels | Precise, ultra-thin conductive/insulating layers |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Engine components, bearings | Thermal barriers, reduced friction, high-temp stability |
| Medical Devices | Implants (joints, pacemakers) | Biocompatibility, wear resistance, corrosion protection |
| Consumer & Decorative Goods | Jewelry, hardware, fixtures | Durable, scratch-resistant aesthetic finishes |
Ready to enhance your product's performance with a PVD coating?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables to support your PVD coating development and quality control processes. Whether you are manufacturing cutting tools, medical implants, or consumer electronics, our solutions can help you achieve the precise surface properties you need.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your application. Let's engineer a better surface for your product.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















