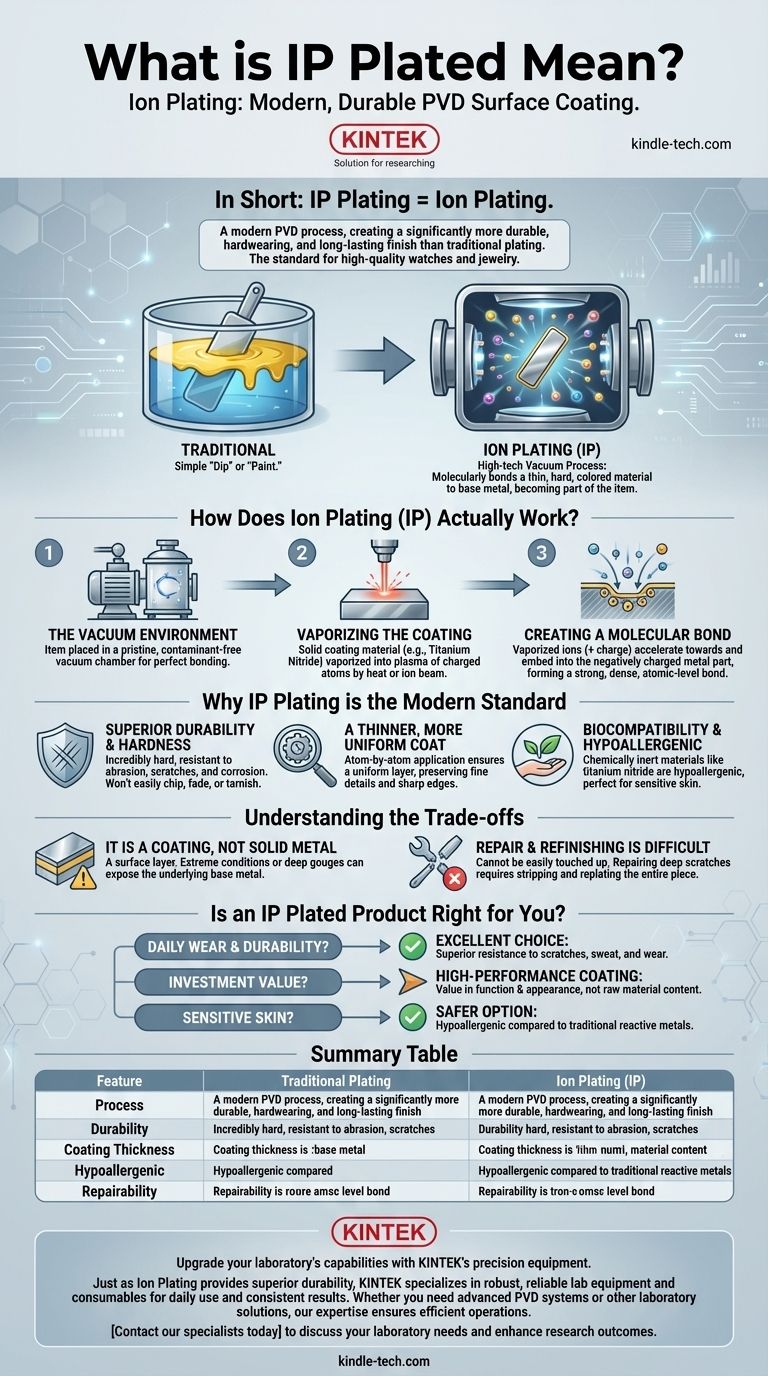
In short, IP Plating stands for Ion Plating. It is a modern surface coating process that uses Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) to create a finish that is significantly more durable, hardwearing, and long-lasting than traditional plating methods. This technique is now the standard for high-quality watches and jewelry.
The crucial difference to understand is that Ion Plating is not a simple "dip" or "paint." It's a high-tech vacuum process that molecularly bonds a thin layer of hard, colored material to the base metal, resulting in a finish that becomes part of the original item rather than just sitting on top of it.
How Does Ion Plating (IP) Actually Work?
To understand why IP plating is superior, you need to understand the process. It's a sophisticated technique that takes place inside a specialized vacuum chamber.
The Vacuum Environment
First, the item to be plated (such as a stainless steel watch case) is placed in a vacuum chamber. All the air is removed to create a pristine, contaminant-free environment, which is critical for a perfect molecular bond.
Vaporizing the Coating Material
A solid piece of the coating material—often a super-hard ceramic like Titanium Nitride—is vaporized by either intense heat or a high-powered ion beam. This turns the solid material into a plasma of charged atoms.
Creating a Molecular Bond
The metal part being coated is given a strong negative electrical charge. The vaporized coating particles, which are positively charged ions, are then powerfully attracted to the negatively charged part. They accelerate towards it and embed themselves into the surface, creating an extremely strong, dense, and uniform bond at the atomic level.
Why IP Plating is the Modern Standard
This complex process yields several distinct advantages over older methods like traditional electroplating, making it the preferred choice for products designed for daily wear.
Superior Durability and Hardness
The primary benefit of IP plating is its exceptional durability. The resulting coating is incredibly hard and resistant to abrasion, scratches, and corrosion. An IP-plated finish won't easily chip, fade, or tarnish like older, softer plating methods.
A Thinner, More Uniform Coat
Because the coating is applied atom by atom in a vacuum, the resulting layer is extremely thin and perfectly uniform. This preserves the fine details and sharp edges of intricate watch or jewelry designs that thicker, less even plating can obscure.
Biocompatibility and Hypoallergenic Properties
The materials commonly used for IP plating, such as titanium nitride (used for gold tones) or titanium carbide (for black), are chemically inert. This makes them hypoallergenic and an excellent choice for individuals with skin sensitivities to metals like nickel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While IP plating is a superior technology, it's essential to maintain an objective perspective. It has characteristics that you must be aware of.
It Is a Coating, Not Solid Metal
Despite its incredible durability, an IP finish is still a surface layer. Under extreme and prolonged abrasive conditions or after a very deep gouge that penetrates the coating, the underlying base metal (usually stainless steel) can become exposed.
Repair and Refinishing is Difficult
Unlike a solid gold watch that can be polished to remove scratches, an IP plated surface cannot be easily "touched up." Repairing a deep scratch would require the entire piece to be stripped and replated, which is often not feasible.
Is an IP Plated Product Right for You?
Making the right choice depends on balancing your expectations for appearance, longevity, and value.
- If your primary focus is daily wear and durability: IP plating is an excellent choice, offering superior resistance to the scratches, sweat, and wear of everyday life.
- If your primary focus is investment value: Recognize that it is a high-performance coating, not solid precious metal. Its value is in its function and appearance, not its raw material content.
- If you have sensitive skin: IP plated jewelry is often a safer, hypoallergenic option compared to items with reactive metals used in traditional plating.
Ultimately, choosing an IP plated item means prioritizing modern, high-performance durability for your accessories.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Plating | Ion Plating (IP) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Electrochemical dip | Vacuum PVD, molecular bonding |
| Durability | Prone to scratches/fading | Extremely hard, abrasion-resistant |
| Coating Thickness | Thicker, less uniform | Thin, uniform, preserves details |
| Hypoallergenic | Varies (may contain nickel) | Excellent (uses inert ceramics) |
| Repairability | Can be replated | Difficult to refinish |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's precision equipment.
Just as Ion Plating provides superior durability for high-end accessories, KINTEK specializes in robust, reliable lab equipment and consumables designed to withstand daily use and deliver consistent results. Whether you need advanced PVD systems for surface coating research or other laboratory solutions, our expertise ensures your operations run efficiently and effectively.
Contact our specialists today to discuss how KINTEK can meet your specific laboratory needs and enhance your research outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between thermal CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the precursor gas in PECVD? The Key to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the examples of CVD method? Discover the Versatile Applications of Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is the difference between CVD and PVD process? A Guide to Choosing the Right Coating Method
- Why is PECVD better than CVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















