In essence, a laboratory heater is a device designed to apply controlled and precise heat to substances as part of a scientific or experimental process. Unlike a simple kitchen stove, these instruments are built for accuracy, uniformity, and safety when working with a wide range of materials, from simple aqueous solutions to volatile organic solvents.
The critical takeaway is that "laboratory heater" is not a single device, but a category of tools. Choosing the correct type—whether a hot plate, heating mantle, or water bath—is essential for the safety of the user and the success of the experiment.

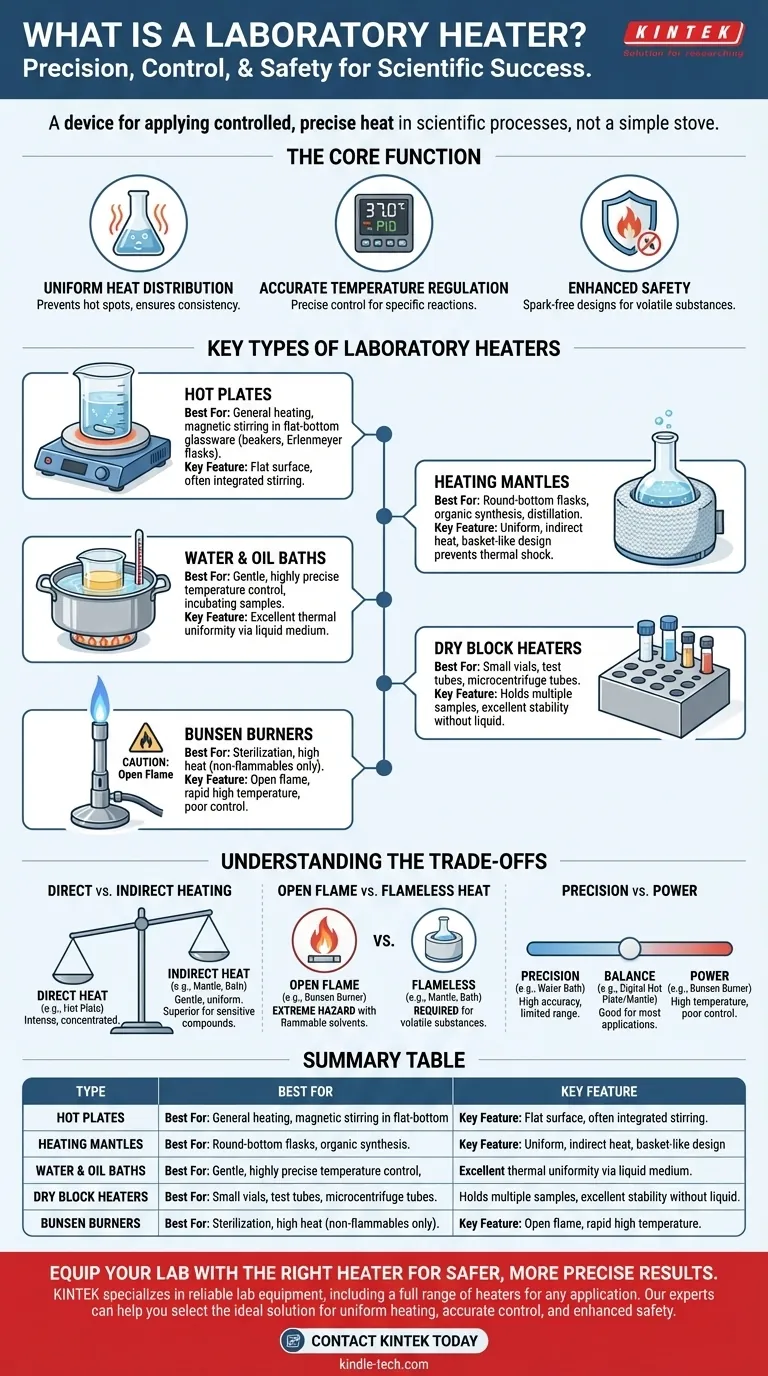
The Core Function: Precision and Control
A laboratory heater's primary purpose is to provide a reliable and repeatable source of thermal energy. This goes far beyond simply making something hot.
Uniform Heat Distribution
One of the main challenges in heating substances is avoiding "hot spots," where one part of the container is significantly hotter than another. Heaters like mantles and water baths are specifically designed to deliver uniform heat, ensuring consistent reaction rates and preventing the decomposition of sensitive materials.
Accurate Temperature Regulation
Scientific experiments demand precision. Laboratory heaters incorporate thermostats and control systems, ranging from simple analog dials to sophisticated digital PID controllers, that allow users to set and maintain a specific temperature with a high degree of accuracy.
Enhanced Safety
Working with chemicals, especially flammable ones, requires specialized equipment. Many laboratory heaters are designed to be spark-free, providing a safe alternative to open flames like Bunsen burners when working with volatile substances.
Key Types of Laboratory Heaters
The specific task dictates the type of heater required. Each design serves a distinct purpose and is suited for different types of glassware and materials.
Hot Plates
The hot plate is the most common heater in a general-purpose lab. It features a flat, heated surface made of ceramic or metal, ideal for heating liquids in flat-bottomed glassware like beakers and Erlenmeyer flasks. Many models also include an integrated magnetic stirrer to ensure the liquid is heated evenly.
Heating Mantles
A heating mantle is a soft or rigid insulated container designed to fit around the bottom of round-bottom flasks. Its "basket-like" design provides extremely uniform heating across the vessel's surface, which is critical for preventing thermal shock that can crack the glass. Mantles are the standard choice for organic synthesis and distillation.
Water and Oil Baths
For gentle and highly stable temperature control, a water bath or oil bath is used. The glassware is placed in a container of heated liquid (water or a specialized oil for higher temperatures), which provides excellent thermal uniformity. These are essential for incubating biological samples or running temperature-sensitive reactions.
Dry Block Heaters
A dry block heater (or heat block) contains precisely drilled holes to hold small vials, test tubes, or microcentrifuge tubes. It provides excellent temperature stability and uniformity for multiple small-volume samples simultaneously, without the need for a liquid medium like a water bath.
Bunsen Burners
The classic Bunsen burner produces an open flame by mixing gas with a controlled amount of air. It can achieve very high temperatures quickly but offers poor temperature control and presents a significant fire hazard, especially when flammable liquids are nearby. Its use is now often restricted to tasks like sterilizing equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong heater can ruin an experiment or create a dangerous situation. The primary considerations revolve around safety and the nature of the substance being heated.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
A hot plate provides direct heat, which can be intense and concentrated. A heating mantle or water bath provides indirect heat, which is gentler and more uniform. For sensitive compounds or round-bottom flasks, indirect heat is almost always the superior choice.
Open Flame vs. Flameless Heat
This is the most critical safety distinction. Never use a Bunsen burner or any open flame to heat a flammable or volatile solvent like ethanol, acetone, or ether. The vapors can easily ignite. A flameless device like a heating mantle or a steam bath is required for these applications.
Precision vs. Power
A water bath offers exceptional temperature precision but is limited to 100°C. A Bunsen burner offers immense power and high temperatures but has very poor control. Digital hot plates and mantles provide a good balance between the two for most common applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heater is fundamental to good laboratory practice. Your choice should always be guided by the specific requirements of your procedure and a commitment to safety.
- If your primary focus is heating non-flammable liquids in beakers or flasks: A standard hot plate, preferably with magnetic stirring capability, is your most versatile tool.
- If your primary focus is heating volatile, flammable solvents or running reactions in round-bottom flasks: A heating mantle is the correct and safe choice.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a precise, gentle temperature for sensitive samples: A water bath or dry block heater provides the best control and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is achieving very high temperatures with no flammable materials present: A Bunsen burner or a furnace may be appropriate, but only with extreme caution and proper safety protocols.
Ultimately, understanding the function and limitations of each type of laboratory heater empowers you to perform your work safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Type of Heater | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Plate | General heating, magnetic stirring | Flat surface for beakers/flasks |
| Heating Mantle | Round-bottom flasks, volatile solvents | Uniform, indirect heat |
| Water/Oil Bath | Gentle, precise temperature control | Excellent thermal uniformity |
| Dry Block Heater | Small vials and test tubes | Holds multiple samples |
| Bunsen Burner | Sterilization, high heat (non-flammables) | Open flame, high temperature |
Equip your lab with the right heater for safer, more precise results.
Choosing the correct laboratory heater is critical for experiment success and user safety. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of heaters suited for any application—from general-purpose hot plates to specialized heating mantles for sensitive synthesis.
Our experts can help you select the ideal equipment to ensure uniform heating, accurate temperature control, and enhanced safety for your specific processes. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's heating needs and discover how KINTEK can support your work with high-quality, dependable solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What role does a benchtop hot press play in densifying composite cathodes? Achieve <10% Porosity with Thermo-Mechanical Flow
- What role do molds play in the formation of Ruthenium sheets? Master High-Density Ruthenium Fabrication
- How is conventional heating different from induction heating? Direct vs. Indirect Heat Explained
- What are the pros and cons of hot forging? Unlock Superior Strength for Critical Components



















