In the world of advanced manufacturing and materials science, metal evaporation is a cornerstone technique for creating ultra-thin films. It is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process where a solid metal source is heated in a high-vacuum chamber until it transitions into a gaseous vapor, which then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface, or substrate, to form a uniform coating.
At its core, metal evaporation is not simply about boiling metal. It is a precisely controlled process for building functional layers on a substrate, atom by atom, with applications ranging from computer chips to mirrored sunglasses. Understanding its principles is key to leveraging its strengths and avoiding its inherent limitations.

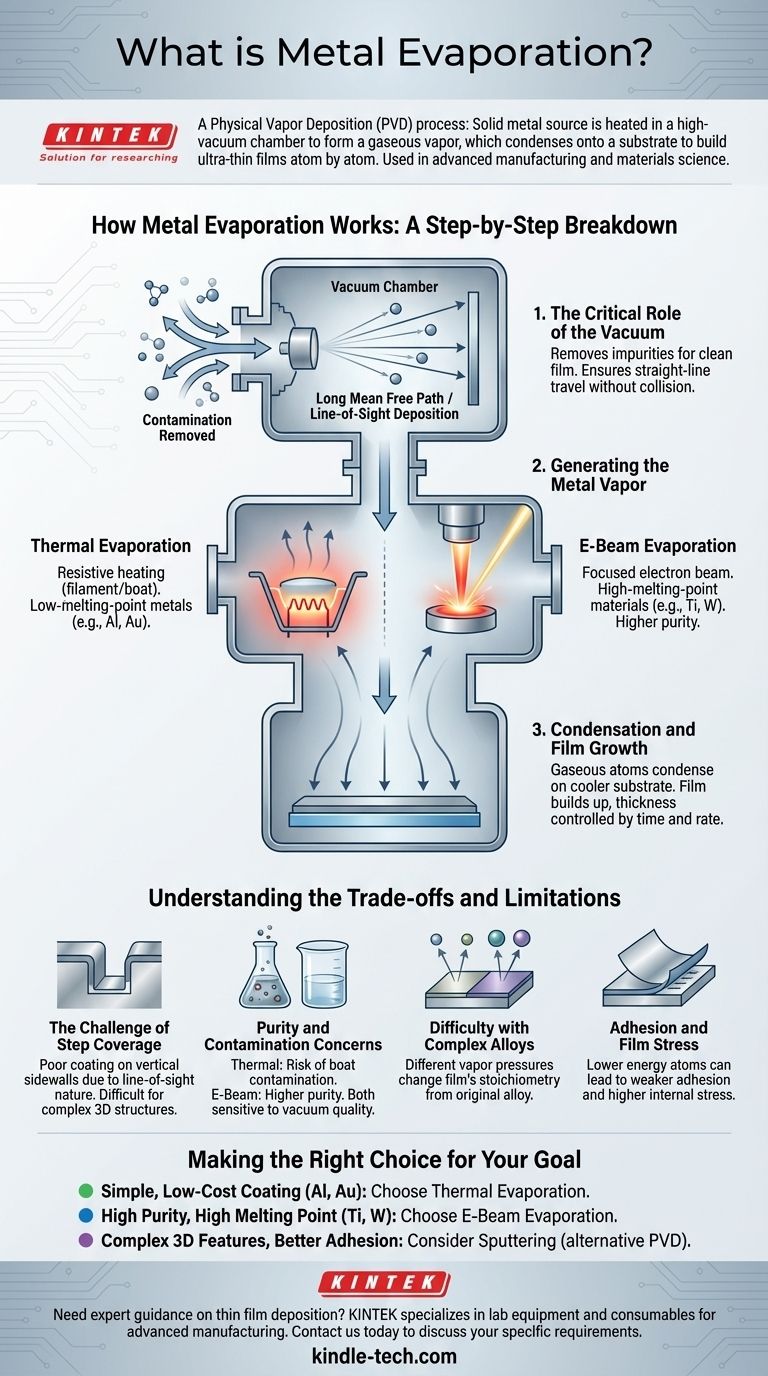
How Metal Evaporation Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Metal evaporation is fundamentally a three-step process that takes place inside a specialized vacuum system. Each step is critical to the quality of the final film.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
Before any heating occurs, the chamber is pumped down to a high vacuum. This is essential for two reasons. First, it removes air and other gases that would otherwise react with the hot metal vapor, causing contamination and impurities in the film.
Second, the vacuum creates a long mean free path. This ensures that the evaporated metal atoms travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate without colliding with other gas molecules, a principle known as line-of-sight deposition.
Generating the Metal Vapor
Once a sufficient vacuum is achieved, the source metal is heated until its vapor pressure becomes high enough for it to sublimate or boil. The atoms leave the source and travel through the vacuum chamber.
Condensation and Film Growth
When the gaseous metal atoms strike the cooler substrate, they lose their energy and condense back into a solid state. This process builds up, layer by layer, to form a thin, solid film on the substrate's surface. The thickness of this film is precisely controlled by monitoring the deposition rate and time.
The Two Primary Methods: Thermal vs. E-Beam
The method used to heat the source material is the primary differentiator in evaporation systems and determines the process's capabilities.
Thermal Evaporation: The Workhorse
Also known as resistive heating, this is the simplest method. A high electrical current is passed through a refractory material—often a tungsten "boat" or filament—that holds the source metal. The boat heats up like a stove-top burner, causing the metal inside to evaporate.
This method is cost-effective and excellent for metals with lower melting points like aluminum, gold, and chromium.
Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation: Precision and Purity
In this more advanced technique, a high-energy beam of electrons is generated and magnetically guided to strike the source material. The kinetic energy of the electrons is instantly converted to thermal energy upon impact, heating a very localized spot on the source to an extremely high temperature.
Because only the metal itself is heated (not a boat), E-beam evaporation produces much purer films and can be used to evaporate refractory materials with very high melting points, such as titanium, platinum, and tungsten.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, metal evaporation is not a universal solution. Its line-of-sight nature creates specific challenges that are critical to understand.
The Challenge of Step Coverage
Because atoms travel in straight lines, they struggle to coat the vertical sidewalls of microscopic features on a substrate. Imagine spray-painting a complex object from directly above; the top surfaces get a thick coat, but the sides get very little. This phenomenon, known as poor step coverage, is a major limitation in modern microelectronics where 3D structures are common.
Purity and Contamination Concerns
With thermal evaporation, there is a risk that the heated boat material can also evaporate slightly, contaminating the final film. While E-beam evaporation avoids this, both methods are highly sensitive to the quality of the vacuum.
Difficulty with Complex Alloys
Evaporating an alloy and achieving the same composition in the resulting film is very difficult. Different elements have different vapor pressures, meaning one element in the alloy will tend to evaporate faster than the other, changing the film's stoichiometry.
Adhesion and Film Stress
Evaporated films are created by relatively low-energy atoms simply condensing on a surface. This can sometimes result in weaker film adhesion and higher internal stress compared to more energetic deposition techniques like sputtering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method requires understanding your project's specific priorities, from cost and material choice to the geometry of the part you are coating.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost coating of a common metal (like aluminum or gold): Thermal evaporation is often the most direct and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is high purity or depositing a high-melting-point material (like titanium or platinum): E-beam evaporation is the superior choice for its clean and powerful heating mechanism.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D features or maximizing film adhesion and density: You should strongly consider sputtering, an alternative PVD technique that offers better step coverage.
Ultimately, choosing the right deposition technology is about matching the tool's inherent capabilities to the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Thermal Evaporation | E-Beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Resistive heating (boat/filament) | Focused electron beam |
| Best For | Low-melting-point metals (Al, Au) | High-melting-point metals (Ti, W) |
| Purity | Good (risk of boat contamination) | High (no boat contact) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Step Coverage | Poor (line-of-sight limitation) | Poor (line-of-sight limitation) |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right thin film deposition method for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables for advanced manufacturing and materials science. Whether you're working on microelectronics, optics, or specialized coatings, our team can help you choose the ideal evaporation or sputtering solution to meet your specific requirements for purity, material compatibility, and application performance. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition


















