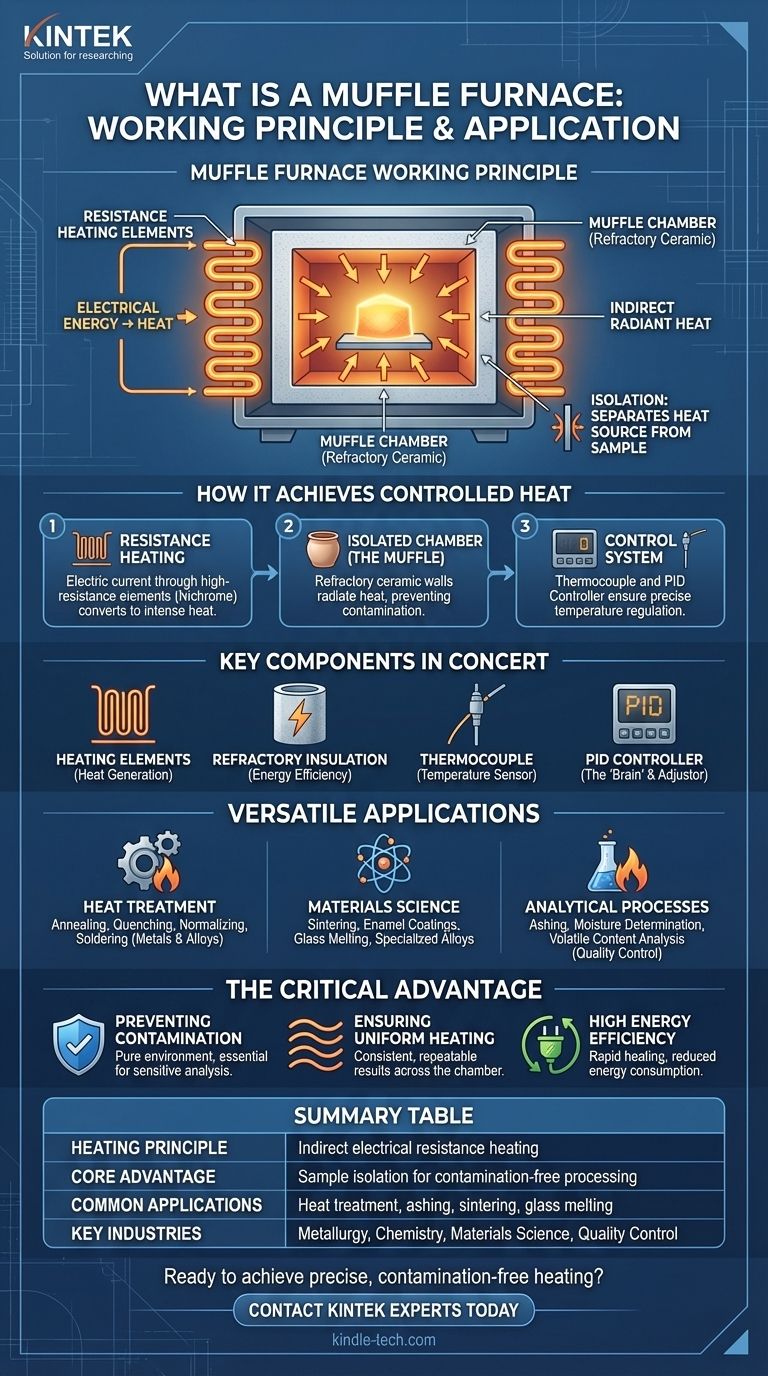
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that heats materials within an isolated chamber. Its working principle is based on indirect heating: electrical energy is converted into intense heat by resistance heating elements, which then radiate that heat into the chamber. This design intentionally separates the material being heated from the heating elements, preventing contamination and ensuring a highly controlled thermal environment.
The critical takeaway is that a muffle furnace's value comes from isolation. By creating a "muffle," or barrier, between the heat source and the sample, it delivers pure, uniform high temperatures essential for sensitive processes in metallurgy, chemistry, and materials science.

How a Muffle Furnace Achieves Controlled Heat
A muffle furnace's operation is a coordinated effort between three main systems: the heating system, the insulating chamber, and the control system.
The Principle of Indirect Electrical Heating
The heat source in a modern muffle furnace is entirely electrical. It works on the principle of resistance heating, sometimes called Joule heating.
An electric current is passed through high-resistance heating elements, often made of materials like Nichrome. As the current encounters this resistance, electrical energy is efficiently converted directly into thermal energy, causing the elements to glow red-hot.
The Role of the Muffle Chamber
This is the defining feature of the furnace. The heating elements do not directly contact the material being processed.
Instead, the elements heat the walls of a sealed inner chamber, known as the muffle. This chamber is constructed from refractory (heat-resistant) ceramic material. The chamber walls then radiate heat uniformly inward, heating the sample through radiation and convection.
This separation is crucial. It isolates the sample from any potential byproducts of combustion that would be present in a gas-fired furnace, ensuring process purity.
Key Components Working in Concert
Several components must work together to provide precise and efficient heating.
- Heating Elements: Convert electricity to heat.
- Refractory Insulation: A thick layer of insulation surrounds the muffle chamber, preventing heat loss and making the furnace highly energy-efficient.
- Thermocouple: A temperature sensor placed inside the chamber to provide real-time temperature feedback.
- PID Controller: The "brain" of the furnace. It receives data from the thermocouple and precisely adjusts the power sent to the heating elements to maintain the desired temperature or follow a specific heating program.
A Versatile Tool Across Industries
The ability to produce high, uncontaminated heat makes the muffle furnace indispensable in a wide range of scientific and industrial applications.
Heat Treatment of Metals and Alloys
This is a primary application where precise temperature control is vital for altering a metal's physical properties.
Common processes include annealing (softening metal), quenching (hardening), normalizing (refining grain structure), and soldering at high temperatures.
Materials Science and Production
Muffle furnaces are central to the development and creation of advanced materials.
They are used for sintering ceramics and powdered metals (fusing particles together with heat), creating enamel coatings on metal, melting glass, and producing specialized alloys.
Analytical and Quality Control Processes
In laboratory settings, the furnace is a standard tool for preparing and analyzing samples.
The most common use is ashing, which involves burning off organic substances to determine the non-combustible ash content of a sample. It is also used to determine moisture and volatile content in materials like coal, biomass, and food products.
The Critical Advantage: Isolation and Purity
Unlike a simple oven, the design of a muffle furnace is built around one core benefit: creating a pure heating environment.
Preventing Contamination
By separating the sample from the direct heat source, the furnace guarantees that no foreign materials from the heating elements can contaminate the sample. This is non-negotiable in analytical chemistry, medical sample prep, and semiconductor research.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
Because the entire chamber radiates heat inward, the sample is heated evenly from all sides. This uniformity eliminates hot spots and ensures consistent, repeatable results, which is critical for both metallurgical treatment and chemical analysis.
Achieving High Energy Efficiency
The combination of direct energy conversion (electrical to thermal) and heavy insulation allows the furnace to reach high temperatures rapidly and maintain them with minimal energy consumption.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific application dictates the most important features of the furnace.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical processing: Your priority is precise temperature programming, including controlled ramp rates and dwell times for processes like annealing.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing (e.g., ashing): You need exceptional temperature accuracy and uniformity across the chamber to ensure your results are valid and repeatable.
- If your primary focus is materials research (e.g., sintering): You require a furnace capable of reaching the highest possible temperatures and maintaining them for extended periods.
Understanding the principle of isolated heating is the key to leveraging the muffle furnace for precise and contamination-free results in any application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Indirect electrical resistance heating |
| Core Advantage | Sample isolation for contamination-free processing |
| Common Applications | Heat treatment, ashing, sintering, glass melting |
| Key Industries | Metallurgy, Chemistry, Materials Science, Quality Control |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free heating for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance muffle furnaces designed for applications like heat treatment, ashing, and sintering. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for superior temperature control and repeatable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Which type of material is used for overheating protection in muffle furnace? A Dual-Layer Safety System Explained
- What are the lab safety rules for heating substances? Essential Protocols to Prevent Accidents
- What is the most common metal used for blacksmithing? Start with Mild Steel for Forging Success
- What is the effect of calcination? Unlock Material Transformation for Industrial Processes
- What is the effect of calcination temperature on the properties of nanoparticles? Master the Trade-Off for Optimal Performance



















