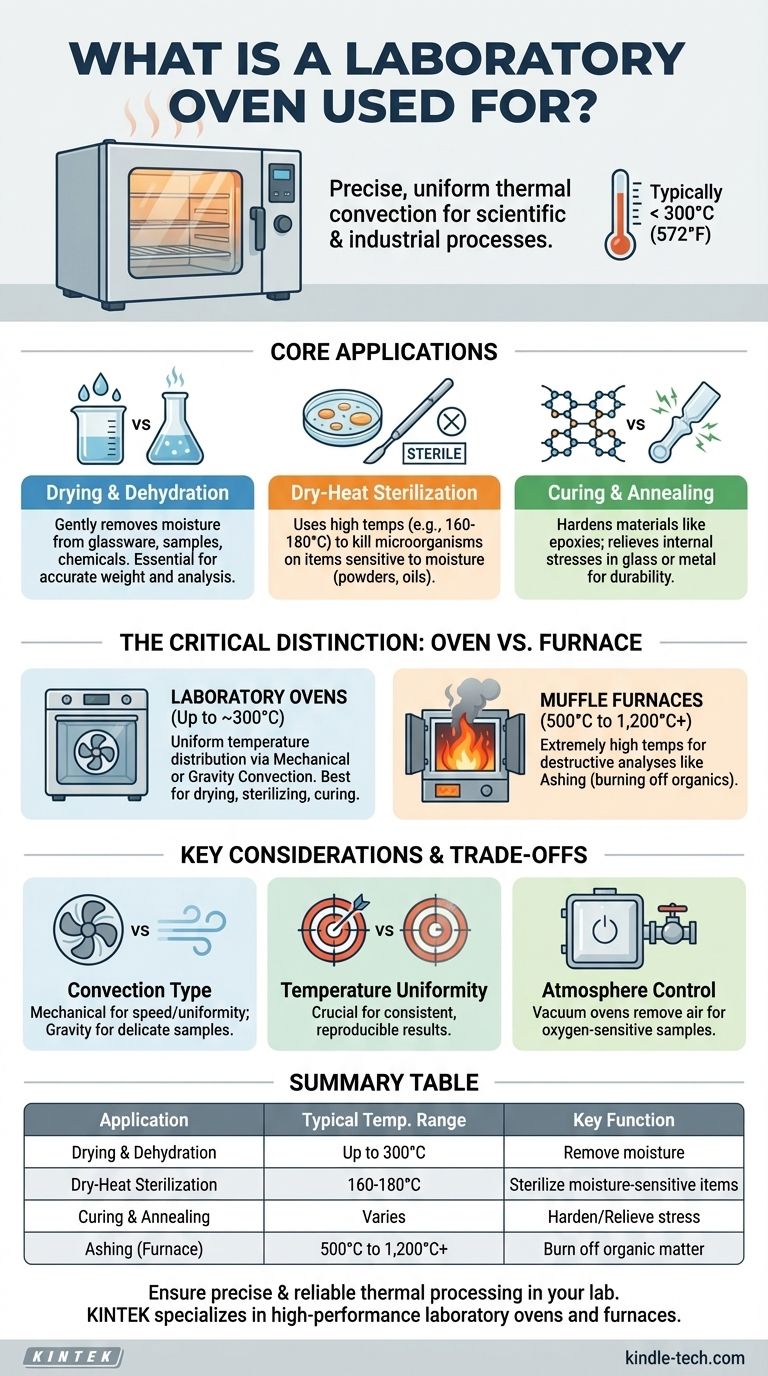
At its core, a laboratory oven provides precise, uniform thermal convection for a wide range of scientific and industrial processes. While specialized high-temperature ovens (furnaces) are used for ashing samples, the most common applications for a standard lab oven are drying glassware, dehydrating samples, sterilizing equipment, and curing materials at temperatures typically below 300°C (572°F).
The function of a "laboratory oven" is thermal processing, but the specific tool depends entirely on the target temperature. Standard ovens are workhorses for low-temperature drying and sterilizing, while high-temperature furnaces are required for destructive analyses like ashing.

Core Applications of a General-Purpose Oven
A standard laboratory oven is an indispensable tool for routine heating and drying applications. Its value comes from its ability to maintain a precise and uniform temperature over long periods.
Drying and Dehydration
This is the most frequent use of a laboratory oven. It involves gently removing moisture from samples, chemicals, or lab equipment like glassware.
Controlled drying prevents damage to sensitive samples and ensures that all moisture is removed before weighing or further analysis, a critical step for accurate results.
Dry-Heat Sterilization
While an autoclave uses pressurized steam, a dry-heat oven uses higher temperatures (e.g., 160-180°C) for a longer duration to sterilize items that cannot be exposed to moisture, such as powders, oils, or certain metal instruments.
This method kills all microorganisms, ensuring equipment is sterile for sensitive biological or chemical work.
Curing and Annealing
Ovens are used to cure materials, a process where heat induces a chemical reaction to harden substances like epoxies, polymers, and plastics.
Annealing involves heating and then slowly cooling materials like glass or metal to relieve internal stresses and improve their durability.
The Critical Distinction: Oven vs. Furnace
The term "oven" is often used loosely, but in a technical setting, it is vital to distinguish between a standard oven and a high-temperature furnace. The application dictates the instrument.
Laboratory Ovens (Up to ~300°C)
These devices typically use a fan (mechanical convection) or natural air currents (gravity convection) to circulate hot air. Their primary design focus is temperature uniformity throughout the chamber.
They are ideal for processes where maintaining a precise, consistent temperature across the entire sample is more important than reaching extreme heat.
Muffle Furnaces (500°C to 1,200°C+)
A furnace is a thermally insulated chamber designed to achieve extremely high temperatures. Its purpose is not gentle drying but rather to fundamentally alter a material through intense heat.
The primary application mentioned in the reference, ashing, falls squarely in this category. Ashing involves burning off all organic matter from a sample to determine the quantity of inorganic residue. This requires temperatures far beyond the range of a standard oven.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
Choosing the right heating instrument requires understanding a few key trade-offs that directly impact the quality of your results.
Gravity vs. Mechanical Convection
Gravity convection ovens are gentler and are best for fine powders or materials that could be disturbed by airflow. However, they heat up more slowly and can have less temperature uniformity.
Mechanical (forced-air) convection ovens use a fan to ensure rapid heating and excellent uniformity, but they are not suitable for delicate materials that might be blown around the chamber.
Temperature Range and Uniformity
Never choose an oven where your target temperature is at its maximum limit. Operating at the top of its range will strain the instrument and lead to poor performance.
Temperature uniformity is a critical specification. An oven with poor uniformity will heat your sample unevenly, leading to inconsistent and non-repeatable results.
Atmosphere Control
Most ovens operate in ambient air. If your sample is sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures, you require a vacuum oven, which allows you to remove the air and replace it with an inert gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the integrity of your work, match the instrument to the specific thermal process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is drying glassware or removing moisture from stable samples: A standard mechanical convection oven is your most efficient and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is ashing a sample to determine its mineral content: You absolutely require a high-temperature muffle furnace.
- If your primary focus is curing polymers or annealing glass: A programmable oven that offers precise temperature control and uniformity is essential.
- If your primary focus is working with air-sensitive compounds: A vacuum oven is the only suitable instrument to prevent unwanted oxidation.
Ultimately, selecting the correct thermal processing tool is a foundational step for achieving accurate and reproducible results in the laboratory.
Summary Table:
| Application | Typical Temperature Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Drying & Dehydration | Up to 300°C | Remove moisture from samples and glassware |
| Dry-Heat Sterilization | 160-180°C | Sterilize moisture-sensitive items |
| Curing & Annealing | Varies by material | Harden polymers or relieve material stresses |
| Ashing (Requires Furnace) | 500°C to 1,200°C+ | Burn off organic matter for inorganic analysis |
Ensure precise and reliable thermal processing in your lab. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory ovens and furnaces designed for drying, sterilization, curing, and high-temperature applications. Our equipment delivers the temperature uniformity and control your research demands. Contact us today to find the perfect heating solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- Why is a laboratory-grade forced air drying oven required for alloy chip moisture analysis? Ensure Data Precision



















