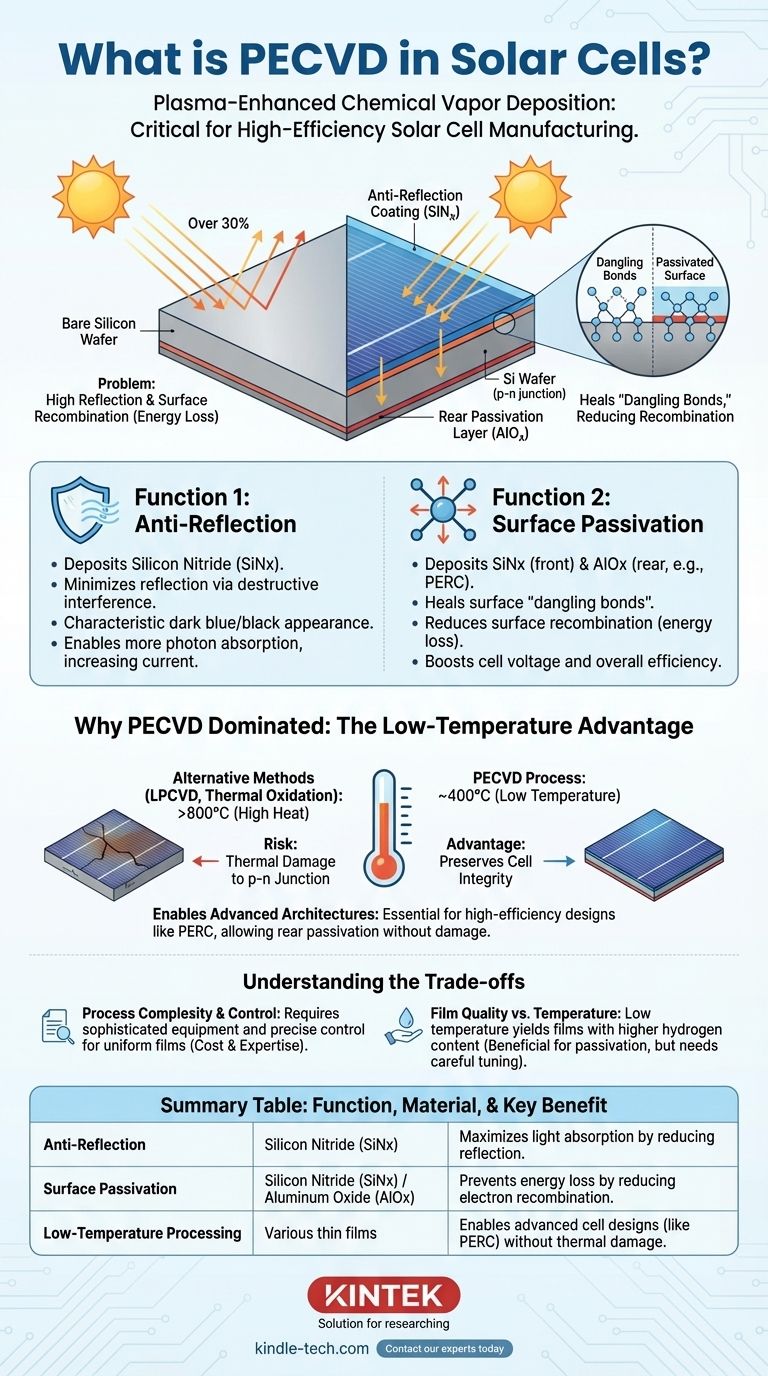
In solar cell manufacturing, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a critical process used to deposit ultra-thin, functional films onto silicon wafers. Specifically, it is the standard method for applying layers of silicon nitride (SiNx) and aluminum oxide (AlOx). These films are not merely protective coatings; they are active components that serve as anti-reflective layers and passivation agents, both of which are essential for maximizing the cell's ability to convert sunlight into electricity.
The core function of PECVD in a solar cell is not just to add a layer, but to fundamentally enhance performance. It solves two critical problems: it prevents light from reflecting away from the cell and stops electrical energy from being lost at the silicon surface, directly boosting the final efficiency.
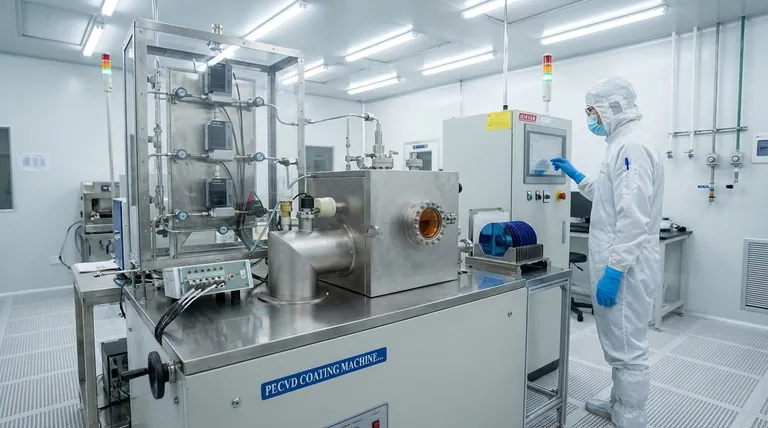

The Core Functions of PECVD in Solar Cells
To understand the importance of PECVD, you must understand the two primary roles its deposited films play. These functions directly combat the major sources of efficiency loss in a standard silicon solar cell.
Function 1: Anti-Reflection
A bare silicon wafer is surprisingly shiny, reflecting over 30% of the light that hits it. Any light that reflects off the surface is lost and cannot be converted into electricity.
PECVD is used to deposit a precise thickness of silicon nitride (SiNx) on the front of the solar cell. This film is engineered with a specific refractive index that minimizes reflection through destructive interference, giving modern solar cells their characteristic dark blue or black appearance. By enabling more photons to enter the silicon, the anti-reflection coating directly increases the current the cell can generate.
Function 2: Surface Passivation
The surface of a silicon crystal, and its rear side, is an area of imperfection with incomplete chemical bonds. These "dangling bonds" act as traps for the electrons and holes generated by sunlight.
When these charge carriers get trapped, they recombine and release their energy as waste heat instead of contributing to the electrical current. This energy loss, known as surface recombination, is a major limiter of a solar cell's voltage and overall efficiency.
The films deposited by PECVD, such as silicon nitride on the front and aluminum oxide (AlOx) on the rear (especially in PERC cells), "passivate" the surface. They effectively heal these dangling bonds, drastically reducing the rate of surface recombination and preserving the energy of the charge carriers.
Why PECVD is the Dominant Technology
Other methods for depositing thin films exist, but PECVD has become the industry standard in solar manufacturing for one overriding reason: its low-temperature processing capability.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
Alternative deposition processes, such as Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) or thermal oxidation, require extremely high temperatures (often >800°C). Exposing a nearly-finished solar cell to such heat can damage the sensitive, carefully created p-n junction within the silicon, degrading its performance.
PECVD avoids this problem. It uses an electromagnetic field (plasma) to energize the precursor gases, allowing the chemical reaction and film deposition to occur at much lower temperatures, typically around 400°C. This preserves the integrity of the underlying solar cell structure while still creating a high-quality film.
Enabling Advanced Cell Architectures
The low-temperature advantage of PECVD is what makes modern, high-efficiency cell designs like PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) commercially viable.
PERC technology relies on adding a passivation layer to the rear of the cell, most commonly aluminum oxide (AlOx). PECVD is the ideal technique for depositing this layer without damaging the rest of the cell, unlocking significant gains in efficiency that now dominate the market.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PECVD is the superior technology for this application, it is important to recognize its associated complexities.
Process Complexity and Control
PECVD reactors are sophisticated and expensive pieces of capital equipment. Achieving a film with perfectly uniform thickness, refractive index, and passivation quality across millions of wafers per year requires immense process control and expertise. Any deviation can negatively impact cell efficiency and yield.
Film Quality vs. Temperature
There is an inherent trade-off between deposition temperature and film properties. While PECVD's low temperature is its key benefit, the resulting films (like SiNx) can contain a higher concentration of hydrogen compared to films from high-temperature processes. This hydrogen is actually beneficial for silicon passivation, but it must be precisely controlled through careful process tuning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding PECVD's role clarifies its impact on both the performance and manufacturability of solar technology.
- If your primary focus is maximizing cell efficiency: Recognize that PECVD is indispensable. Its anti-reflection and passivation functions directly combat the primary optical and electronic loss mechanisms in a silicon solar cell.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing viability: Acknowledge that PECVD's low-temperature process is the enabling factor that allows high-efficiency cell designs to be produced at an industrial scale without thermal damage.
Ultimately, PECVD is the technology that elevates a simple silicon wafer into a highly efficient and durable device for converting sunlight into clean energy.
Summary Table:
| Function | Material Deposited | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflection | Silicon Nitride (SiNx) | Maximizes light absorption by reducing reflection |
| Surface Passivation | Silicon Nitride (SiNx) / Aluminum Oxide (AlOx) | Prevents energy loss by reducing electron recombination |
| Low-Temperature Processing | Various thin films | Enables advanced cell designs (like PERC) without thermal damage |
Ready to enhance your solar cell manufacturing or laboratory research? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for the solar and semiconductor industries. Our expertise in deposition technologies can help you achieve superior film quality and maximize cell efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can power your innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















