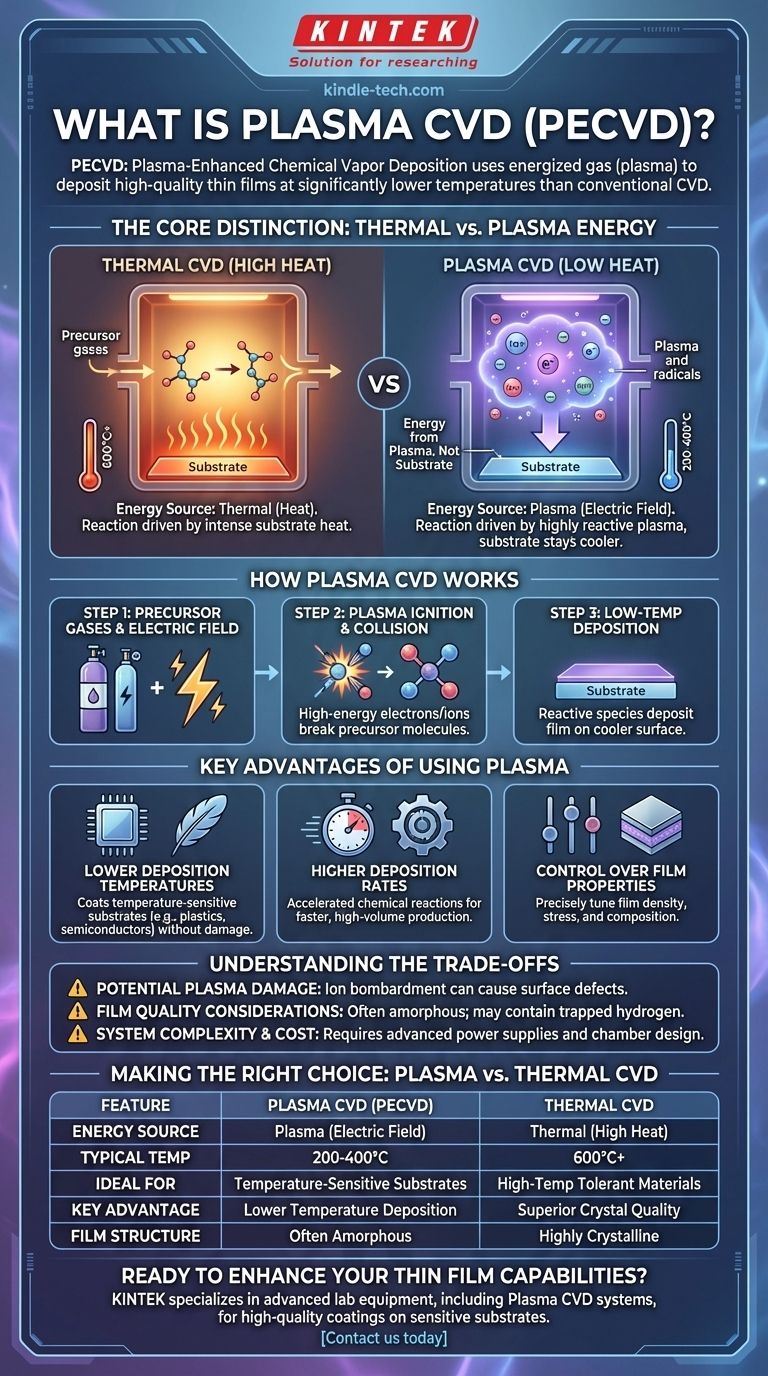
In short, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a process that uses plasma—an energized gas—to deposit high-quality thin films onto a surface. Unlike conventional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) which relies on high heat to drive the chemical reactions, PECVD can perform these reactions at much lower temperatures. This makes it ideal for coating materials that cannot withstand intense heat.
The core difference is the energy source. While traditional CVD uses thermal energy (heat) to break down precursor gases, PECVD uses the energy from a plasma. This fundamental shift allows for film deposition at significantly lower temperatures, expanding the range of possible applications.

From Thermal to Plasma: The Core Distinction
To understand plasma CVD, we must first understand the process it enhances. The key difference lies in how the necessary reaction energy is supplied to the system.
The Foundation: How Standard CVD Works
Conventional CVD is a thermally-driven process. Gaseous chemical precursors are introduced into a reaction chamber where they come into contact with a heated substrate, often at temperatures of 600°C or higher.
This intense heat provides the energy needed to break chemical bonds, initiating a reaction that deposits a solid, thin film on the substrate's surface. The remaining gaseous byproducts are then vented from the chamber.
Introducing Plasma: A New Energy Source
Plasma is often called the "fourth state of matter." It is a gas that has been energized, typically by a strong electric or magnetic field, until its atoms are ionized.
This creates a highly reactive environment filled with a mixture of ions, electrons, radicals, and neutral molecules. This energetic "soup" can transfer its energy to other molecules far more efficiently than heat alone.
How Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) Works
In a PECVD process, an electric field is applied to the precursor gases inside the chamber, igniting a plasma. The high-energy electrons and ions within the plasma collide with the precursor gas molecules.
These collisions break the precursor molecules apart, creating the reactive species needed for deposition. Because the energy comes from the plasma, not the substrate, the substrate can remain at a much lower temperature (e.g., 200-400°C), while still achieving a high-quality film.
Key Advantages of Using Plasma
Leveraging plasma as the energy source introduces several critical advantages that make PECVD a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Lower Deposition Temperatures
This is the most significant benefit. The ability to deposit films without high heat allows for coating temperature-sensitive substrates. This includes plastics, fully-fabricated semiconductor wafers with delicate transistors, or organic materials that would be destroyed by conventional CVD temperatures.
Higher Deposition Rates
The highly reactive nature of plasma can significantly accelerate the chemical reactions responsible for film growth. This often leads to faster deposition rates compared to other low-temperature techniques, which is a major advantage for high-volume industrial production.
Control Over Film Properties
By carefully tuning the plasma parameters—such as power, frequency, and gas pressure—engineers can precisely influence the properties of the resulting film. This allows for fine-tuning of a film's density, internal stress, and chemical composition to meet specific performance requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is not a universal solution. It comes with specific trade-offs that must be considered.
Potential for Plasma Damage
The high-energy ions that drive the reaction can also physically bombard the substrate surface. This ion bombardment can sometimes introduce defects or damage into the substrate or the growing film, which may be unacceptable for highly sensitive electronic devices.
Film Quality Considerations
PECVD films are often amorphous or have a different crystalline structure compared to films grown via high-temperature thermal CVD, which can be highly crystalline. They can also contain trapped hydrogen from precursor gases, which may affect electrical or optical properties.
System Complexity and Cost
PECVD reactors are more complex than their thermal counterparts. They require RF or DC power supplies, impedance matching networks, and more sophisticated chamber designs to generate and sustain a stable plasma, increasing both the initial cost and operational complexity.
Making the Right Choice: Plasma vs. Thermal CVD
Choosing the correct deposition method depends entirely on the requirements of your substrate and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible crystal quality and film purity: Standard high-temperature thermal CVD is often the superior choice, provided your substrate can tolerate the heat.
- If your primary focus is depositing on a temperature-sensitive substrate: Plasma CVD (PECVD) is the definitive solution, enabling high-quality film deposition without causing thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is achieving high throughput at moderate temperatures: Plasma CVD can offer faster deposition rates than other low-temperature processes, making it ideal for industrial production of items like solar cells or protective coatings.
Ultimately, understanding the role of plasma as an alternative energy source is the key to selecting the right deposition strategy for your specific material and goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Plasma CVD (PECVD) | Thermal CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Plasma (electric field) | Thermal (high heat) |
| Typical Temperature | 200-400°C | 600°C+ |
| Ideal For | Temperature-sensitive substrates | High-temperature tolerant materials |
| Key Advantage | Lower temperature deposition | Superior crystal quality |
| Film Structure | Often amorphous | Highly crystalline |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise thin film deposition?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including Plasma CVD systems, to help you achieve high-quality coatings on even the most sensitive substrates. Whether you're working with semiconductors, polymers, or advanced materials, our solutions are designed to meet your specific research and production needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in lab equipment and consumables can support your innovative projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















