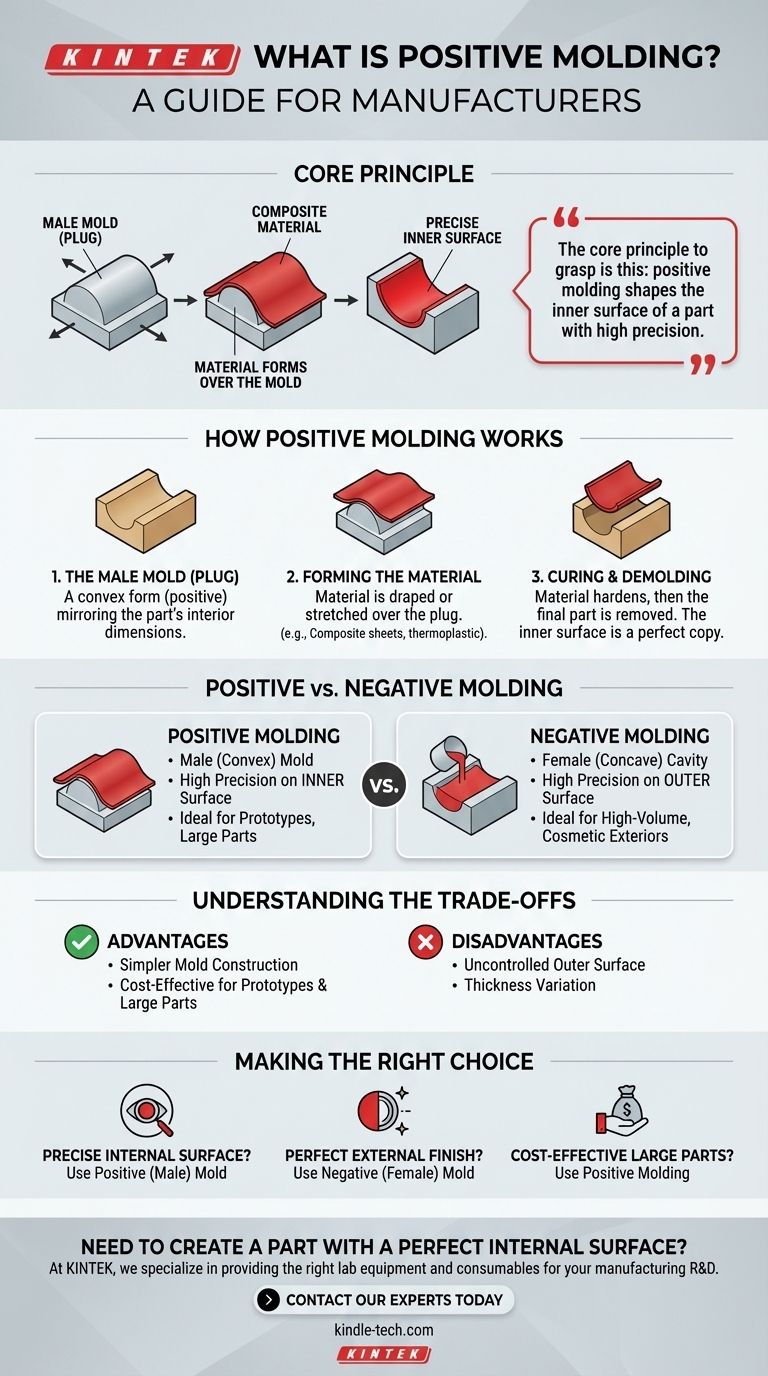
In manufacturing, positive molding is a process where the mold, also known as a male mold or plug, is a convex shape that is a direct replica of the desired part. The raw material, such as a composite sheet or thermoplastic, is then formed over the surface of this mold. This technique is fundamentally about shaping a material around a positive form rather than pressing it into a negative cavity.
The core principle to grasp is this: positive molding shapes the inner surface of a part with high precision, as that is the side in direct contact with the mold. It is the direct counterpart to negative molding, which shapes the outer surface with high precision.
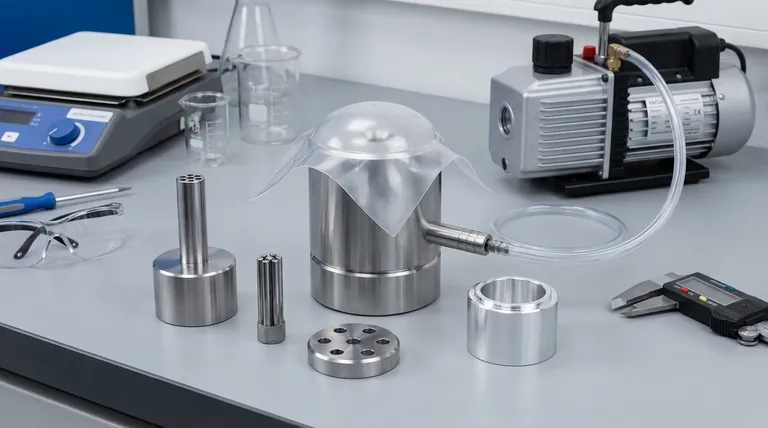

How Positive Molding Works: The Core Principle
Positive molding is conceptually straightforward, making it a common choice for specific applications, particularly with composites and thermoforming. The process follows a clear sequence.
The 'Male' Mold or Plug
The process begins with the mold itself. This is a positive form, meaning it is a convex shape that has the exact dimensions and contours intended for the final part's interior surface. This "plug" can be made from various materials, including wood, high-density foam, or machined metal, depending on the required durability and production volume.
Forming the Material
With the mold prepared, the fabrication material is draped or stretched over its surface. In composites manufacturing, this involves laying sheets of fiberglass or carbon fiber, saturated with resin, onto the plug. In thermoforming, a sheet of plastic is heated until pliable and then vacuum-formed over the mold.
Curing and Demolding
Once the material is in place, it is cured—allowed to harden. For composites, this is a chemical reaction of the resin. For thermoplastics, it's simply a matter of cooling. After the part has become rigid, it is separated from the male mold, a process called demolding. The resulting part is a hollow shell whose inner surface is a perfect copy of the mold.
The Counterpart: Understanding Negative Molding
To fully appreciate positive molding, you must understand its opposite. Negative molding is more common in high-volume processes like injection molding.
The 'Female' Cavity
In negative molding, the mold is a concave cavity. Think of an ice cube tray—the tray is the negative mold. Material is poured, injected, or pressed into this cavity to take its shape.
Precision on the Outer Surface
Because the material is pressed against the outer walls of the cavity, a negative mold produces a part with a highly precise and smooth external surface. This "A-side" finish is critical for consumer products where appearance is paramount. The internal surface, by contrast, is less controlled.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between positive and negative molding is a decision driven by engineering and cost trade-offs. Neither method is universally superior; they are simply tools for different jobs.
Advantage: Simpler Mold Construction
For large, simple shapes like a boat hull or a bathtub, creating a male plug (positive mold) is often significantly easier, faster, and less expensive than machining a massive, precise female cavity (negative mold). This makes it ideal for prototyping and low-volume production.
Disadvantage: Uncontrolled Outer Surface
The primary trade-off of positive molding is the finish on the part's outer surface. Since this side is not in contact with the mold (it's the "bag side" in vacuum bagging), it is less dimensionally accurate and often has a rougher texture. It may require significant secondary finishing work, like sanding and painting, if a cosmetic appearance is needed.
Disadvantage: Thickness Variation
When draping or stretching material over a convex mold, the material can thin out as it conforms to sharp corners or complex curves. This can be a critical structural consideration that must be managed during the design and layup process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The decision to use a positive or negative mold should be based entirely on the final part's functional and aesthetic requirements.
- If your primary focus is a precise and smooth internal surface: Use a positive (male) mold, as this is the surface that will be in direct contact with the tool.
- If your primary focus is a perfect external finish and sharp detail: Use a negative (female) mold, as the exterior of your part will be the cosmetically perfect 'A-side'.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of large parts or prototypes: Positive molding is often the simpler and more economical path, provided the rougher outer surface is acceptable.
Ultimately, understanding whether you need to control the inside or the outside of your part is the key to selecting the most effective manufacturing strategy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Positive Molding | Negative Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Type | Male (Convex) Plug | Female (Concave) Cavity |
| Surface Precision | High on Inner Surface | High on Outer Surface |
| Ideal For | Prototypes, Large Parts, Internal Fit | High-Volume, Cosmetic Exteriors |
| Mold Cost | Generally Lower & Simpler | Often Higher & More Complex |
Need to create a part with a perfect internal surface? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your manufacturing R&D. Whether you're prototyping with composites or developing new thermoforming processes, our solutions help you achieve precise, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project with reliable equipment tailored to your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- No Demolding Lab Infrared Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory manual slicer
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What technical characteristics are required for specialty pressure molds used in the compaction of Li10GeP2S12? Expert Tips
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity















