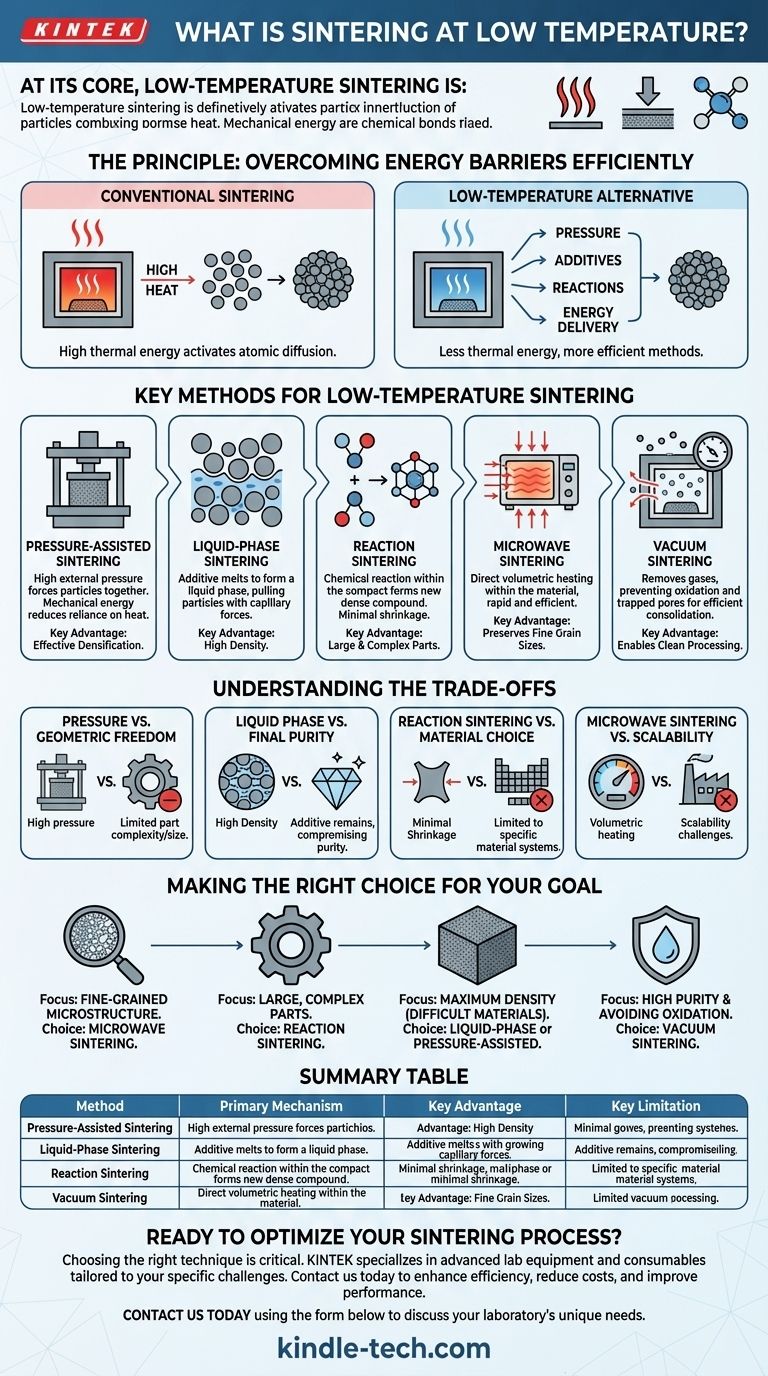
At its core, low-temperature sintering is a category of advanced manufacturing processes that achieve material densification without relying solely on extreme heat. These methods use alternative driving forces—such as high pressure, chemical reactions, or targeted energy delivery—to bind particles into a solid mass at temperatures significantly lower than conventional sintering requires.
The central challenge in sintering is providing enough energy for atoms to bond and eliminate pores. While traditional methods use high heat as their primary tool, low-temperature techniques find more efficient ways to achieve this, often by introducing pressure, liquid phases, or chemical reactions to do the heavy lifting.

The Principle: Overcoming Energy Barriers Efficiently
Traditional sintering is a simple but energy-intensive process. By understanding its mechanism, we can see why alternatives are necessary.
How Conventional Sintering Works
Conventional sintering subjects a loose powder compact to high temperatures, typically below the material's melting point. This thermal energy activates atomic diffusion, causing atoms to migrate from particle surfaces to the "necks" forming between them, gradually closing the pores and creating a dense, solid part.
The Low-Temperature Alternative
The goal of low-temperature sintering is to facilitate this densification with less thermal energy. This is critical for saving costs, speeding up production, and, most importantly, preserving fine-grained microstructures or processing temperature-sensitive materials.
Key Methods for Low-Temperature Sintering
Several distinct strategies exist to lower the required sintering temperature. Each operates on a different principle and is suited for different applications.
Pressure-Assisted Sintering
This is the most direct approach. By applying high external pressure to the powder compact, particles are physically forced into close contact. This mechanical energy reduces the reliance on thermal energy to close pores, allowing densification to occur at a much lower temperature.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
In this technique, a small amount of an additive is mixed with the primary powder. This additive is chosen to have a melting point lower than the main material. At the sintering temperature, the additive melts, creating a liquid phase that wets the solid particles. Capillary forces pull the particles together, and the liquid acts as a rapid transport path for atoms to dissolve and re-precipitate, quickly filling pores and achieving high density.
Reaction Sintering
This method involves a chemical reaction within the powder compact. Instead of simply bonding existing particles, the starting materials react to form a new, dense ceramic compound. Because the reaction itself provides a strong driving force for consolidation, the process temperature can be relatively low. A key advantage is its minimal shrinkage, making it ideal for large and complex parts.
Microwave Sintering
Microwave sintering uses a fundamentally different heating mechanism. Instead of heating the material from the outside in, microwaves generate heat directly within the material. This rapid, volumetric heating is highly efficient and can significantly reduce the time needed to reach sintering temperatures. While the peak temperature may still be high, the speed of the process helps preserve fine grain sizes, a primary goal often associated with low-temperature processing.
Vacuum Sintering
While not a low-temperature method on its own, creating a vacuum is a critical enabling condition. Removing atmospheric gases from the furnace prevents oxidation and eliminates trapped gases within pores that would otherwise inhibit densification. This cleaner environment makes the entire sintering process more efficient, often allowing for success at a lower temperature or for a shorter duration than would be possible in air.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering method requires a clear understanding of its inherent compromises. There is no single "best" solution.
Pressure vs. Geometric Freedom
Using high pressure is effective for densification, but it requires robust and often expensive tooling (dies and presses). This can severely limit the size and complexity of the parts you can produce.
Liquid Phase vs. Final Purity
In liquid-phase sintering, the additive that forms the liquid becomes a permanent part of the final material's microstructure. This is unacceptable for applications requiring high chemical purity.
Reaction Sintering vs. Material Choice
Reaction sintering is powerful but is limited to material systems where a suitable chemical reaction can produce the desired final compound. You cannot apply this method universally to any material.
Microwave Sintering vs. Scalability and Compatibility
Microwave sintering is typically best for small, single components and can have trouble with materials that are highly conductive or do not couple well with microwave energy. Scaling the process for large-volume production remains a significant engineering challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your method based on the most critical outcome for your project.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine-grained or nano-scale microstructure: Microwave sintering's speed is a major advantage.
- If your primary focus is producing large, complex-shaped parts with high dimensional accuracy: Reaction sintering is the leading candidate due to its minimal shrinkage.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in a difficult-to-sinter material: Liquid-phase or pressure-assisted sintering provides powerful driving forces for densification.
- If your primary focus is ensuring high purity and avoiding oxidation: Vacuum sintering is an essential process condition to enable efficient, clean consolidation.
Ultimately, choosing the right sintering process means matching the mechanism to your specific material and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Mechanism | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure-Assisted | High External Pressure | Effective Densification | Limited Part Complexity/Size |
| Liquid-Phase | Additive Melting (Capillary Forces) | High Density | Compromised Final Purity |
| Reaction Sintering | In-Situ Chemical Reaction | Minimal Shrinkage | Limited to Specific Materials |
| Microwave Sintering | Volumetric Heating (Speed) | Preserves Fine Microstructure | Scalability Challenges |
| Vacuum Sintering | Absence of Oxidizing Gases | Enables Clean Processing | Not a Standalone Low-Temp Method |
Ready to Optimize Your Sintering Process?
Choosing the right low-temperature sintering technique is critical for achieving your material's desired properties, whether it's a fine-grained microstructure, high dimensional accuracy, or maximum density. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific sintering challenges.
Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the performance of your materials. Don't let sintering limitations hold back your innovation.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how we can support your laboratory's unique needs and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- How does a vacuum oven contribute to solid electrolyte membrane formation? Achieve Dense, Defect-Free Materials
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing



















