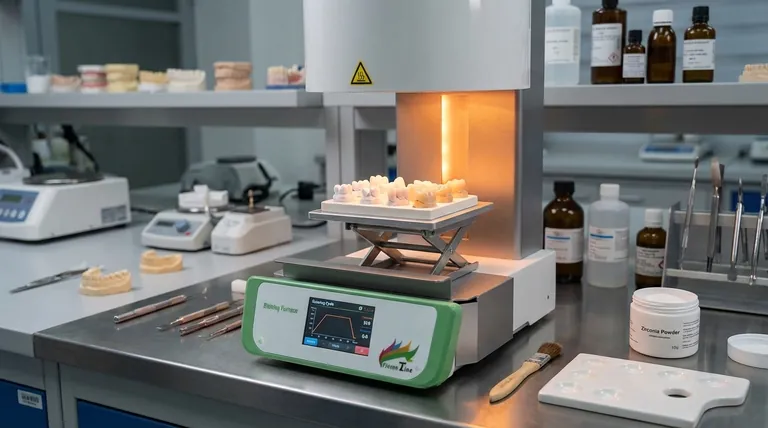
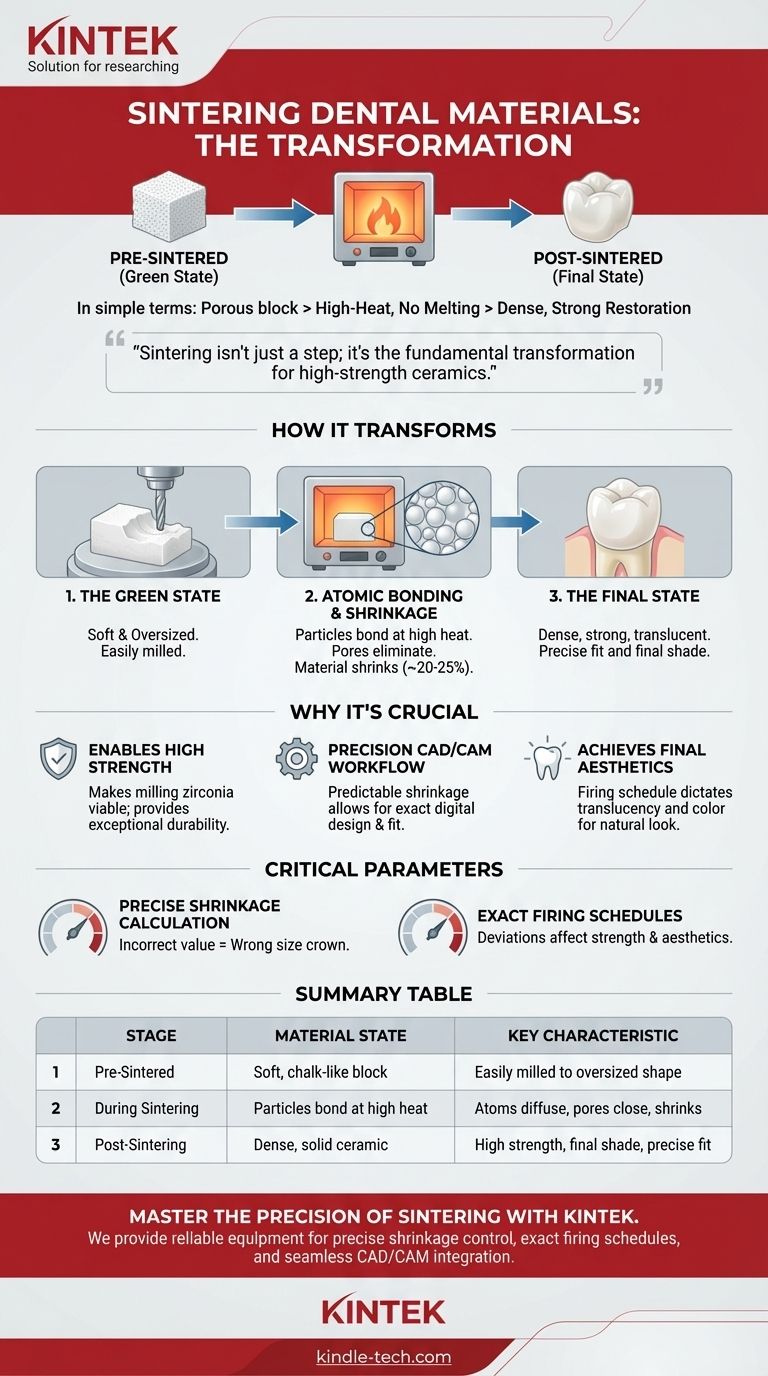
In simple terms, sintering is a high-temperature heating process that transforms a porous, chalk-like block of dental material into a solid, dense, and final restoration. It fuses the material's particles together without melting them, much like compacting a snowball into a hard ice ball using pressure and time. This process is what gives materials like zirconia their exceptional strength and aesthetic properties.
Sintering isn't just a step in the process; it is the fundamental transformation that makes modern, high-strength ceramic restorations possible. It bridges the gap between a fragile, easily-milled pre-form and the final, durable crown or bridge.

How Sintering Transforms Dental Materials
To understand sintering, you must first understand the material's journey from a soft block to a final, robust restoration. The process involves a radical change in the material's physical properties.
The "Green State": The Unfired Material
Before sintering, a ceramic like zirconia exists in a "green state" or "pre-sintered" form. In this stage, it has the consistency of a piece of chalk.
This softness is intentional. It allows dental laboratories to easily mill the crown, bridge, or coping from a block of the material using a CAD/CAM system with minimal wear on the milling burs. The restoration is milled to a proportionally larger size to account for the next step.
The Atomic-Level Process: Fusing Without Melting
The milled restoration is then placed into a specialized high-temperature oven. As the temperature rises—well below the material's melting point—the individual particles of the ceramic powder begin to bond.
Atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, causing the contact points to grow and merge. This eliminates the pores between the particles, pulling the entire structure together into a dense, solid mass.
The Final State: Strength and Shrinkage
As the pores are eliminated, two critical things happen:
- Shrinkage: The material shrinks significantly and predictably, often by 20-25%. The dental software and lab technician must precisely calculate this shrinkage to ensure the final restoration fits the patient's tooth perfectly.
- Densification: The material becomes incredibly dense and hard. The once-chalky zirconia is transformed into one of the strongest and most fracture-resistant materials used in dentistry today. It also gains its final translucency and shade.
Why Sintering is Crucial for Modern Dentistry
Sintering isn't just an interesting scientific process; it is the enabling technology behind the most common tooth-colored restorations used today.
Enabling High-Strength Ceramics (Zirconia)
Fully sintered zirconia is too hard to be efficiently milled in a dental lab. The process would be slow, expensive, and would rapidly destroy milling tools.
Sintering provides the perfect workaround: mill the material when it's soft, then sinter it to achieve its final, super-strong state. Without sintering, monolithic zirconia restorations would not be a viable option.
Precision Through CAD/CAM Workflow
The digital dentistry workflow relies on the predictability of sintering. A digital scan of the patient's mouth is used to design a restoration. The software then automatically enlarges the design to compensate for the exact shrinkage percentage of the specific zirconia block being used.
The oversized restoration is milled and then sintered, shrinking down to the precise, intended dimensions for a perfect fit.
Achieving Final Aesthetics
The sintering process is also critical for aesthetics. The firing schedule—the specific temperatures and times used in the oven—has a direct impact on the material's final translucency and color.
Proper sintering ensures the restoration matches the desired tooth shade and allows light to pass through it in a natural way, avoiding a flat, opaque look.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Parameters
While essential, the sintering process must be perfectly controlled. Errors at this stage can compromise the entire restoration.
The Critical Factor of Shrinkage
The most significant variable is shrinkage. Each batch and brand of zirconia has a specific shrinkage factor that must be programmed into the CAD/CAM software. An incorrect value will result in a crown that is either too small or too large, rendering it useless.
The Importance of Firing Schedules
Following the manufacturer's recommended firing schedule is non-negotiable. Sintering too quickly or at the wrong temperature can create internal stresses, reduce strength, or negatively affect the translucency and shade of the ceramic.
Not All Materials Are Sintered
It's important to note that sintering is primarily associated with ceramics like zirconia and some metal powders (SLM/DMLS). Other dental materials have different processing methods. For example, lithium disilicate (e.max) is typically pressed or milled and then crystallized in a glaze oven, while traditional metal crowns are cast from molten alloy.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding sintering helps you appreciate the technical precision required for modern restorations. Your takeaway depends on your role in the process.
- If you are a clinician: Trust that your dental lab has mastered this critical process. Any issues with the fit, strength, or shade of a zirconia restoration can often be traced back to a deviation in the sintering protocol.
- If you are a lab technician: Recognize that the sintering oven is one of the most important pieces of equipment you own. Meticulous calibration, adherence to manufacturer instructions, and precise shrinkage calculations are the foundation of a successful restoration.
- If you are a student or patient: Appreciate that this sophisticated heating process is what makes it possible to have a strong, beautiful, tooth-colored crown that is designed and made with digital precision.
Ultimately, sintering is the unseen but essential step that transforms a simple digital file into a durable, lifelike part of a patient's smile.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Material State | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Sintered (Green State) | Soft, chalk-like block | Easily milled to an oversized shape |
| During Sintering | Particles bond at high heat | Atoms diffuse, pores close, material shrinks |
| Post-Sintering | Dense, solid ceramic | High strength, final shade, precise fit |
Master the precision of sintering with KINTEK.
As a leading provider of laboratory equipment and consumables, KINTEK understands that a reliable sintering furnace is the cornerstone of a successful dental lab. Proper sintering is non-negotiable for achieving the strength, fit, and aesthetics your clients expect from zirconia restorations.
Our expertise ensures you have the right equipment to:
- Guarantee precise shrinkage control for perfect-fitting crowns and bridges.
- Follow exact firing schedules to maximize material strength and translucency.
- Integrate seamlessly into your digital CAD/CAM workflow for consistent, high-quality results.
Elevate your lab's capabilities. Contact our dental equipment specialists today to find the perfect sintering solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the components of dental porcelain? A Guide to Engineered Strength and Beauty
- What are the different types of ceramics in dentistry? Choose the Right Material for Strength & Aesthetics
- What are the consequences of incorrect pressing time when processing pressed ceramics? Ensure Perfect Dental Restorations
- Can ceramic crowns be repaired? A Dentist's Guide to Assessing the Damage
- What are the most natural-looking crowns for teeth? Achieve a Seamless, Lifelike Smile
- What is dental ceramics composed of? A Guide to Glass, Crystal, and Clinical Applications
- What is the average lifespan of a dental restoration? Maximize Your Investment with the Right Material
- What is ceramic dental restoration? A Guide to Modern, Aesthetic, and Durable Tooth Repair



















